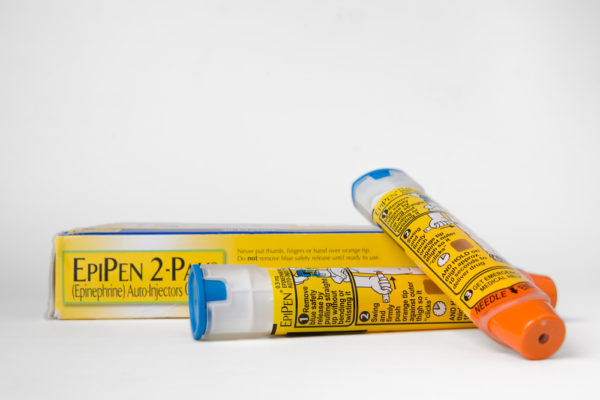
WashU Expert: EpiPen controversy highlights need for price controls
Recent scandals involving high-priced generic drugs should prompt us to consider price controls for pharmaceutical companies, says an expert on the health care industry at the School of Law at Washington University.
Sam Fox School fall Public Lecture Series
The Sam Fox School of Design & Visual Art will launch its fall Public Lecture Series Sept. 14 and 19 with architect Xiaodu Liu and artist Dario Robleto. Subsequent speakers will include legendary illustrator Seymour Chwast and celebrated alumni Laylah Ali and Tom Friedman.
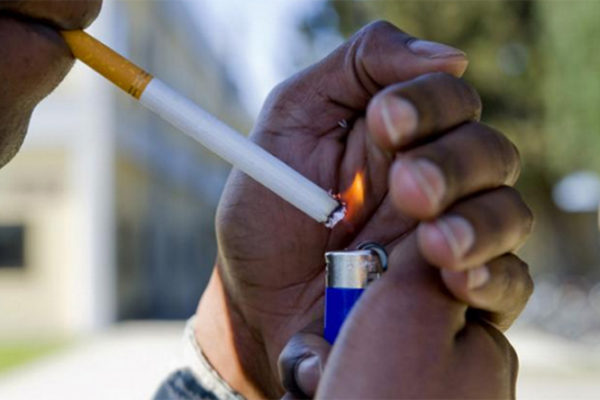
Helping low-income smokers quit
The Brown School’s Health Communication Research Laboratory (HCRL) at Washington University in St. Louis has received a five-year, $2.6 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and National Cancer Institute to study ways to help low-income smokers quit smoking through specialized quitlines and helping with basic needs.
Harvard leader appointed associate vice chancellor, dean of Center for Diversity and Inclusion
Emelyn dela Peña, assistant dean of student life for equity, diversity and inclusion in the Office of Student Life at Harvard College, has been appointed associate vice chancellor for student affairs and dean of the Center for Diversity and Inclusion at Washington University in St. Louis, effective Oct. 31.
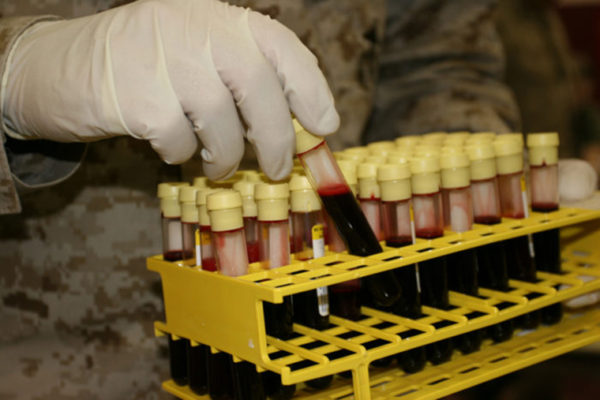
Why ‘O’ blood types may be more likely to die of cholera
People with blood type O often get more severely ill from cholera than people of other blood types. New research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis may explain why.
Amy Owens, Kirt Pavitt present Liederabend Sept. 18
Coloratura soprano Amy Owens will perform Richard Strauss’ notoriously difficult “Amor” Sept. 18 as part of Washington University’s annual Liederabend. Also on the program will be music of Johannes Brahms, Franz Schubert, Antonin Dvořák and Carl Millöcker.
Center for Diabetes Translation Research gets $3.7 million grant
The Center for Diabetes Translation Research, led by Debra Haire-Joshu, the Joyce Wood Professor at the Brown School, has been awarded $3.7 million to continue five years of funding by the National Institute for Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, a National Institutes of Health institute.
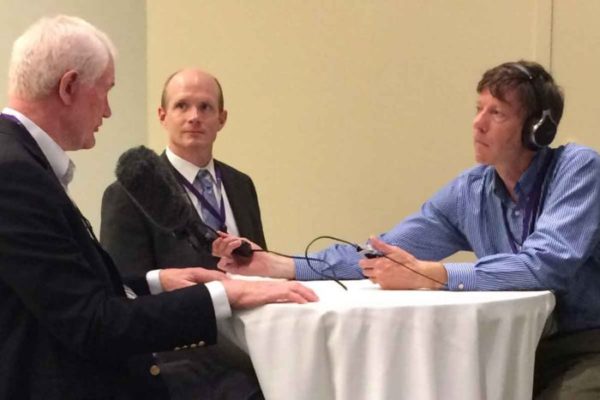
University to host Alan Alda ‘Communicating Science’ workshops
Washington University will host a four-day symposium Sept. 26-29 called “Communicating Science 2016.” The event, to be held at the Eric P. Newman Education Center on the Medical Campus, is geared toward helping scientists share news of their work effectively with people outside of their specific disciplines.
Olin announces new graduate degree track
Washington University in St. Louis has announced a new degree track at Olin Business School: Wealth and Asset Management, to be offered as part of the Masters of Finance degree.
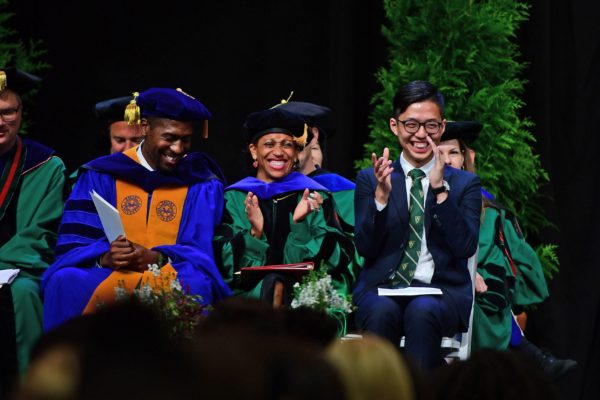
‘You are here for such a time as this’
Leaders of the Washington University community gathered in the Athletics Complex Aug. 25 to celebrate the Class of 2020 and to offer its 1,780 members some words of wisdom.
View More Stories