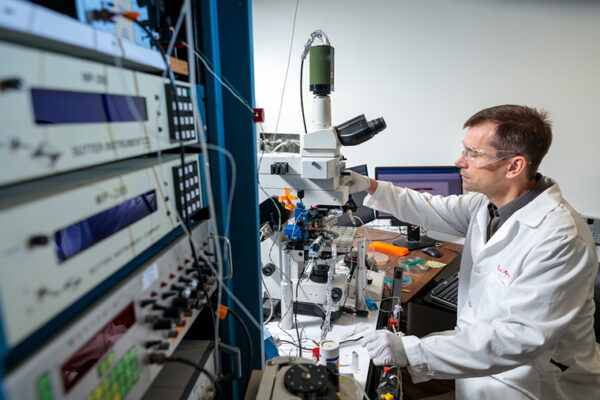
$12.2 million to fund new Conte Center to study neurosteroids
The National Institute of Mental Health has awarded Washington University School of Medicine a $12.2 million grant to create a center aimed at advancing research into neurosteroids as treatments for depression and other psychiatric disorders.
Creed honored for research involving mood, chronic pain, substance use
Meaghan Creed, assistant professor of anesthesiology at Washington University School of Medicine, received the 2021 Freedman Prize from the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation. The prize recognizes exceptional basic research in mental illness.
$35 million to support study of sleep disorder linked to neurodegeneration
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine, the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and The Neuro of McGill University have received a five-year grant expected to total $35.1 million for an extension of a study designed to develop biomarkers that indicate which people with REM sleep behavior disorder will go on to develop neurodegenerative diseases.
‘Fight or flight’ – unless internal clocks are disrupted, study in mice shows
Neuroscientists in Arts & Sciences discovered that the daily release of hormones depends on the coordinated activity of clocks in two parts of the brain, a finding that could have implications for human diseases.
McDonnell Foundation awards Roediger $750,000 for memory research
Henry “Roddy” Roediger and James Wertsch, both in Arts & Sciences, will use a grant from the James S. McDonnell Foundation to encourage the interdisciplinary study of collective memory.
Who’s in cognitive control?
A new study into cognitive control from the lab of Todd Braver promises to be the first of many aimed at understanding its origins in the brain and its variations between people and among groups.
Neurons in visual cortex of the brain ‘drift’ over time
New research from physicists in Arts & Sciences reveals that neurons in the visual cortex — the part of the brain that processes visual stimuli — respond differently to the same kind of stimulus over time.
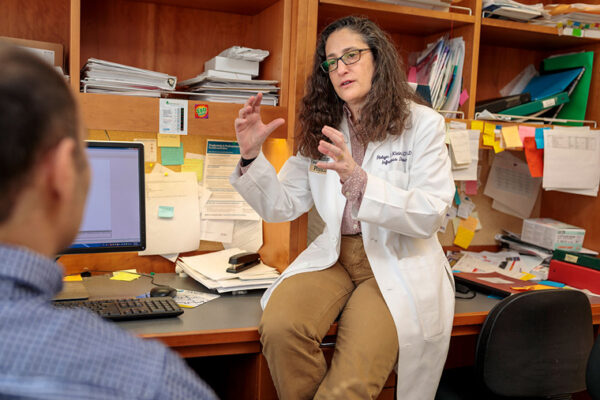
Memory disorders after viral infections focus of $8.7 million grant
The School of Medicine’s Robyn Klein, MD, PhD, has received an $8.7 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to investigate how viruses may cause diseases of “pathological forgetting.”
17-year study of children associates poverty with smaller, slower-growing subcortical regions
Research from the lab of Deanna Barch shows a lasting relationship between childhood poverty, brain development.
Study finds brain areas involved in seeking information about bad possibilities
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have identified the brain regions involved in choosing whether to find out if a bad event is about to happen. The findings are published June 11 in Neuron.
Older Stories