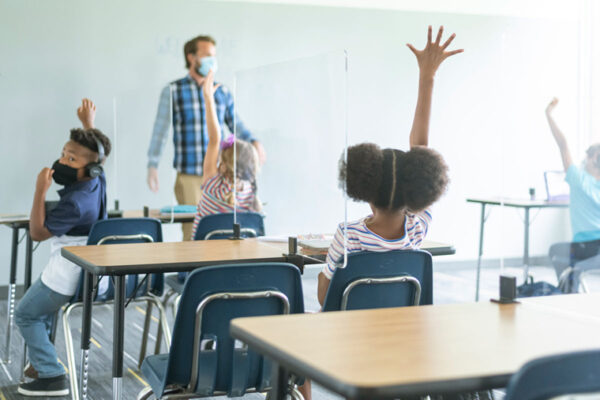
School-based COVID-19 testing initiative focuses on vulnerable populations
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have received $8 million from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) for two school-based projects — one in St. Louis County and the other in Maryland — aimed at safely returning students and staff to in-person school.
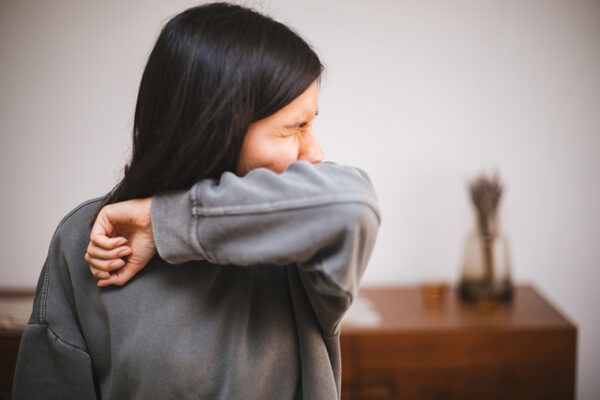
What makes us sneeze?
A team led by researchers at the School of Medicine has identified, in mice, specific cells and proteins that control the sneeze reflex. Better understanding of what causes sneezing may point to treatments to slow the spread of infectious respiratory diseases.
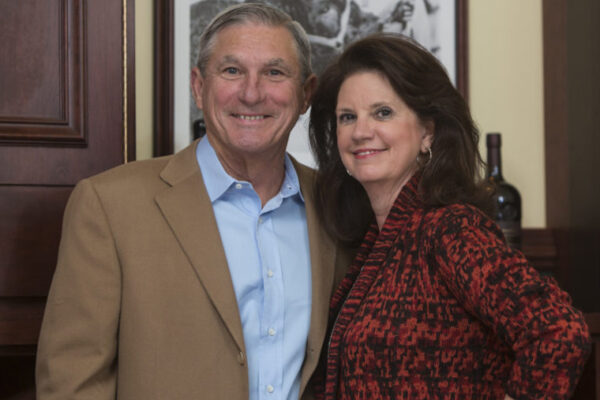
Judy and Jerry Kent to receive Harris Award
Judy and Jerry Kent have been selected as the 2021 recipients of the Jane and Whitney Harris St. Louis Community Service Award for their contributions to the St. Louis community.
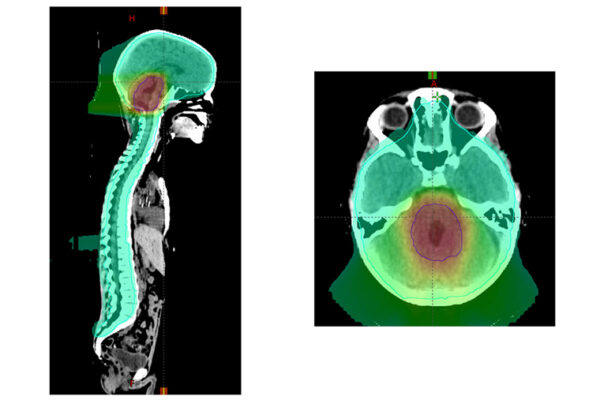
Study sheds light on treatment options for devastating childhood brain cancer
A new study led by Washington University School of Medicine provides new guidance on the treatment of medulloblastoma, a pediatric brain cancer. Some aspects of radiation therapy may be reduced while still providing effective treatment.
