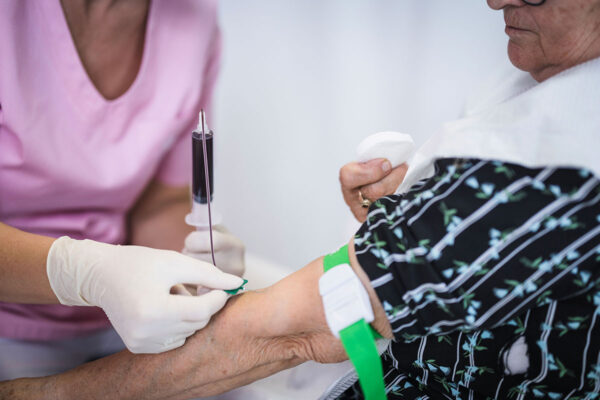
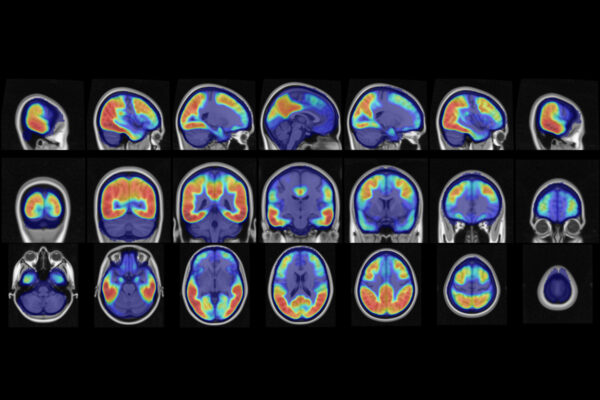
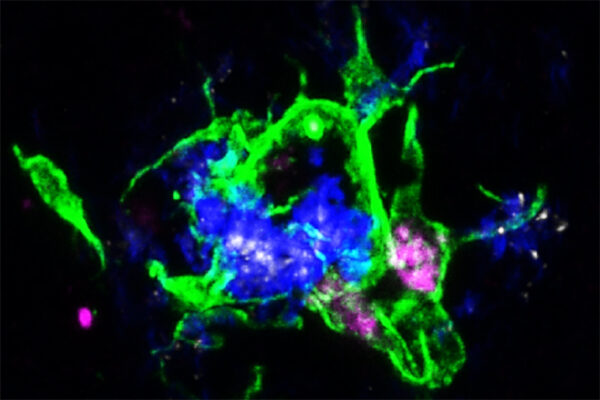
Accuracy of diagnostic blood tests for Alzheimer’s disease varies
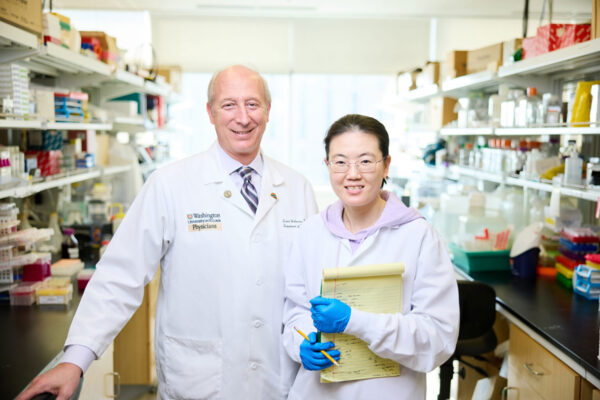
A head-to-head comparison of six commercially available blood tests for Alzheimer’s disease led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis reveals that two are accurate enough to replace brain scans and spinal taps in some patients with cognitive impairments.
Holtzman, Chen recognized for exceptional Alzheimer’s research
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis faculty members David M. Holtzman, MD, and Xiaoying Chen were awarded the inaugural Jeffrey L. Morby Prize from the Cure Alzheimer’s Fund.
Racial disparities in dementia determined by social factors
Racial disparities in dementia are due to social determinants of health, with genetic ancestry playing no role, according to a new study led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Link between childhood adverse events, Alzheimer’s disease to be studied
Brian A. Gordon, an assistant professor of radiology at the School of Medicine, has received an award from the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center and the Alzheimer’s Association to study how adverse events in childhood affect the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Lucey receives sleep science award
Brendan P. Lucey, MD, a professor of neurology at the School of Medicine, has been awarded the 2024 Sleep Science Award from the American Academy of Neurology in recognition of his distinguished contributions to the neurology and neuroscience of sleep.
Understanding role of T cells in Alzheimer’s disease is aim of new grant
Naresha Saligrama, an assistant professor of neurology at the School of Medicine, has received a $200,000 grant from the Cure Alzheimer’s Fund to investigate whether other aspects of the immune system also contribute to the disease, specifically T cells.
Alzheimer’s biomarker sTREM2 plays a causal, potentially modifiable, role in disease
Carlos Cruchaga, a professor of psychiatry at the School of Medicine, has shown that the protein sTREM2 plays a causal role in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, meaning that targeting the protein may affect the course of the disease.
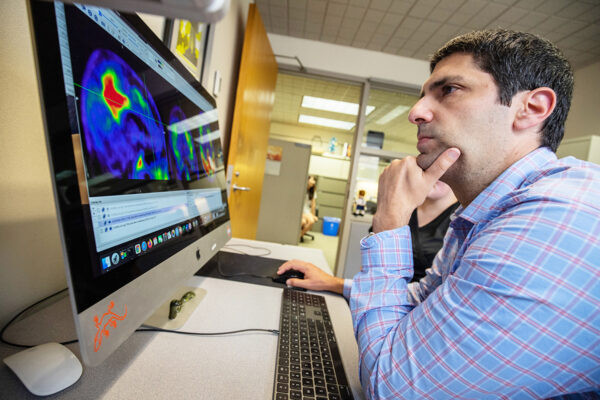
Tau protein deposition patterns predict Alzheimer’s severity
Researchers at the School of Medicine have devised a method to gauge Alzheimer’s disease severity by analyzing the patterns of tau pathology in brain scans. The findings could lead to a way to determine how far the disease has progressed in individuals.
Alzheimer’s disease progresses faster in people with Down syndrome
A new study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis shows that Alzheimer’s disease both starts earlier and moves faster in people with Down syndrome. The finding may have important implications for the treatment and care of this vulnerable group of patients.
Immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease shows promise in mouse study
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found a different and promising way to remove amyloid beta plaques in the brain: by directly mobilizing immune cells to consume them. The study was published in Science Translational Medicine.
Older Stories