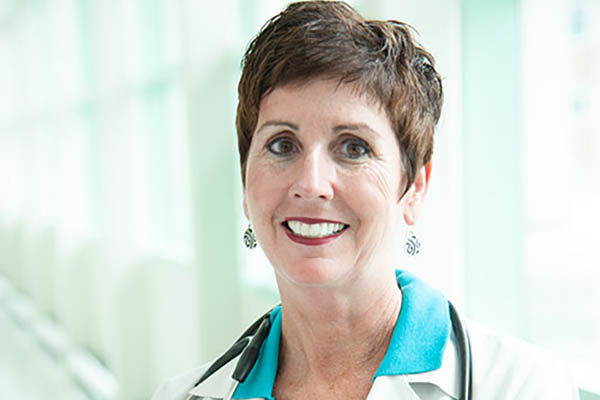
Loe, Salles recognized by American Medical Association
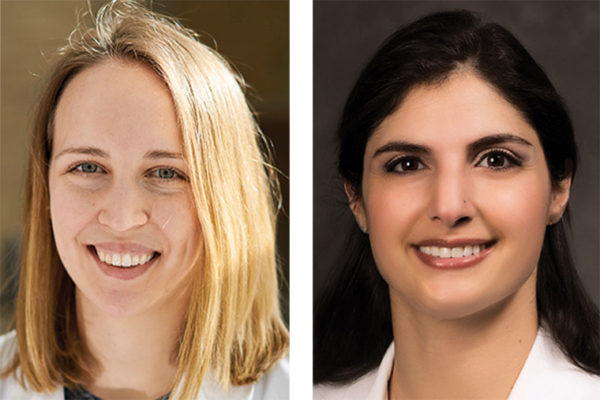
Maren Loe (left), a third-year medical and doctoral student, and Arghavan Salles, MD, PhD, assistant professor of surgery, both at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, have received a $10,000 grant from the American Medical Association to study gender bias in medical education.
Mind’s quality control center found in long-ignored brain area
The cerebellum, once thought to be limited to controlling movement, is involved in every aspect of higher brain function — including attention, thinking, planning and decision-making — according to a new study by researchers at the School of Medicine.
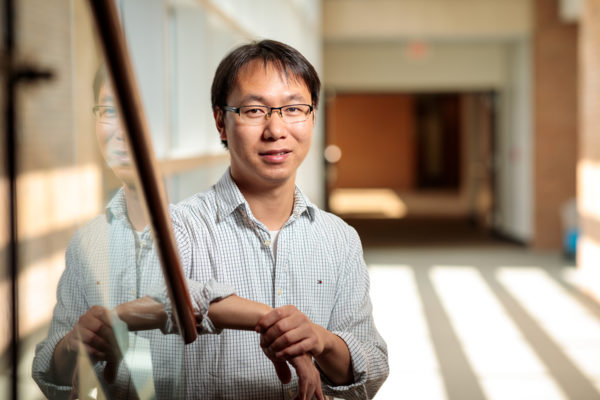
Postdoc researcher Zhang receives STAT honor
Rong Zhang, a postdoctoral researcher at Washington University School of Medicine who studies how viruses cause disease, has been named a 2018 Wunderkind by the national biomedical publication STAT News. The award honors young scientists and doctors who are blazing new trails in research and public health.
Obituary: William T. Shearer, former trustee, 81
William T. Shearer, MD, PhD, a former trustee of Washington University in St. Louis and a School of Medicine alumnus and former faculty member, died Tuesday, Oct. 9, 2018, at his home in Houston. He was 81.
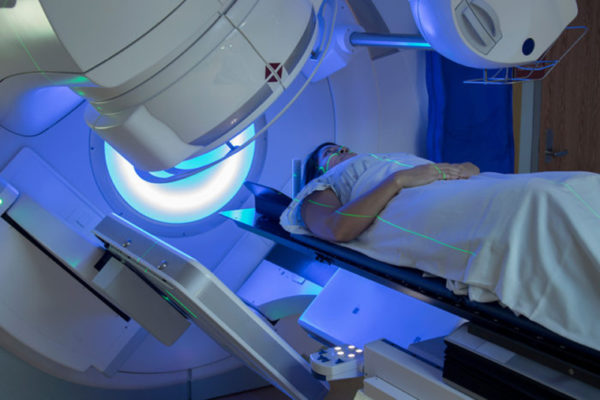
It’s safe to use skin creams before radiation therapy
A new study demonstrates that patients can safely use skin creams before undergoing radiation therapy. This contradicts common advice from radiation oncologists, according to researchers at the School of Medicine and the University of Pennsylvania.
Course teaches medical trainees how to provide care in developing countries
A recent two-week crash course on global health helped prepare medical students, residents and fellows for clinical rotations and long-term careers in developing countries. Caring for such patients requires a different mindset for trainees accustomed to working in modern medical centers with updated technology and no shortage of supplies or medications.
Diemer recognized by Association of American Medical Colleges
Kathryn Diemer, MD, assistant dean for career counseling and professor of medicine at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, will receive the 2018 Excellence in Medical Student Career Advising Award from the Association of American Medical Colleges on Nov. 2 in Austin, Texas.
Druley addresses childhood cancer at U.S. Capitol
Todd E. Druley, MD, PhD, associate professor of pediatrics, of genetics and of developmental biology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, represented pediatric cancer researchers in September at the U.S. Capitol in Washington for Childhood Cancer Awareness Month.
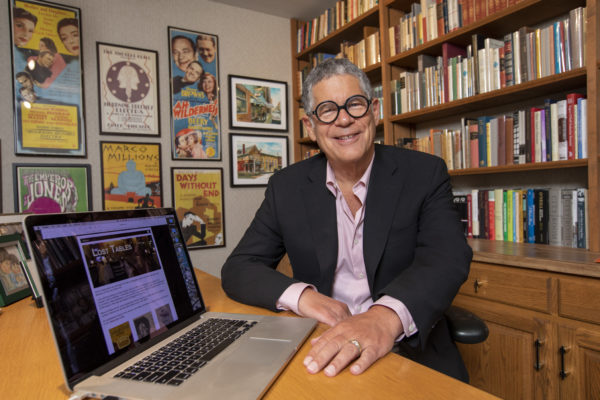
Keeping track of lost restaurants
For his main dish, alumnus Harley Hammerman is a radiologist and entrepreneur. On the side, he collects historical memorabilia, including of playwright Eugene O’Neill and long-gone beloved restaurants in the St. Louis area.
Klingensmith named director of school’s Academy of Health Professions Educators
Mary E. Klingensmith, MD, the Mary Culver Distinguished Professor and vice chair for education in the Department of Surgery at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has been named the inaugural director of the school’s Academy of Health Professions Educators.
View More Stories