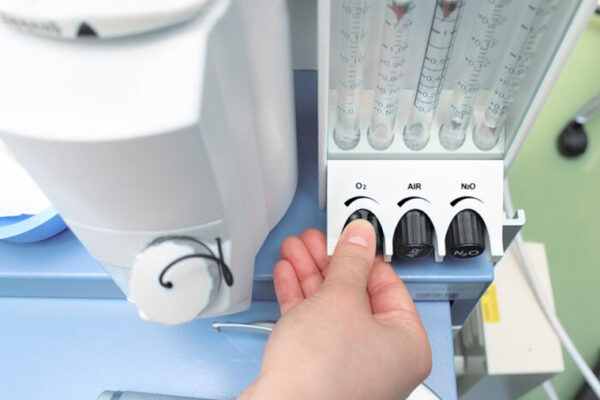
Laughing gas relieves symptoms in people with treatment-resistant depression
Researchers at the School of Medicine and the University of Chicago have found that a single, one-hour treatment that involves breathing in laughing gas can significantly improve symptoms in people with treatment-resistant depression.
Global travelers pick up numerous genes that promote microbial resistance
New School of Medicine research shows that international travelers often return home with new bacterial strains jostling for position within the gut microbiome. Such travel is contributing to the rapid global increase and spread of antimicrobial resistance.
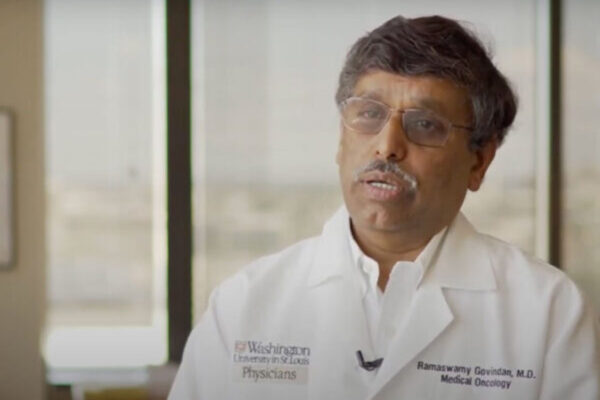
Newly approved drug effective against lung cancer caused by genetic mutation
The new drug sotorasib reduces tumor size and shows promise in improving survival among patients with lung tumors caused by a specific DNA mutation, according to results of a global phase 2 clinical trial. The study is led by scientists at the School of Medicine and other institutions.
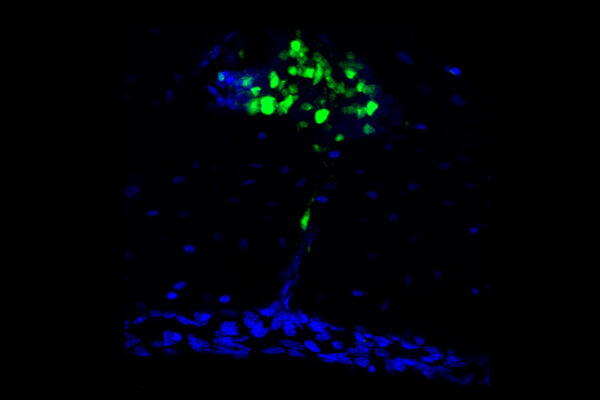
Studies reveal skull as unexpected source of brain immunity
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have discovered that the immune cells stationed in the protective tissue known as the meninges come primarily from the skull. The finding opens up the possibility of developing therapies to target such cells as a way to prevent or treat brain conditions.
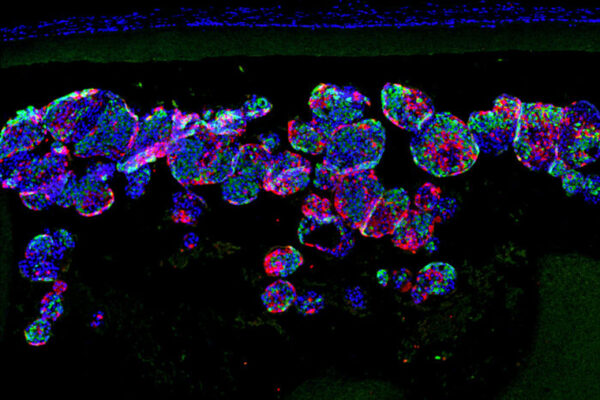
Tiny implant cures diabetes in mice without triggering immune response
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine and Cornell University have implanted insulin-secreting cells into diabetic mice to normalize their blood sugar.
Synthetic data mimics real health-care data without patient-privacy concerns
Washington University investigators now have access to a new research tool that allows them to conduct clinical studies using synthetic patient data. Synthetic data produced by the new tool, called MDClone, accurately mimics real patient data without the privacy concerns.
View More Stories