Day of Dialogue & Action explores commitment to diversity and inclusion
The Washington University community will come together for the sixth annual Day of Dialogue & Action. The conference includes two full days of talks, panel discussions and workshops that will give participants an opportunity to learn about and engage with ongoing efforts to improve university culture and climate.
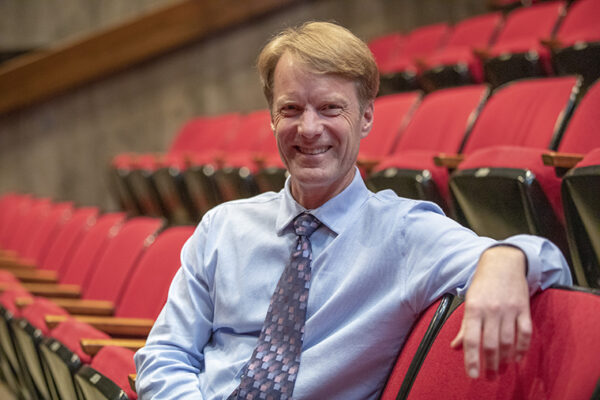
Keeping the arts central to campus life
As business manager of Edison Theatre and the 560 Music Center, Bill Larson is responsible for a variety of duties, from booking shows to selling tickets to even mopping the stage. “I want to make the 560 and Edison a destination for everybody on campus,” he said.
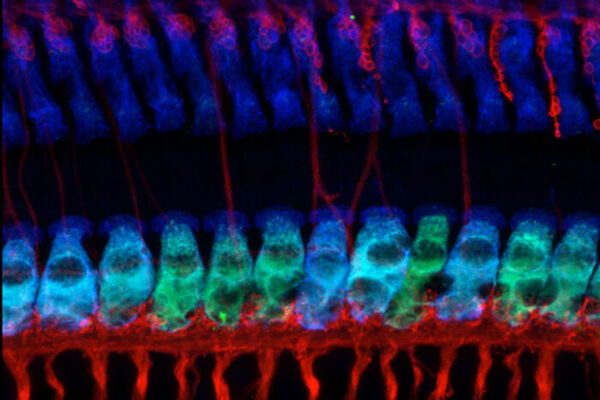
Noise-induced hearing loss blocked with drug compound
Studying mice, researchers at the School of Medicine and their colleagues have shown that a drug compound can block damage caused by too much glutamate signaling, raising the possibility of medication that prevents noise-induced hearing loss.
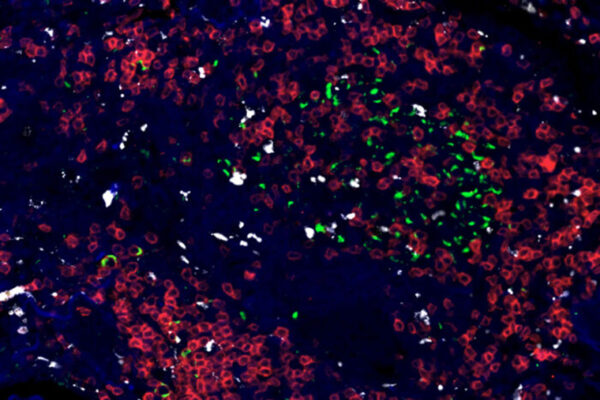
Immune responses to tuberculosis mapped across 3 species
A new study led by the School of Medicine lays out a genetic road map of immune responses to tuberculosis (TB) infection across three species.
1 in 4 kids who get antibiotics in children’s hospitals are prescribed the drugs incorrectly
New research led by the School of Medicine indicates that 1 in 4 of the children given antibiotics in U.S. children’s hospitals are prescribed the drugs inappropriately. The overuse of antibiotics poses an increasing threat to children who develop — or already have — drug-resistant infections.
‘Jumping genes’ help stabilize DNA folding patterns
New School of Medicine research indicates that “jumping genes” play a surprising role in stabilizing the 3D folding patterns of the DNA molecule inside a cell’s nucleus.
$29 million for new phase of international Alzheimer’s study
School of Medicine researchers have received $29 million from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health to continue a long-running, international Alzheimer’s study aimed at understanding how the disease develops and progresses.
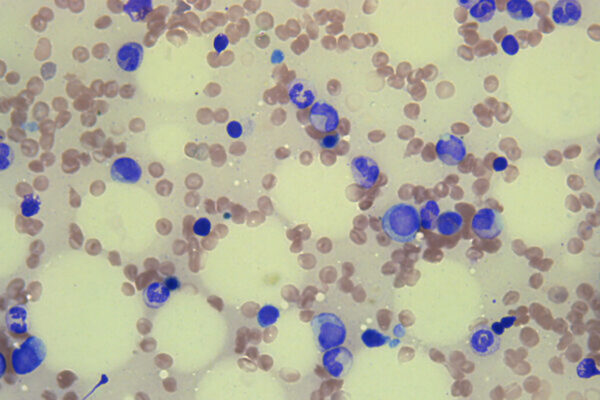
Mutations in donors’ stem cells may cause problems for cancer patients
A new study from the School of Medicine suggests that bone marrow — or blood stem cells — from healthy donors can harbor extremely rare mutations that can cause health problems for the cancer patients who receive them. Such stem cell transplants are important for treating blood cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia.
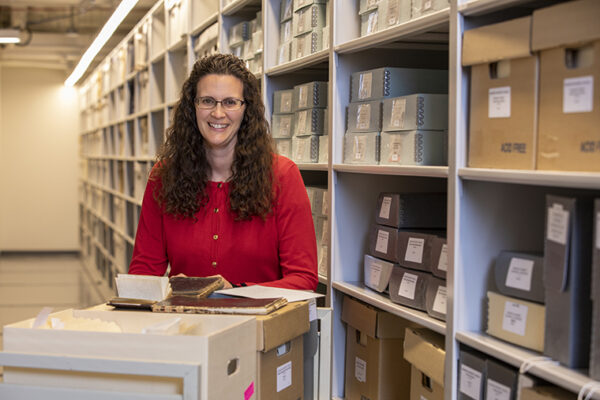
Washington People: Sonya Rooney
As university archivist, Sonya Rooney is charged with keeping track of the university’s institutional history as well as helping people find answers to their research questions.
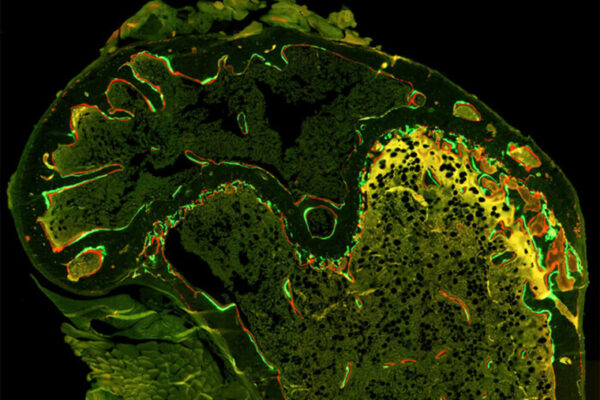
Investigational drugs block bone loss in mice receiving chemotherapy
Exposure to chemotherapy and radiation during cancer treatment leads to bone loss and increases the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. A new School of Medicine study identifies the trigger for this bone loss and suggests ways to prevent it.
View More Stories