Risk, resiliency in aging brain focus of $33 million grant
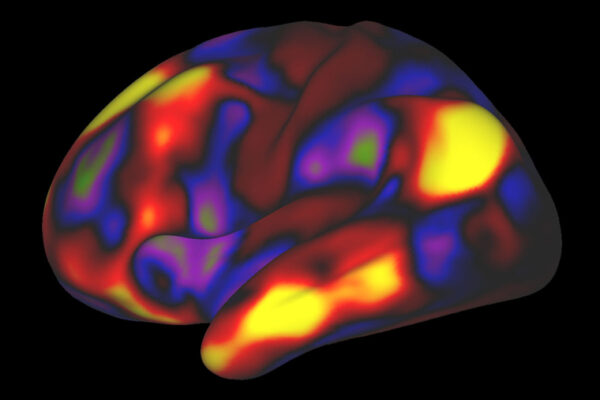
Funded by a $33.1 million grant from the National Institute on Aging, researchers from the School of Medicine and other institutions have launched a large study that investigates just what keeps our brains sharp as we age and what contributes to cognitive decline.
Older people’s resilience during pandemic focus of $9 million grant
The National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has awarded researchers at Washington University School of Medicine a five-year $9.1 million grant to study resilience in older adults before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as the pandemic’s cognitive and emotional effects on older adults.
$7.5 million to study elusive cell type important in aging, cancer, other diseases
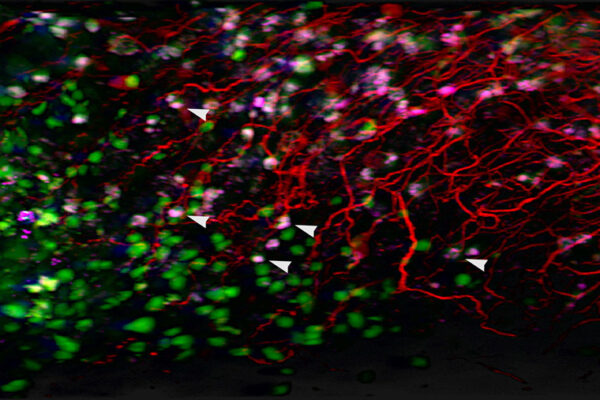
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has joined the NIH’s SenNet, a national research network focused on understanding senescent cells, an elusive but important cell type that plays key roles in the diseases of aging.
Fall-prevention program can help reduce harmful in-home falls by nearly 40%
New research from Washington University School of Medicine suggests that in-home falls can be reduced by nearly 40% with a community-based program that helps older adults make modifications to their homes to prevent such mishaps.
NIH funds Rudra, Jackrel to improve vaccines for elderly
Washington University’s Meredith Jackrel and Jai Rudra and are researching nanofiber materials that will eliminate the need for vaccine adjuvants.
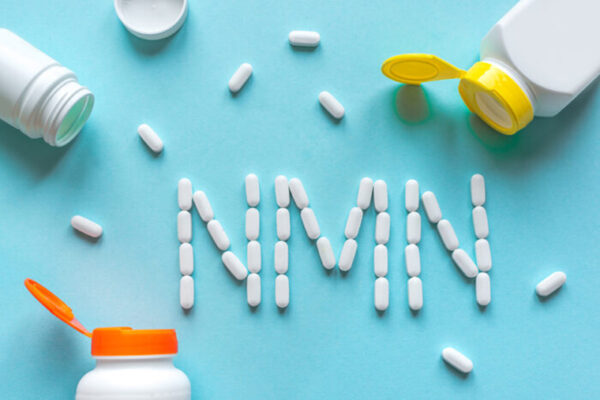
Anti-aging compound that improves metabolic health in mice improves muscle glucose metabolism in people
In the first clinical trial of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), School of Medicine researchers have found that the compound previously demonstrated to counteract aspects of aging and improve metabolic health in mice also has clinically relevant effects in people.
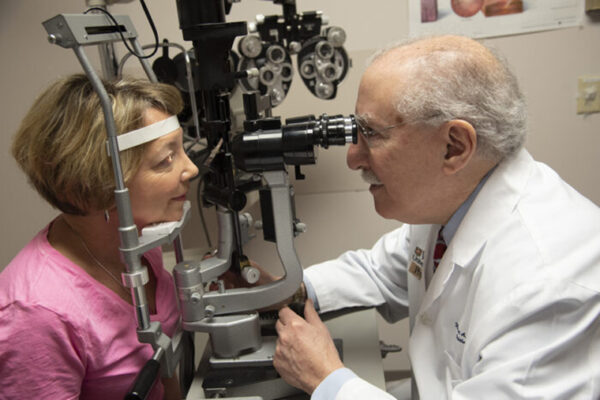
Treatment not always needed to prevent vision loss in patients with elevated eye pressure
More than 20 years after the launch of a landmark clinical trial led by the School of Medicine’s Michael A. Kass, MD, follow-up exams and analyses found that not all patients with elevated eye pressure need pressure-lowering treatment to prevent vision loss from glaucoma.
Reagh named APS ‘Rising Star’
Zachariah Reagh, assistant professor of psychological and brain sciences in Arts & Sciences, has been named a “Rising Star” by the Association for Psychological Sciences.
Can changes in driving habits predict cognitive decline in older adults?
Researchers at the School of Medicine have received three grants totaling more than $10 million to study the factors that contribute to deterioration in driving skills in older adults and to determine ways to identify people whose driving skills have begun to decline or are on the verge of slipping.
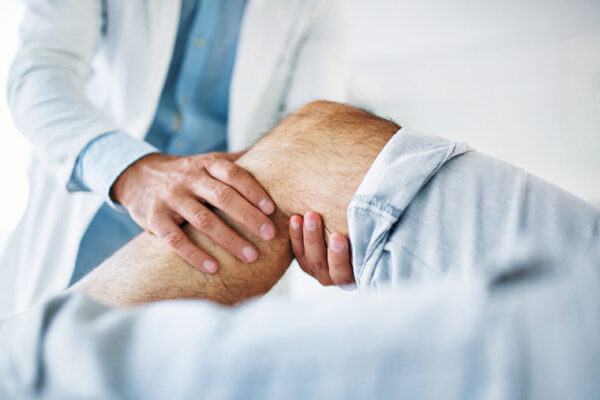
Gene that protects against osteoarthritis identified
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine, working in mice, have found that a molecule previously linked to diabetes, cancer and muscle atrophy also seems to be involved in the development of osteoarthritis. It may offer a useful treatment target.
Older Stories