WashU ExpressCare offers same-day appointments
WashU ExpressCare is open to the public, 18 and older, for same-day care for minor health concerns seven days a week, including holidays. The clinic offers appointments with a WashU emergency medicine physician virtually from home, or when necessary, in-person.
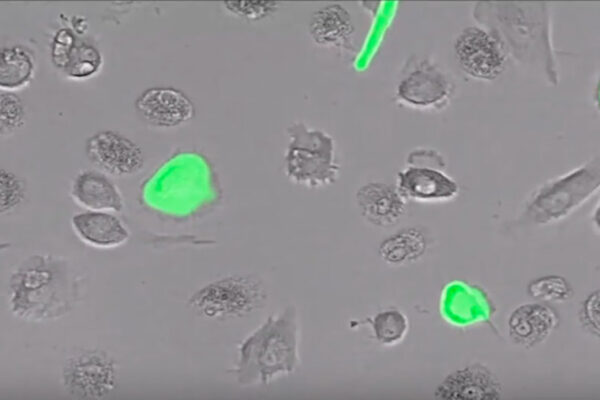
Human immune cells have natural alarm system against HIV
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis describes a strategy that could lead to therapies for clearing HIV infection. The researchers showed that human immune cells have a natural alarm system that detects the activity of a specific HIV protein.
Faculty receive grant for heart health research
Weikai Li, along with Michael J. Greenberg, both at the School of Medicine, and Michael L. Gross, in Arts & Sciences, received a three-year $750,000 grant from American Heart Association for their research titled “Interdisciplinary structural studies of iron homeostasis in cardiovascular health.”
Boschert receives award from laboratory animal science association
Kenneth R. Boschert, DVM, associate director of the Division of Comparative Medicine at Washington University School of Medicine, has received the Charles A. Griffin Award from the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science. The award recognizes those in veterinary medicine who have demonstrated ethical scientific or technological advancements in humane experimentation or improved animal care practices.
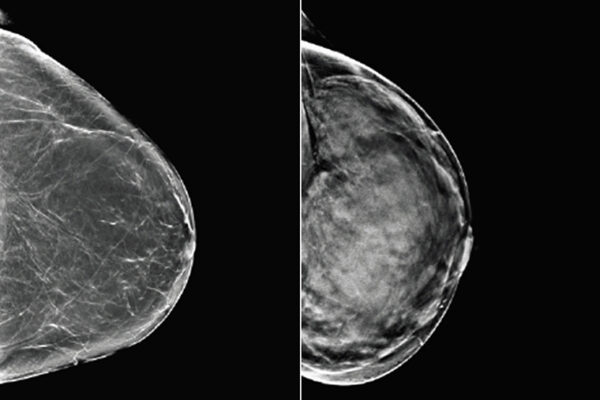
Algorithm analyzes mammograms, signals need for more breast cancer screening
Researchers at the School of Medicine and Whiterabbit.ai have developed a software that assesses breast density and can help identify women who could benefit from additional screening.
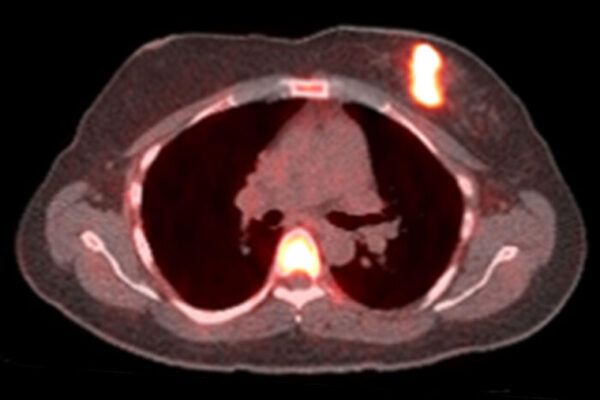
Imaging identifies breast cancer patients unlikely to benefit from hormone therapy
In a small study, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine found that only women whose tumors responded to estrogen challenge benefited from hormone therapy. The findings could help doctors choose the treatments most likely to help their patients.
Ludmerer, DuBois named Hastings Center Fellows
James M. DuBois, the Steven J. Bander Professor of Medical Ethics and Professionalism, and Kenneth M. Ludmerer, MD, the Mabel Dorn Reeder Distinguished Professor of the History of Medicine at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, have been named Hastings Center Fellows. The Hastings Center addresses social and ethical issues in health care, science and technology.
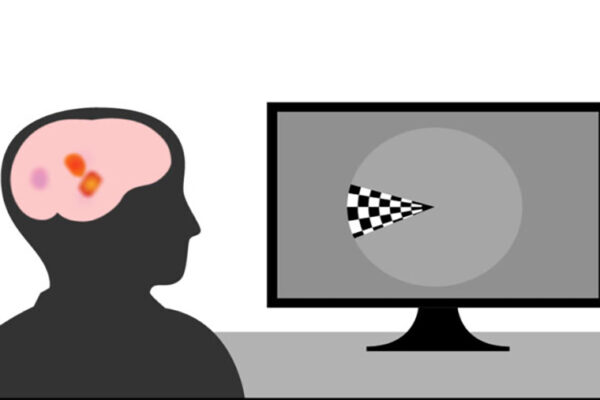
Brain signals decoded to determine what a person sees
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have used light to decode brain signals and identify what image a person sees. It could be a step toward helping people who are unable to express themselves because of brain injury or disease communicate.
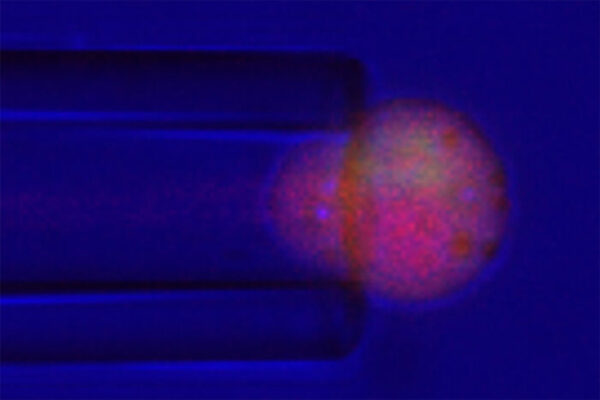
‘Smart’ cartilage cells programmed to release drugs when stressed
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have engineered cartilage cells to release an anti-inflammatory drug in response to stresses such cells undergo when they are compressed during weight bearing and movement.
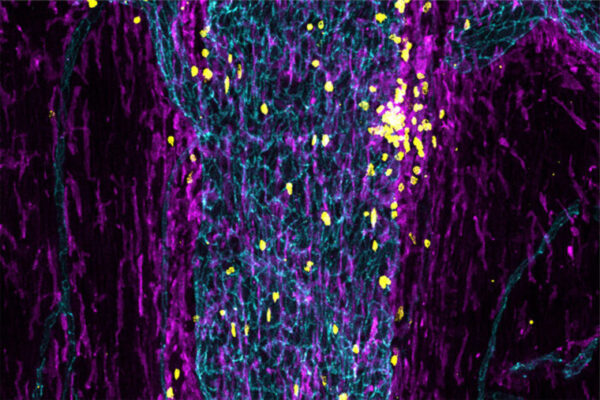
How does the immune system keep tabs on the brain?
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have found that immune cells stationed in such sinuses monitor the brain and initiate an immune response if they detect a problem.
View More Stories