Immunotherapy that involves treating cancer with the body’s own immune cells, or those of a matched donor, shows promise in clinical trials for some patients, but not all.
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis suggests that the age of certain immune cells used in such therapy plays a role in how effective the immunotherapy is. These cells — natural killer (NK) cells — appear to be more effective the earlier they are in development, opening the door to the possibility of an immunotherapy that would not utilize cells from the patient or a matched donor. Instead, they could be developed from existing supplies of what are called human pluripotent stem cells.
“We are trying to improve the effectiveness of immunotherapy for more patients,” said senior author Christopher M. Sturgeon, assistant professor of medicine. “This special source of natural killer cells has the potential to fill some of the gaps remaining with adult NK cell therapy. There is early evidence that they are more consistent in their effectiveness, and we would not need to process cells from a donor or the patient. They could be manufactured from existing cell supplies following the strict federal guidelines for good manufacturing practices. The characteristics of these cells let us envision a supply of them ready to pull off the shelf whenever a patient needs them.”
Unlike the adult versions of NK cells used in most investigational therapies, earlier versions of such cells do not originate from bone marrow. Rather, these NK cells are a special type of short-lived immune cell that forms in the yolk sac of the early mammalian embryo. But for therapeutic purposes, such cells do not need to originate from embryos — they can be developed from human pluripotent stem cells, which have the ability to give rise to many different cell types, including these specialized natural killer cells. Manufacturing such cells — which many academic medical centers already have the ability to do — would make them available quickly, eliminating the time needed to process the patient’s or donor’s cells, which can take weeks.
The study appears March 19 in the journal Developmental Cell.
“Before a certain time point in early development, there is no such thing as bone marrow, but there is still blood being made in the embryo,” Sturgeon said. “It’s a transient wave of blood that the yolk sac makes to keep the embryo going until bone marrow starts to form. And that’s the blood cell generation that’s making these unique natural killer cells. This early blood appears to be capable of things that adult blood simply can’t do.”
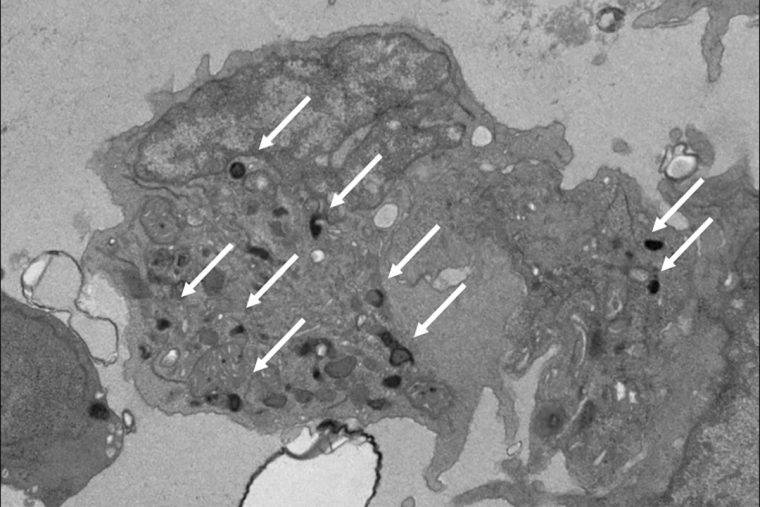
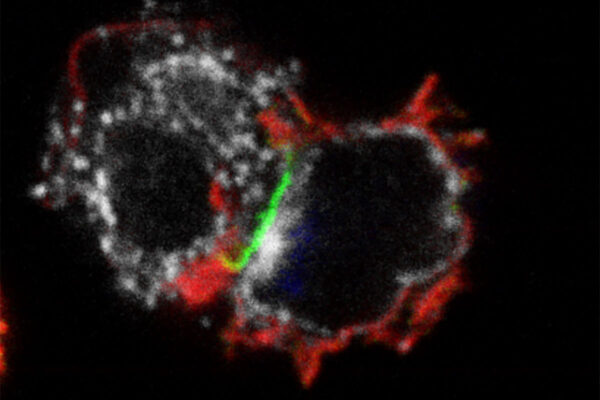
Studying mouse and human induced pluripotent stem cells that have been coaxed into forming these unique NK cells, the researchers showed that the NK cells are better at releasing specific anti-tumor chemicals — a process called degranulation — than their adult counterparts. Even NK cells derived from umbilical cord blood do not respond as robustly. NK cells of adult origin also release different chemicals that trigger harmful inflammation, but this response is not necessarily effective against cancer.
Past work by other groups suggested NK cells from earlier development might be more effective, but how and why this was the case remained unknown. The specific origin of these cells was also a mystery.
“Now we know where these special natural killer cells come from and that we can never get them from an adult donor, only a pluripotent stem cell,” Sturgeon said. “Based on their unique behavior alone, there is one small clinical trial of these cells that is ongoing. Now that we know how to manufacture them and how they work, it opens the door for more trials and for improving upon their function.”
According to Sturgeon, such cells could be produced from existing lines of pluripotent stem cells that would not need to come from a matched donor because, in general, NK cells do not heavily attack the body’s healthy tissues, as many T cell therapies can. T cells are another type of immune cell often used to treat blood cancer as part of a stem cell transplant, commonly called a bone marrow transplant. Even when NK cells do cause harm, they do not stay in the body for long periods of time.
From a basic science standpoint, Sturgeon also is interested in understanding why these cells are present in the early embryo in the first place and where they go in later development and after birth.
“We can only speculate at this point, but it’s possible that during early embryonic development, when there is so much rapid cell division, these cells are there as a surveillance mechanism to protect against pediatric cancers or infection,” he said.