Among COVID-19 survivors, an increased risk of death, serious illness
A new study from the School of Medicine shows that even mild cases of COVID-19 increase the risk of death in the six months following diagnosis. The comprehensive study also catalogues the wide-ranging and long-term health problems often triggered by the infection, even among those not hospitalized.
Feldman, Khader, Philips elected to American Academy of Microbiology
Three researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have been elected to the American Academy of Microbiology in recognition of their scientific achievements and original contributions that have advanced the field of microbiology.
Njoku named director of pediatric anesthesiology division
Dolores B. Njoku, MD, a noted clinician, researcher and mentor, has been named director of pediatric anesthesiology at the School of Medicine and anesthesiologist-in-chief at St. Louis Children’s Hospital. She also will be the new Rudolph L. and Mary Frances Wise Endowed Chair in Pediatric Anesthesiology.
Researchers elected to American Society for Clinical Investigation
Five physician-scientists at the School of Medicine have been elected members of the American Society for Clinical Investigation in recognition of original, creative and independent investigations in the clinical or allied sciences of medicine.
Graduate student wins NIH fellowship
Macy Sprunger, a graduate student in Meredith Jackrel’s lab in the Department of Chemistry in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, won a three-year $136,560 National Research Service Award from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Such fellowships support predoctoral students conducting research in scientific health-related fields.
Odibo named director of maternal-fetal & ultrasound division in OB-GYN
Anthony Odibo, MD, an internationally respected maternal-fetal medicine expert, has been named director of the Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine & Ultrasound in the Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology at the School of Medicine.
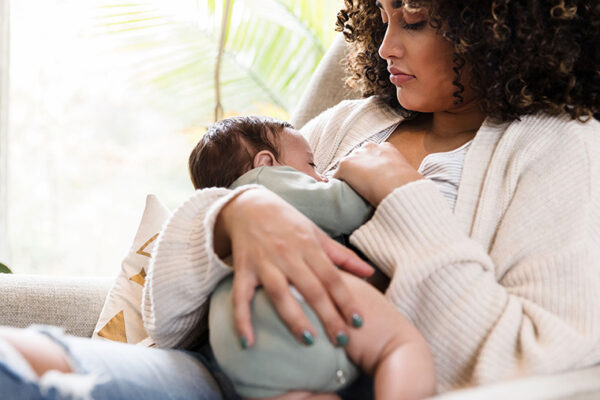
For breastfeeding moms, COVID-19 vaccinations may also protect babies
New research from Washington University School of Medicine suggests that nursing mothers who receive a COVID-19 vaccine may also protect their babies from the virus.
Sacks named division director in plastic and reconstructive surgery
Justin M. Sacks, MD, a highly respected microvascular surgeon with expertise in complex surgeries involving cancer and trauma, has been named director of the Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at the School of Medicine. Sacks also has been installed as the Sydney M. Shoenberg Jr. and Robert H. Shoenberg Endowed Chair in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, an endowment supported through The Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital.
Study predicts which kids hospitalized with RSV likely to worsen
Children hospitalized with breathing problems due to infection with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are likely to get sicker and remain hospitalized if they have high levels of defective copies of the virus, according to a new study by researchers at the School of Medicine.
Holmes awarded HHMI fellowship for promising early-career scientists
Virologist Autumn Holmes, a postdoctoral researcher at the School of Medicine, has been named a Hanna H. Gray Fellow by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI). The fellowship provides up to $1.4 million over eight years to outstanding early-career scientists.
Older Stories