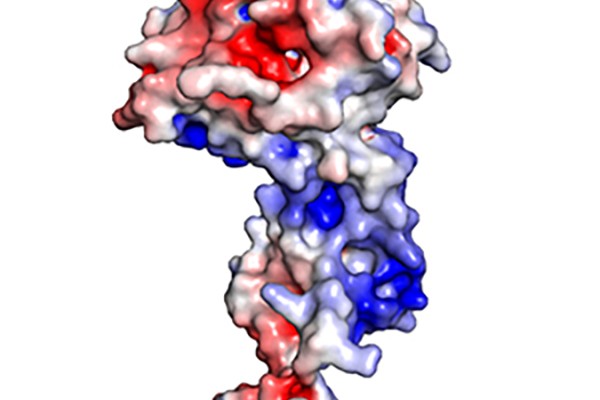
New Ebola study points to potential drug target
Opening the door for potential treatments for the deadly Ebola virus, scientists at Washington University and elsewhere have found that a way to kill the virus by interfering with its replication.
Medical Campus students perform 10th annual musical April 16-18
Students on the Medical Campus will present their 10th annual musical, “How to Succeed in Business Without Really Trying,” at 8 p.m April 16, 17 and 18 in the Olin Residence Hall Gym on the Medical Campus.
McCaskill holds roundtable discussion on aging at Washington University
As part of her series of Senior Listening Sessions across Missouri, Sen. Claire McCaskill held a roundtable discussion with experts on retirement security, elder justice and healthy aging March 31 at the Brown School’s Goldfarb Hall. Among the roundtable participants were seven from Washington University in St. Louis.
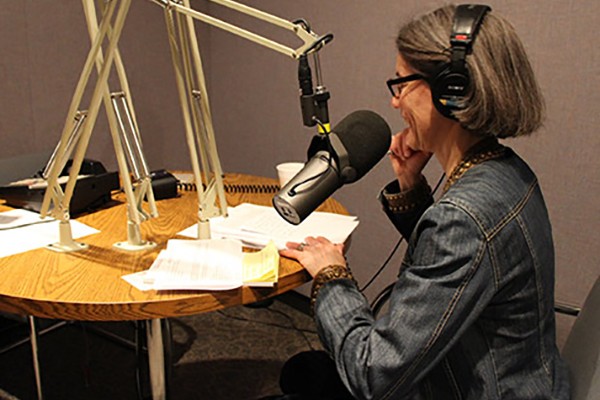
School of Medicine faculty educate, entertain on ‘Science Friday’
Beatriz Carreno, PhD, was featured Friday, April 3, on the syndicated radio show “Science Friday,” where she talked about School of Medicine research involving personalized melanoma vaccines. Carreno is the fourth faculty member in recent months to appear on the show.
Feibel named director of Center for History of Medicine
Robert M. Feibel, MD, has been named director of the Center for History Of Medicine of Washington University. The center is housed in the Bernard Becker Medical Library at the School of Medicine.
Traffic flow, shuttle routes adjusted for Medical Campus construction
Over the next several months, construction projects at and near Washington University Medical Center will continue to affect traffic flow and shuttles as improvements to parking and intersections continue.
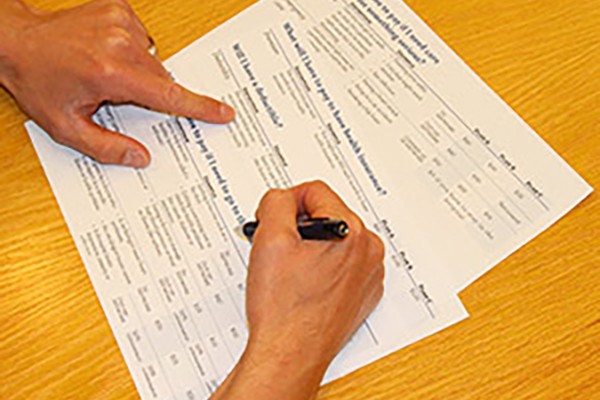
Study suggests ways to simplify health insurance enrollment
While the federal health-care law has reduced the number of uninsured people by about 10 million, challenges remain, including how to educate new enrollees about their coverage options. New research at Washington University shows that communicating information about the Affordable Care Act can be made simple.
Maher receives Susan G. Komen career award
Christopher A. Maher, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has received a three-year, $450,000 Susan G. Komen Career Catalyst Award for research focused on understanding the role of long noncoding RNAs in estrogen-positive breast cancer treatment resistance. Maher’s lead mentor is Elaine R. Mardis, PhD, the Robert E. and Louise F. Dunn Distinguished Professor of Medicine.
Louis Sullivan visits the university April 9
Louis W. Sullivan, MD, president emeritus of Morehouse School of Medicine, and former secretary of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services (HHS), will speak about healthy equity and diversity in the health professions in two talks April 9 at Washington University.
Personalized melanoma vaccines marshal powerful immune response
Personalized melanoma vaccines can be used to marshal a powerful immune response against unique mutations in patients’ tumors, according to early data in a first-in-people clinical trial at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The research is a boost to cancer immunotherapy, a treatment strategy that unleashes the immune system to seek out and destroy cancer.
View More Stories