Zika diagnostic test granted market authorization by FDA
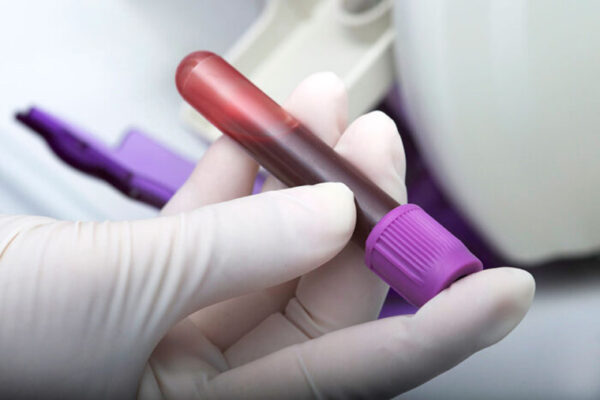
A test for signs of Zika infection has been granted market authorization by the Food and Drug Administration. The test is based in part on an antibody developed by researchers at the School of Medicine.
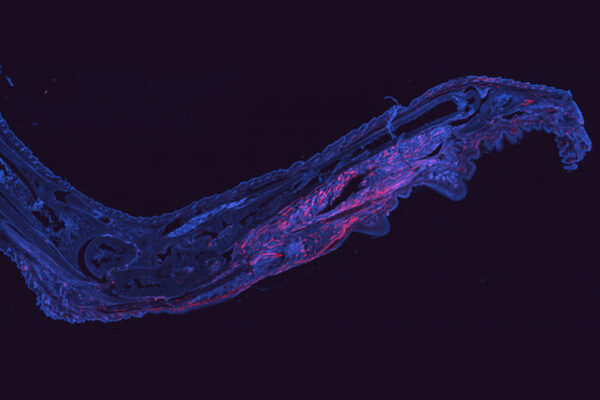
Arthritis-causing virus hides in body for months after infection
Researchers at the School of Medicine have developed a way to fluorescently tag cells infected with chikungunya virus. The technique opens up new avenues to study how the virus persists in the body and potentially could lead to a treatment.
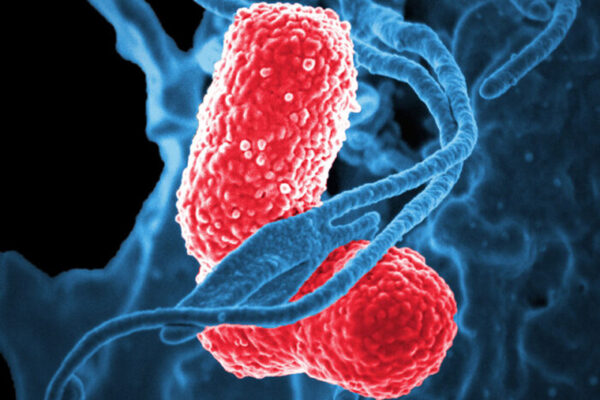
Vaccine against deadly superbug Klebsiella effective in mice
Researchers at the School of Medicine in St. Louis and the biotech startup VaxNewMo have developed a vaccine that is effective, in mice, against hypervirulent strains of Klebsiella that can cause life-threatening infections in healthy adults.
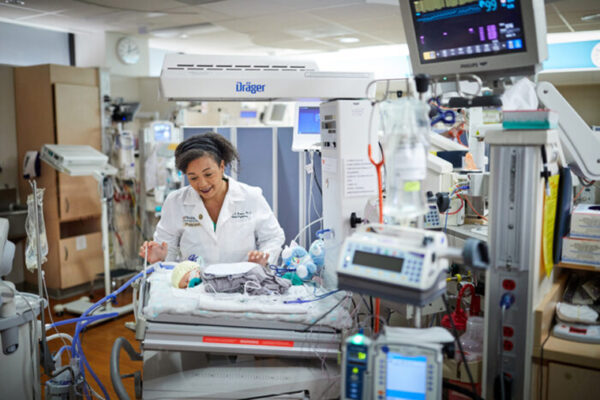
Stable home lives improve prospects for preemies
A new School of Medicine study has found that as premature babies grow, their mental health may be related less to medical challenges they face after birth than to the environment the babies enter once they leave the newborn intensive care unit.
$15 million supports quest for personalized leukemia therapies
Investigators at Siteman Cancer Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have been awarded a $15 million grant to better understand the genetic changes that drive acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a deadly blood cancer, and predict patients’ responses to therapy. The findings also may enable investigators to develop more effective therapies tailored to patients, based on the genetic characteristics of their cancer cells.
Why initial UTIs increase susceptibility to further infection
Researchers at the School of Medicine have discovered that an initial urinary tract infection (UTI) triggers changes to immune and other cells in the bladder that can prime the bladder to overreact to bacteria, worsening subsequent UTIs.
Children with mild asthma can use inhalers as needed
A new study from the School of Medicine finds that African American children with mild asthma can take their steroid inhalers as needed, based on symptoms, rather than at set times daily regardless of symptoms.
Genes linked to Alzheimer’s risk, resilience ID’d
A team led by researchers at the School of Medicine in St. Louis has identified a pair of genes that influence risk for Alzheimer’s disease. The genes — known as MS4A4A and TREM2 — affect the brain’s immune cells. They influence Alzheimer’s risk by altering levels of TREM2, a protein that is believed to help microglia cells clear excessive amounts of the Alzheimer’s proteins amyloid and tau from the brain.
Gut makeup could make diarrhea less likely
Researchers at the School of Medicine have found the molecular signature of a healthy gut microbial community – the kind that can keep the intestinal bacteria Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) from overgrowing and causing diarrhea.
Finnish people’s unique genetic makeup offers clues to disease
A study of the genetics of the people of Finland, conducted in part by researchers at the School of Medicine, has revealed new clues to common diseases.
View More Stories