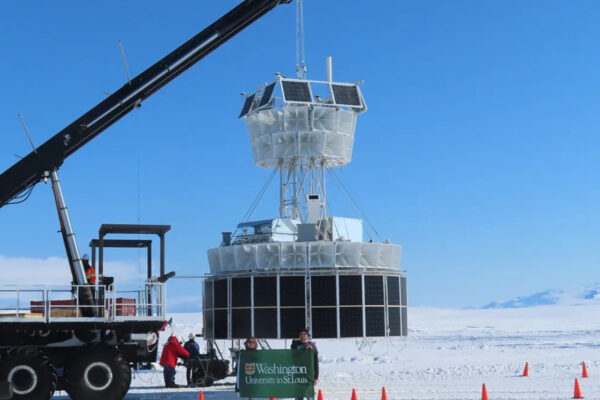
PUEO’s Antarctic flight advances neutrino research
WashU researchers will be looking over data about high-energy neutrinos, retrieved during a balloon flight over Antarctica in January.
WashU among top 100 granted US patents
WashU has been named to the National Academy of Inventors’ Top 100 Worldwide Universities granted U.S. utility patents in 2025. The university is ranked 49 on the list, with 70 total patents.
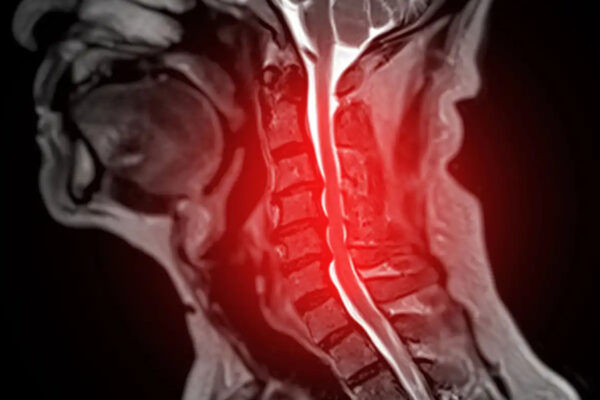
Clinically informed AI outperforms foundation models in spinal cord disease prediction
Machine learning researchers at Washington University in St. Louis used artificial intelligence to help with early detection of spinal cord disease.
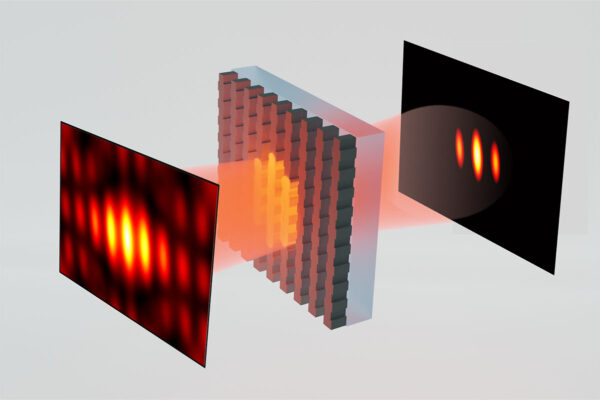
Light gives boost to image processing, optical systems
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have found a way to use light to boost the efficiency of image processing and optical neural networks.
Specific brain signals rapidly eliminate body fat in mice
A study by researchers at WashU Medicine reveals how the body reprograms stable fat cells to eliminate stubborn fat reserves.
Reinforcement learning for arbitrarily large systems is possible
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis are developing mathematically rigorous and computationally efficient techniques to transform extremely complex reinforcement learning problems into a manageable domain.
WashU Medicine researchers receive Falk Catalyst Awards
Jin-Moo Lee, MD, PhD, and Jeffrey R. Millman, PhD, at WashU Medicine were selected for the prestigious Falk Catalyst Awards, which supports bold early-stage research with the potential to transform patient care.
Model developed in Zhang lab recognized by Mozilla
Mozilla AI recently highlighted the PIGuard model developed in the lab of Ning Zhang, a computer scientist at Washington University in St. Louis. The model was among the best at protecting LLMs from prompt injection attacks.
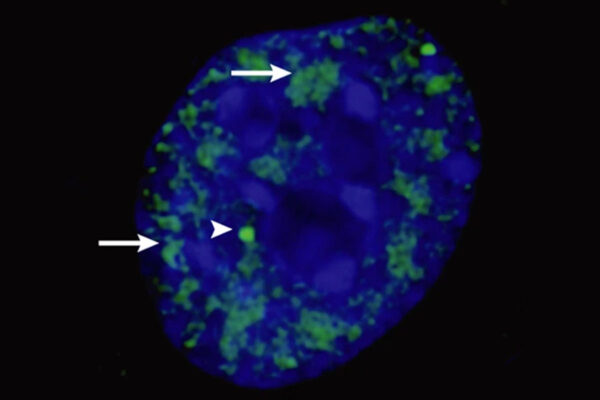
Spying on speckles
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have investigated how assemblies of molecules called microphases could be a useful target in developing treatments for neurodegenerative disorders.
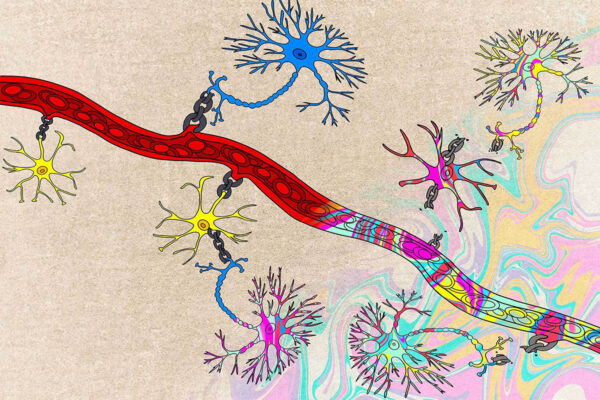
Psychedelics disrupt normal link between brain’s neuronal activity and blood flow
WashU Medicine researchers show that psychedelic compounds such as psilocybin appear to distort the link between blood flow and brain-cell functioning, which scientists use to track brain activity.
View More Stories