Previously undetected brain pulses may help circuits survive disuse, injury
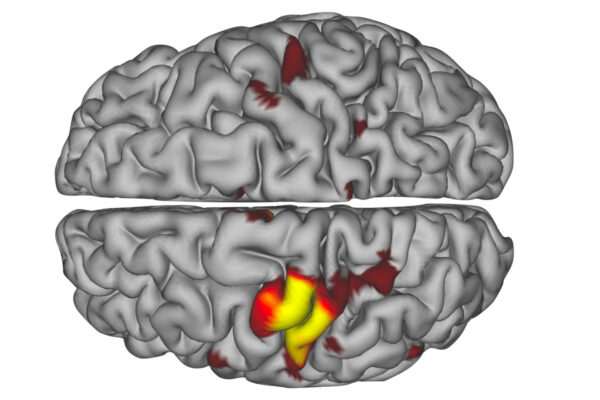
A neuroscientist’s arm cast led him and fellow School of Medicine researchers to find previously undetected neuronal pulses in the human brain that activate after an immobilizing illness or injury. The pulses appeared on MRI scans used to measure brain activity.
How an invention gets out of the lab and into the world
Life-changing innovations continue to emerge from the university thanks to creative faculty research, cross-collaboration and the aid of the Office of Technology Management.
What does science tell us about Adam and Eve?
In his book The Genealogical Adam & Eve: Surprising Science of Universal Ancestry, S. Joshua Swamidass, MD, associate professor of Pathology & Immunology in the School of Medicine and of Biomedical Engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering, uses science to show that Adam and Eve could have existed and that theology and science don’t lie nearly so far apart.
Mokalled receives national early career award
Mayssa H. Mokalled, assistant professor of developmental biology at Washington University School of Medicine, has received the 2020 H.W. Mossman Award in Developmental Biology from the American Association for Anatomy.
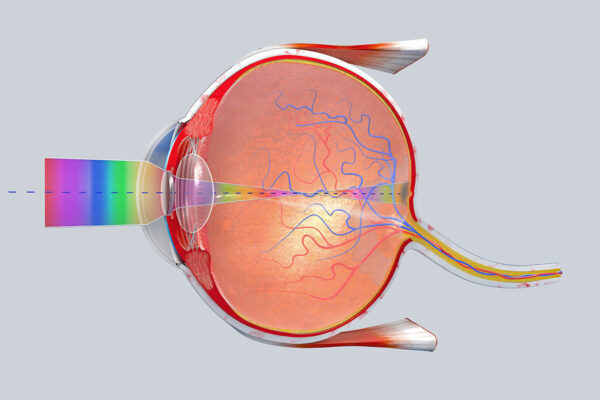
Scientists map how human retinal cells relay information to brain
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine report that specific types of retinal cells that carry the vast majority of visual signals from the human retina to the brain efficiently process and compress that information so it can be transferred. The study may advance our understanding of eye diseases involving the retina.
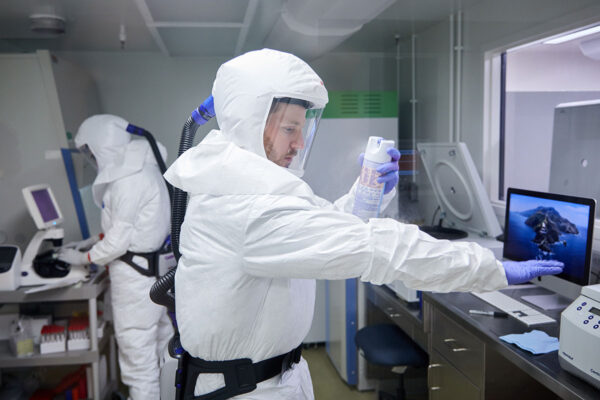
Patients with COVID-19 donate specimens to advance research efforts
School of Medicine physicians led efforts to create a repository for storing and managing specimens collected from patients with COVID-19. The samples are being distributed to investigators conducting COVID-19 research across the university.
Wambach receives award from American Thoracic Society
Jennifer A. Wambach, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics in the Division of Newborn Medicine at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has received the Robert B. Mellins, MD, Outstanding Achievement Award from the American Thoracic Society Pediatric Assembly.
COVID-19 mouse model will speed search for drugs, vaccines
Scientists at the Washington University School of Medicine have developed a mouse model of COVID-19 that is expected to speed up the search for drugs and vaccines for the potentially deadly disease.
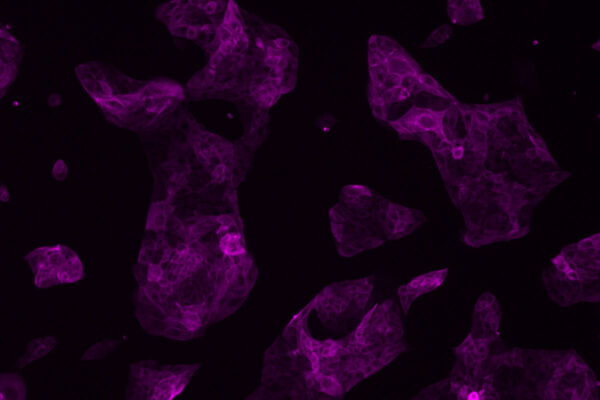
Scientists generate early stem cells that form human placenta
Scientists at Washington University School of Medicine have developed a way to guide human stem cells into becoming important precursor cells that give rise to the placenta. These stem cells could help scientists understand miscarriage or preeclampsia.
Burnham recognized by national microbiology society
Carey-Ann D. Burnham, professor of pathology and immunology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has received the Award for Research and Leadership in Clinical Microbiology from the American Society for Microbiology.
View More Stories