On the edge: middle neighborhoods
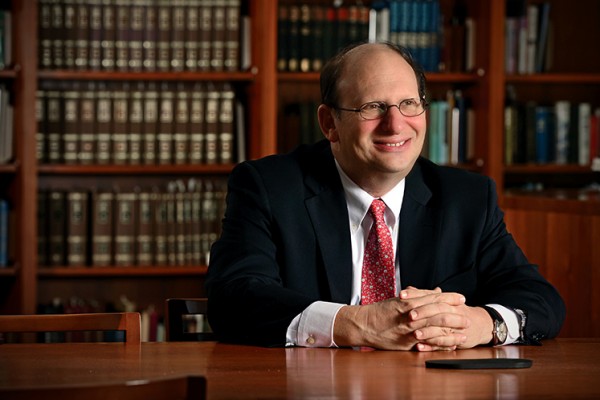
Paul Brophy, a leading expert in economic development and the editor of “On the Edge: America’s Middle Neighborhoods” will be at Washington University in St. Louis on Thursday, April 27, to discuss why middle neighborhoods matter. He’ll join with Executive Vice Chancellor Henry S. Webber and author Alan Mallach, who both contributed to “On the Edge,” and a panel of local civic leaders.
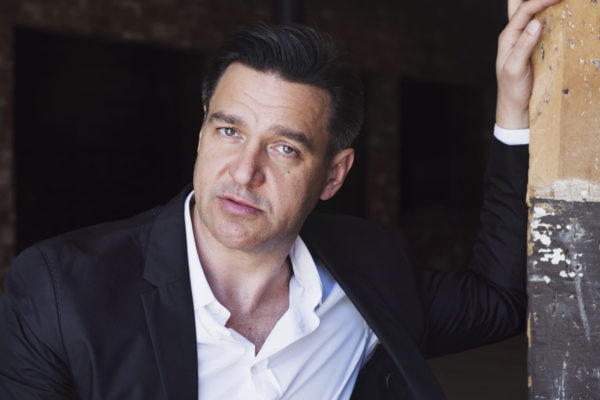
Great Artists Series welcomes Nathan Gunn May 5
Internationally acclaimed baritone Nathan Gunn will perform works by Henry Purcell, Benjamin Britten, Dominick Argento, Roger Quilter, Ben Moore, Iain Bell and Charles Ives May 5 as part of Washington University’s inaugural Great Artist Series.
College Prep scholars urged to shine their light
All 25 members of the inaugural cohort of the College Prep Program at Washington University have been accepted into college, and the group has received more than $4 million in scholarship offers. Lerone A. Martin, assistant professor, told the scholars: “Do not hide your light to make other people comfortable.”
Speaking of Science
Ten Washington University scientists were each given one minute to explain why they’re scientists. This is what they said.
Clark-Fox Policy Institute launches
The Maxine Clark and Bob Fox Policy Institute at the Brown School, a center for public policy engagement, officially opened with a launch event April 19 in Hillman Hall.
Class Acts: Charting a new course for veterans
Veterans continue their serving ways as student leaders, encouraging and supporting each other’s personal and educational growth and advancement at the university and beyond.
Goetz: ‘Yes you can!’
Jennifer Goetz came to the Brown School to develop better systems to serve veterans.
Slack: ‘A bond of trust’
Jon Slack applied to Olin Business School because of its stellar faculty and track record placing graduates in top jobs. But he also chose Olin because of another veteran.
Peacock: ‘Put us together and magic happens’
University College’s Angela Peacock will graduate Phi Beta Kappa and will continue her Washington University education at the Brown School studying veteran issues.
Baker installed as Kirsch Professor
Scott Baker has been installed as the inaugural William F. and Jessica L. Kirsch Professor at Washington University in St. Louis. A lecture and reception to mark the occasion were held in Anheuser-Busch Hall.
View More Stories