Apte receives Catalyst Award for innovative approaches to research
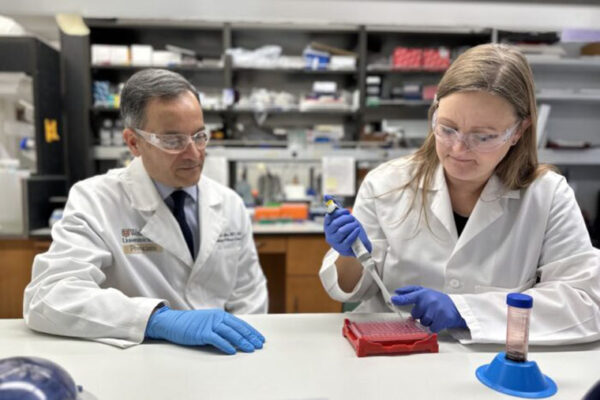
Rajendra Apte, MD, PhD, the Paul A. Cibis Distinguished Professor in the John F. Hardesty, MD, Department of Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences at the School of Medicine, has received a $300,000 Research to Prevent Blindness/American Macular Degeneration Foundation Catalyst Award.
Engineering, OT students work with patients to design assistive tech
About 40 engineering and occupational therapy students collaborated during Washington University in St. Louis’ inaugural Assistive Tech Make-A-Thon, designing products for St. Louisans with mobility and other physical challenges.
University’s technology, innovation hub celebrates 100th faculty startup
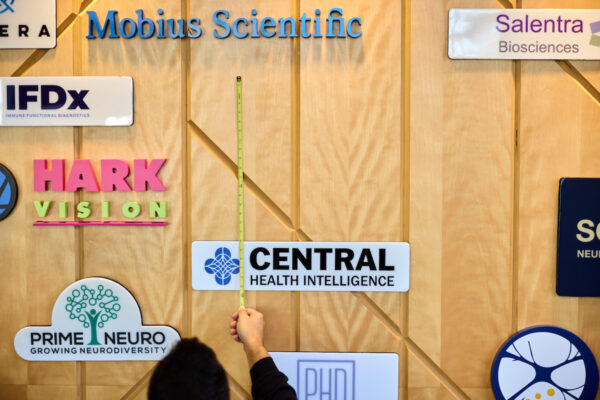
The Office of Technology Management at Washington University in St. Louis recently celebrated a milestone of 100 university startups.
WashU awarded up to $20M to create portable device to scan for eye diseases
Chao Zhou, a professor of biomedical engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, has been awarded an up to $20 million contract from the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health to improve optical coherence tomography systems that can conduct high-resolution imaging of the eyes.
How does waste leave the brain?
School of Medicine scientists have discovered a brain structure that allows fluid waste to leave the brain. The researchers think these structures, and the cells and molecules positioned around them, may help lead to new therapies for neuroinflammatory diseases.
Raghuraman named director of clinical research division in OB-GYN
Nandini Raghuraman, MD, a physician-scientist who specializes in caring for patients with complex high-risk pregnancies, has been named director of the Division of Clinical Research in the Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology at the School of Medicine.
Genin awarded Savio L-Y. Woo Translational Biomechanics Medal
Guy Genin, the Harold and Kathleen Faught Professor of Mechanical Engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering, has been awarded the Savio L-Y. Woo Translational Biomechanics Medal from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Pediatric Heart Network names medical school a core site for heart disease research
The School of Medicine has joined the Pediatric Heart Network, a multicenter collaboration of leading hospitals and research institutions that works to improve care for pediatric heart disease patients.
Kwon, Newland named to antibiotic resistance advisory council
Jennie H. Kwon, DO, an associate professor of medicine in infectious diseases, and Jason G. Newland, MD, a professor of pediatrics, both at the School of Medicine, have been selected to serve on the Presidential Advisory Council on Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria.
Washington University and Deerfield Management launch VeritaScience to drive drug discovery
Washington University in St. Louis and Deerfield Management, a health-care investment firm, announced the launch of VeritaScience, a new private R&D collaboration designed to advance the discovery, clinical development and commercialization of promising therapeutic and diagnostic candidates with potential to benefit human health.
Older Stories