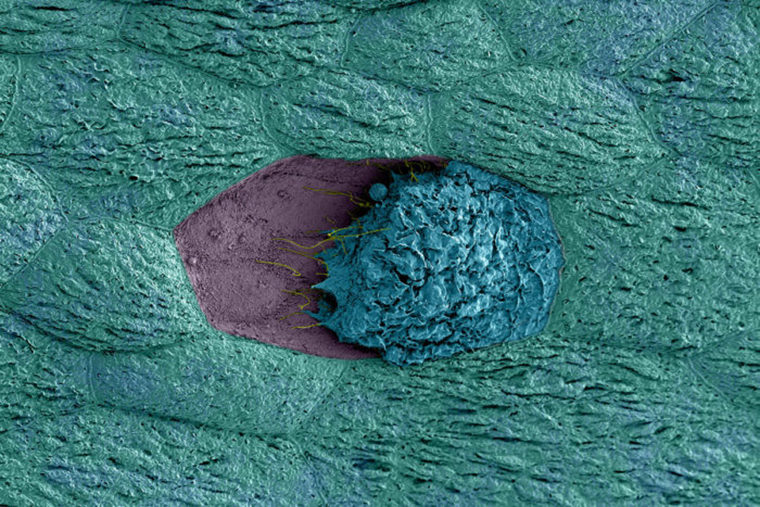
About half of all women will experience urinary tract infections in their lifetimes, and despite treatment, about a quarter will develop recurrent infections within six months of initial infection.
A new study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has uncovered a trigger of recurrent UTI infections: a type of vaginal bacteria that moves into the urinary tract.
The research, in mice, is published March 30 in PLOS Pathogens.
UTIs most often occur when bacteria that live inside the bowel make their way into the urinary tract. The infections can occur anywhere along the urinary tract but commonly develop in the bladder. UTIs are treated with antibiotics, but each time a UTI comes back makes it even more likely the infection will recur yet again.
In young, sexually active women, about 80 percent of UTIs are caused by E. coli. Conventional thinking holds that recurrence occurs when E. coli is reintroduced into the urinary tract. But the new research suggests another way for a subsequent UTI to develop: The vaginal bacterium Gardnerella vaginalis triggers E. coli already hiding in the bladder to cause another UTI. G. vaginalis also may be a contributor to more serious – and potentially deadly – kidney infections, the study suggests.
“We found that a particular vaginal bacterium, Gardnerella vaginalis, did not cause infection during exposure to the urinary tract, but it damaged the cells on the surface of the bladder and caused E. coli from a previous UTI to start multiplying, leading to another bout of disease,” said the study’s senior author, Amanda Lewis, an assistant professor of molecular microbiology and of obstetrics and gynecology at Washington University.
Previous studies already had established that E. coli bacteria can create dormant hiding places for E. coli in the bladder and later be reactivated to cause infection. But this is the first study to identify a plausible trigger.
The reasons why UTIs recur is not fully understood, but the researchers, including obstetrics and gynecology instructor Nicole Gilbert, PhD, and graduate student Valerie O’Brien, saw a clue in bacterial vaginosis, which is caused by an overgrowth of harmful bacteria, resulting in vaginal odor and discharge. The condition is associated with UTIs.
As part of the study, the researchers infected the bladders of female mice with E. coli, initiating UTIs, and then let them recover. One month after infection, no E. coli was detected in the animals’ urine. However, previous studies had shown that a small population of E. coli can persist in the bladder at levels undetectable in the urine.
Next, the researchers introduced into the bladders of the mice either Lactobacillus crispatus, a normal vaginal bacterium; G. vaginalis, which is associated with bacterial vaginosis; or sterile saltwater, as a control. Both kinds of vaginal bacteria were eliminated from the bladder within 12 hours, but this short sojourn in the bladder was enough for E. coli to reappear in the urine of more than half of the mice exposed to G. vaginalis, indicating a recurrent UTI. Mice given the normal vaginal bacteria or sterile saltwater were about five times less likely to develop another UTI compared with those given G. vaginalis.
“The mice are not being reinoculated with E. coli,” O’Brien said. “Instead, the bacterial reservoirs already in the bladder emerge out of the tissue, multiply and cause another infection.”
Moreover, in some of the mice with G. vaginalis, bacteria traveled from the bladder up the urinary tract to the kidneys. In women, kidney infections are rare – just 1 percent of women with bladder infections go on to develop one – but serious. Kidney infections involve back pain, fever, nausea and vomiting, and can be deadly.
“When we looked, we could see that this severe kidney damage was almost exclusively happening in the G. vaginalis group,” Lewis said.
All of the mice that had either G. vaginalis or E. coli in their urinary tracts showed some degree of kidney damage. But of the mice that had both species, 6 percent showed severe kidney damage, high levels of E. coli in the kidney and signs that E. coli had moved from the kidney to the bloodstream, a form of UTI that can kill. In other words, the presence of G. vaginalis made E. coli more likely to cause severe kidney disease.
The researchers said G. vaginalis is not normally a concern for women with UTIs but that perhaps it should be.
“If a clinical lab finds G. vaginalis in a UTI sample, perhaps they shouldn’t assume it’s just a contaminant from the vagina,” Gilbert said. “Our results suggest it could be contributing to the disease.”
The researchers suggest that new clinical studies are needed to inform doctors treating women for UTIs – especially kidney infections – to look at whether bacterial vaginosis may put some women at greater risk for this severe form of UTI. Both UTIs and bacterial vaginosis are treatable with antibiotics, but different kinds are required. Standard UTI antibiotics will not rid a patient of G. vaginalis.
The findings also may explain why some women experience recurrent UTIs after having sex.
“A lot of women swear that every time they have sex they get a UTI, and obviously that’s a huge burden,” Lewis said. “We don’t doubt that re-infection with E. coli is partly responsible, but we think we’ve found another pretty compelling reason why the connection between sexual activity and recurrent UTI might exist: Vaginal bacteria like G. vaginalis are moved into the urinary tract during sex.”