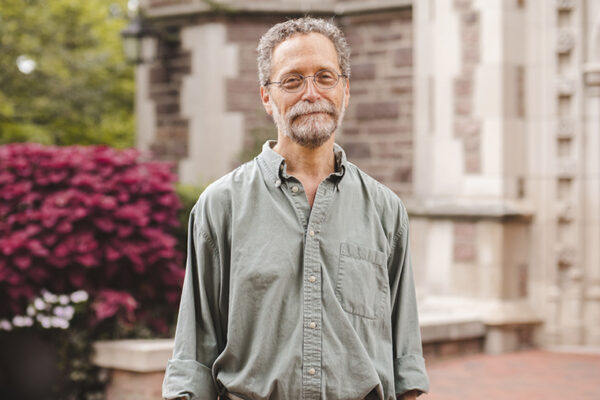
Washington People: Stan Braude
Stan Braude, professor of practice in biology, is a talented teacher who instills in his students the skills they need to prepare for life outside of Washington University. Take it from his students, though — because if you ask him, he will give all the credit to Joe (his St. Bernard).
Understanding criticality and the brain’s neural networks
New research from Washington University in St. Louis confirms that the brain tunes itself to a point where it is as excitable as it can be without tipping into disorder, similar to a phase transition. The new research from Keith Hengen, assistant professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, is published Oct. 7 in the journal Neuron.
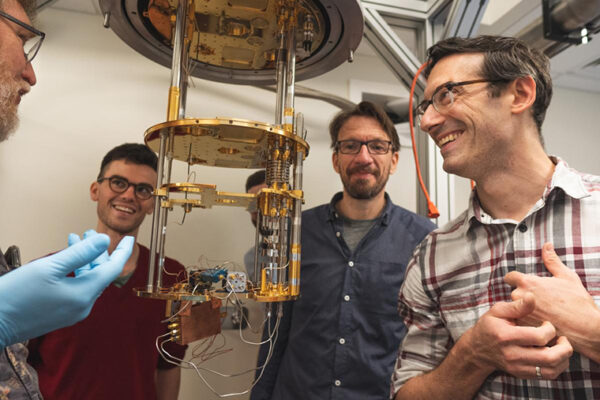
Complex energies, quantum symmetries
New research from Washington University in St. Louis realizes one of the first parity time-symmetric quantum systems, allowing scientists to observe how that symmetry — and the breaking of it — leads to previously unexplored phenomena. These and future PT symmetry experiments have potential applications to quantum computing. The work from the laboratory of Kater Murch, associate professor of physics in Arts & Sciences, is published Oct. 7 in the journal Nature Physics.
Brave new world
Faced with extreme weather events and unprecedented environmental change, animals and plants are scrambling to catch up — with mixed results. A new model developed by Carlos Botero, assistant professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, helps to predict the types of changes that could drive a given species to extinction.
Konecky wins American Geophysical Union early career award
Bronwen Konecky, assistant professor of earth and planetary sciences in Arts & Sciences, works at the cutting edge of an emerging research area that combines paleoclimate data with climate models. She received the Nanne Weber Early Career Award from the Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology Section of the American Geophysical Union.
NSF funding to support new ‘Quantum Leap’ effort
Washington University’s collaborative Center for Quantum Sensors was awarded a Quantum Leap Challenge Institute (QLCI) conceptualization grant from the National Science Foundation to help advance applications of quantum information science.
Hiding in plain sight
Early rice growers unwittingly gave barnyard grass a big hand, helping to give root to a rice imitator that is now considered one of the world’s worst agricultural weeds. The new research from biologist Kenneth Olsen in Arts & Sciences was published this week in Nature Ecology & Evolution.
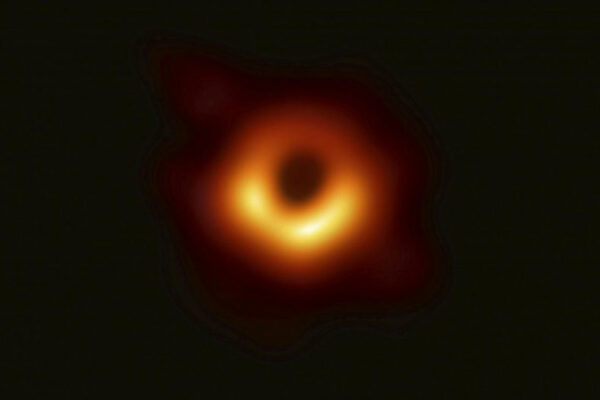
Nowak, collaborators win Breakthrough Prize for black hole image
Michael Nowak, research professor of physics in Arts & Sciences, is a member of the Event Horizon Telescope collaboration that won the 2020 Breakthrough Prize in Fundamental Physics. The award recognizes the team’s achievement of making the first image of a supermassive black hole, “taken by means of an Earth-sized alliance of telescopes.”
Ancient DNA study tracks formation of populations across Central Asia
Ethically sourced and informed by archaeology, an ambitious new study reports genome-wide DNA information from 523 ancient humans collected at archaeological sites across the Near East and Central and South Asia. Washington University in St. Louis brought key partners together to generate the world’s largest study of ancient DNA, published this week in the journal Science.
Time to retire the ‘pristine myth’ of climate change
Anthropologist T.R. Kidder in Arts & Sciences contributed to one of the first “big data” studies in archaeology to tackle broader questions of how humans have reshaped landscapes, ecosystems and potentially climate over millennia. The analysis published Aug. 30 in the journal Science challenges conventional ideas that man’s impact has been “mostly recent.”
View More Stories