Tan named president-elect of EMS organization
David K. Tan, MD, an associate professor of emergency medicine at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has been elected president-elect of the National Association of EMS Physicians.
Link connecting garages to medical buildings opens March 1
The link connecting four Medical Campus garages to other campus buildings will open March 1. The link will be accessible from the St. Louis Children’s Hospital staff, Duncan Central, Duncan-Taylor and Metro garages.
New collaboration with Pfizer aimed at speeding drug discovery
Washington University in St. Louis is collaborating with the biopharmaceutical company Pfizer Inc. on research aimed at speeding the development of new drugs. The university is the first academic institution in the Midwest to join Pfizer’s Centers for Therapeutic Innovation’s (CTI) collaborative network.
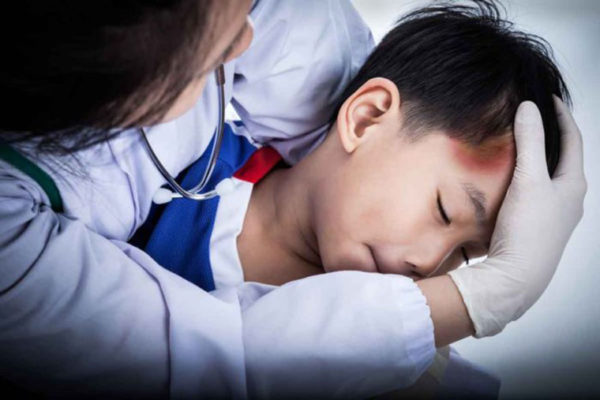
New guidance developed for children hospitalized with mild head trauma
In new research, pediatric neurosurgeons at the School of Medicine developed a risk scoring system intended to help determine whether a child with mild traumatic brain injury and an abnormal CT scan can be monitored safely in a general hospital ward or requires the increased surveillance of an intensive care unit (ICU).
Three questions with Gautam Dantas on antibiotic resistance
A microbiology professor discusses antibiotic resistance and his lab’s efforts to help physicians fight antibiotic-resistant infections.
Siteman survivor symposium March 2
The Siteman Cancer Center is holding a Spring Symposium on Survivorship from noon to 4:30 p.m. March 2 on the Medical Campus. The free event aims to encourage collaboration on cancer survivorship research. Registration is required.
Babcock named VP of health-care epidemiology group
Hilary M. Babcock, MD, an associate professor of medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has been named vice president of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA), a professional group that promotes research, education and advocacy for safe health care.
Gehlert inducted as president of social work organization
Sarah Gehlert, the E. Desmond Lee Professor of Racial and Ethnic Diversity at the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis, has been inducted as the new president of the American Academy of Social Work and Social Welfare.
Better than a pill
With a new $1.7 million award from the National Institutes of Health, a team from Washington University in St. Louis plans to develop a silk-based system to better alleviate the pain and discomfort of osteoarthritis.
Brain network connections may underlie social behavior linked to autism
Researchers at School of Medicine, with colleagues from the multicenter Infant Brain Imaging Study (IBIS) network, have found associations between brain connectivity and a key social behavior that is a central feature of autism.
View More Stories