The secret life of bee genes
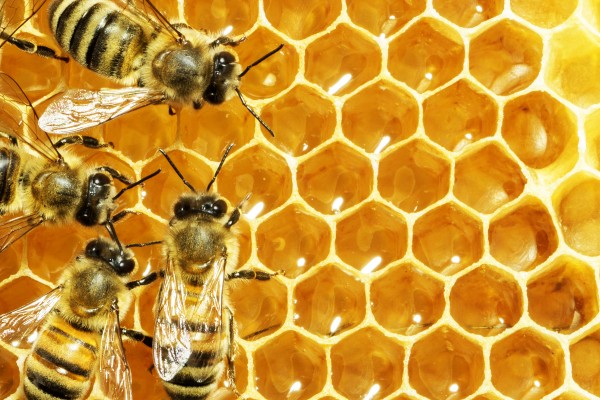
Genes inherited from mothers (matrigenes) and fathers (patrigenes) usually work harmoniously in the offspring. However, kin selection theory predicts these genes may be in conflict in interactions among relatives in which they are unequally represented (half-siblings). In honey bees, patrigenes are predicted to favor daughters that lay eggs themselves rather than remaining sterile and rearing their half-sisters’ offspring. An experimental test bears out this prediction.
Bose named Packard Fellow
Arpita Bose, PhD, assistant professor of biology in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, has been named a Packard Fellow, a prestigious distinction awarded to only 18 top young researchers nationwide this year. Bose plans to use the grant to work with unusual microbes that can take electrons directly from an outside source to draw down atmospheric carbon dioxide or make sustainable biofuels.
Washington People: Mike Dyer
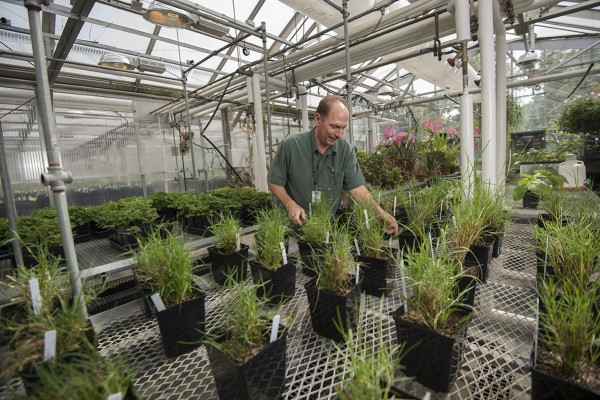
Mike Dyer, supervisor of the greenhouse on the campus of Washington University in St. Louis, has the job many of us probably wish we had — but only because we think he spends the day pottering around watering plants. Instead, his job requires everything from the mechanical and engineering skills needed to suppress the greenhouse’s voracious appetite for energy; extensive knowledge of insects; and the ability to grow any plant he is handed under the conditions specified. It’s not exactly relaxing, but he enjoys it that way.
WashU Expert: Brace yourself, it’s fall-back time again
Falling back is easier on us than springing forward, says Erik Herzog, a biologist at Washington University in St. Louis who has devoted his career to studying body clocks and circadian rhythms. But it is never a good idea to force our body clocks to follow abrupt changes in mechanical clocks. We should get rid of daylight savings time, Herzog says.
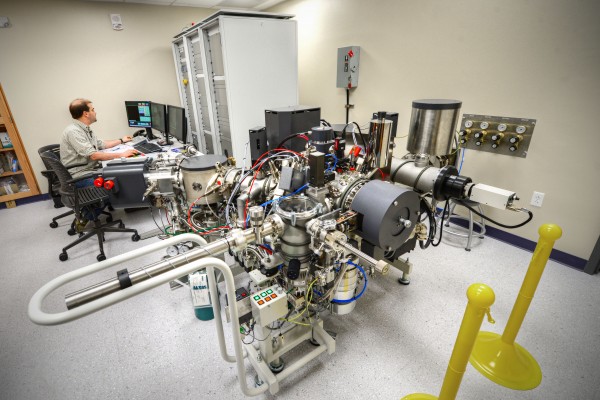
$2.4 million instrument upgrade will let scientists see what is happening inside microbes
The U.S. Department of Energy has awarded David Fike, PhD, associate professor of earth and planetary sciences, $2.4 million to adapt a powerful chemical microscope called the 7F-GEO SIMS for biological samples. The updated instrument’s ability to map the chemistry inside cells will boost research on microbes that are promising candidates for biofuel or bioenergy production.
Bacterial infection makes farmers out of amoebae
A bacterial infection turns non-farming social amoebae into farmers, Washington University evolutionary biologists report in the Aug. 24 issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Fish that have their own fish finders
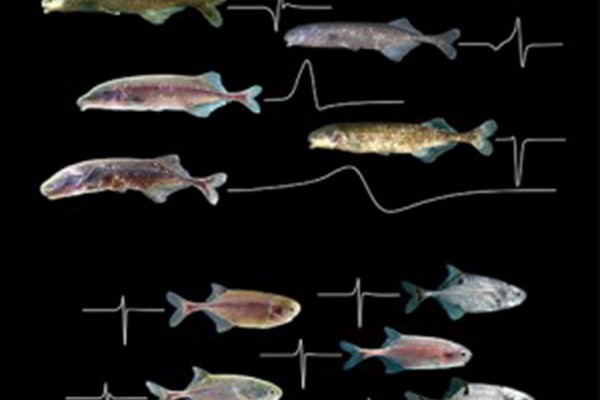
African fish called mormyrids communicate by means of electric signals. Fish in one group can glean detailed information from a signal’s waveform, but fish in another group are insensitive to waveform variations. Research at Washington University in St. Louis has uncovered the neurological basis for this difference in perception.
Do cheaters have an evolutionary advantage?
What is it with cheating? Cheaters seem to have an immediate advantage over cooperators, but do they have an evolutionary advantage? A study published in Current Biology suggests the benefits of cheating change with its prevalence,in a population. Cheaters may succeed, for example, only when they are rare, and fail when they become so numerous they push out cooperators.
Student Nwumeh wins undergraduate science award
Ron Nwumeh, a junior studying biology and research assistant in the lab of Joseph Jez, PhD, in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, recently received the 2015 Merck Undergraduate Science Research Scholarship Award.
Biologist Strader receives CAREER award from NSF
Lucia Strader, PhD, assistant professor of biology in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, has received a five-year, $866,000 CAREER award from the National Science Foundation (NSF) for research titled “Roles for Indole-3-butyric Acid in Plant Development.”
View More Stories