Jolly elected to Missouri Foundation for Health board
Andwele M. Jolly, manager of business operations for the Divisions of Allergy & Immunology and of Rheumatology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has been elected to the board of directors of the Missouri Foundation for Health.
Rett Spectrum Clinic to open on Medical Campus
The Rett Spectrum Clinic, a specialty clinic designed to care for and support children with Rett syndrome and related disorders including CDKL5, will open Jan. 30 on the Medical Campus.
Faculty featured as leaders in new efforts to promote dissemination and implementation
A new tool kit for dissemination and implementation, developed by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute in Washington, D.C., prominently features the work of several university faculty members, including the groundbreaking 2012 book, “Dissemination and Implementation Research in Health: Translating Science to Practice.”
Pro-marijuana ‘tweets’ are sky-high on Twitter
Analyzing every marijuana-related Twitter message sent during a one-month period in early 2014, researchers at the School of Medicine have found that the “Twitterverse” is a pot-friendly place. In that time, more than 7 million tweets referenced marijuana, with 15 times as many pro-pot tweets sent as anti-pot tweets.
Virgin receives several multiyear grants
Herbert W. Virgin IV, MD, PhD, the Edward Mallinckrodt Professor of Pathology and Immunology and head of the Department of Pathology and Immunology, has received several multiyear grants.
Viruses may play unexpected role in inflammatorybowel diseases
Inflammatory bowel diseases are associated with a
decrease in the diversity of bacteria in the gut, but a new study led by
researchers at the School of Medicine has linked these same illnesses to an increase in the diversity of viruses.
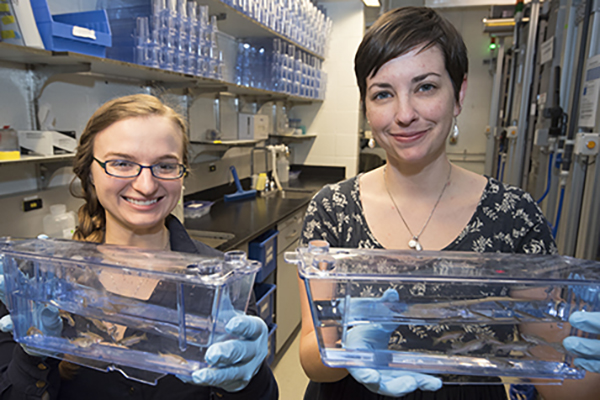
Scientists find gene vital to central nervous system development
Using Washington University’s state-of-the-art zebrafish facility, scientists have identified a gene that helps regulate how well nerves of the central nervous system are insulated. The finding may have implications for human diseases such as multiple sclerosis, in which this insulation is lost.
Trustees grant faculty promotions
At last month’s Board of Trustees meeting, several Washington University in St. Louis faculty members from the School of Medicine were promoted with tenure.
Medical school’s Health Happening Fair is Jan. 30
School of Medicine employees are invited to visit the annual Health Happening Fair from 8 a.m. to 4 p.m. Friday, Jan. 30, in the Eric P. Newman Education Center for free health screenings and information on a wide variety of health topics.
School of Medicine annual art show underway
The School of Medicine’s 11th Annual Art Show is underway in the Farrell Learning and Teaching Center atrium, 520 S. Euclid Ave. Visitors may view the art through Feb. 11.
View More Stories