An investigational cancer drug that starves tumors of their energy supply also shows evidence of improving whole body metabolism, leading to improved weight control, according to a new study in mice from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
The findings are published in the journal Cell Reports Medicine.
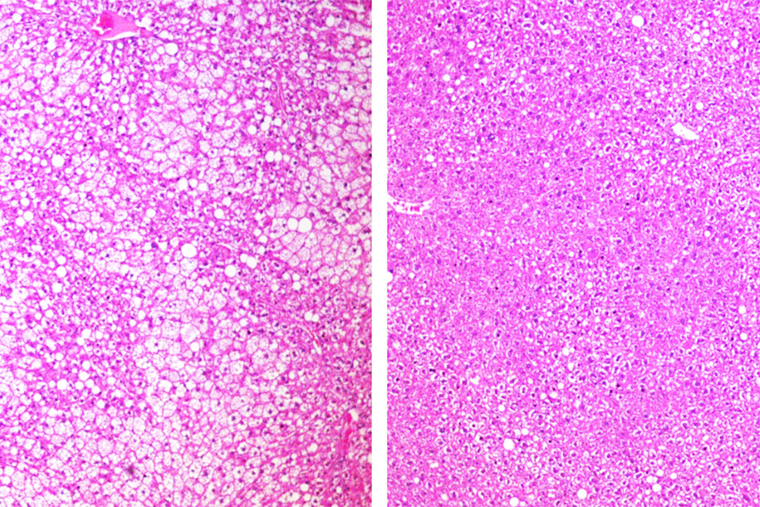
In a group of mice genetically prone to obesity and in a separate group of mice that became obese due to a high-fat, high-sugar diet, treatment with the drug ADI-PEG 20 increased insulin sensitivity, improved cholesterol levels, reduced fat buildup in the liver and lowered inflammation. For the mice genetically prone to obesity from birth, treatment with the drug protected them from their typical weight gain. And for the mice that became obese on a high-fat, high-sugar diet, treatment with the drug caused the mice to lose weight.
The drug is being investigated for potential use as a treatment for a number of cancers, including sarcoma, breast and pancreatic cancers. The drug breaks down the amino acid arginine in the blood, which deprives cancer cells of a key source of fuel. The researchers became interested in studying the drug after finding that genes responsible for breaking down arginine are dialed up tremendously when the body is in a fasting state. They wondered if the drug could mimic this effect of fasting.
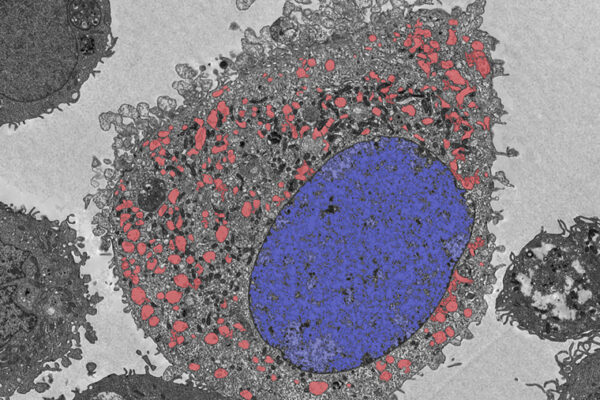
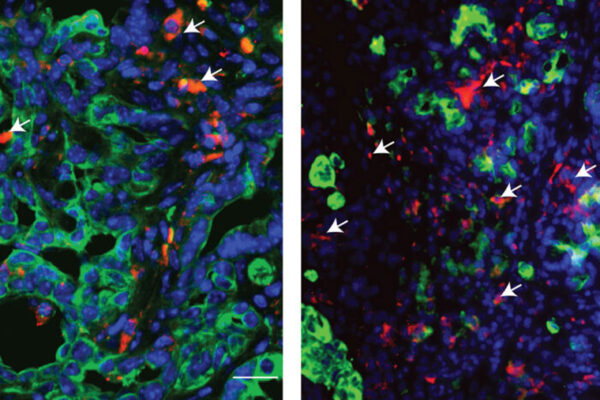
Indeed, the researchers found that the drug triggers cells to undergo a process called autophagy, or self-eating, a cellular-level housecleaning process. Cells undergoing autophagy burn their own cellular waste products for fuel. During fasting, when no new fuel is coming from the outside, cells shift to autophagy, turning inward for their fuel supply.
“Giving this drug seems to mimic some of the metabolic and therapeutic effects of fasting,” said senior author Brian DeBosch, MD, PhD, associate professor of pediatrics. “I was surprised by how large the effect was. In the mice prone to weight gain, the group that received the drug ended up weighing about 25% less than the mice that didn’t get the drug. And in the mice on the high-fat, high-sugar diet, we saw similar weight loss from the drug. Also, we don’t think that the preponderance of the drug’s metabolic benefits are from changes in body weight. In fact, for several outcome measures, the metabolic changes preceded significant changes in weight.”
The drug has been tested in clinical trials investigating its safety and efficacy in treating several tumor types, including breast, prostate, pancreatic and liver cancers. In general, metabolic therapies tend to have fewer side effects and are safer than chemotherapy, radiation and even newer immunotherapies used to treat cancer.
DeBosch, a pediatric gastroenterologist who treats patients at St. Louis Children’s Hospital, said the research team would like to conduct a clinical trial of the drug to see if it triggers similar metabolic benefits and weight loss in people who are overweight or obese. One question that remains is whether the drug is safe to take long term. It’s not a small molecule, like a statin, that can be taken for decades. The drug is a protein, so there is a possibility that patients could develop an immune response to it over time. However, DeBosch still sees a potential role for such a treatment over a matter of weeks to months.
“Many patients with obesity who are considering bariatric surgery must first lose some weight to make the procedure safer,” DeBosch said. “It can be difficult for such patients to lose up to 10% of their body weight before the surgery. This type of therapy could potentially serve as a bridge to help patients lose weight before bariatric surgery, to reduce the risk of complications during and after the procedure.”
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), grant numbers 1R01DK126622-01A1, 1R01HL147968-01A1, 1R21AT010520-01, UL1TR002345 and R56 DK115764; a Pilot Research Award from the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease; an AGA-Gilead Sciences Research Scholar Award in Liver Disease; the AGA-Allergan Foundation Pilot Research Award in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease; the Washington University Digestive Disease Research Core Center, grant number P30DK52574; the Washington University Diabetes Research Center, grant number P30DK020579; the Nutrition & Obesity Research Center, grant number P30DK056341; the Association for Aging Research Junior Faculty Award; the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation; the Washington University Center for Autophagy Therapeutics Research; the Longer Life Foundation; and a Washington University School of Medicine Pediatric Gastroenterology Research Training Grant, number T32DK077653.
Part of this study was funded via a sponsored research agreement awarded by Polaris Pharmaceuticals. DeBosch holds two patents related to the work. Co-author Bomalaski is an employee of Polaris Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Zhang Y, Higgins CB, Van Tine B, Bomalaski JS, DeBosch BJ. Pegylated arginine deiminase (ADI-PEG 20) drives arginine turnover and systemic autophagy to dictate energy metabolism. Cell Reports Medicine. Jan. 18, 2022.
Washington University School of Medicine’s 1,700 faculty physicians also are the medical staff of Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children’s hospitals. The School of Medicine is a leader in medical research, teaching and patient care, and is among the top recipients of research funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Through its affiliations with Barnes-Jewish and St. Louis Children’s hospitals, the School of Medicine is linked to BJC HealthCare.