Class Acts: Running on solar power
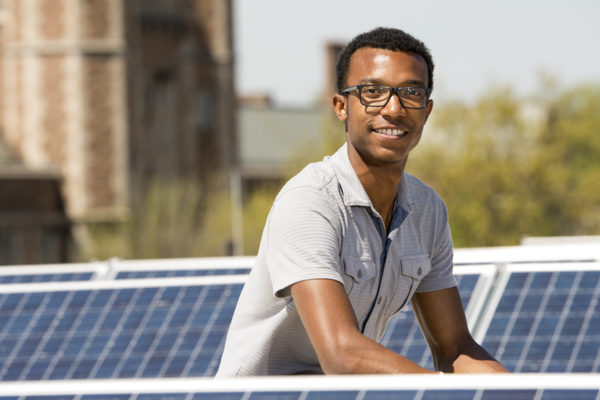
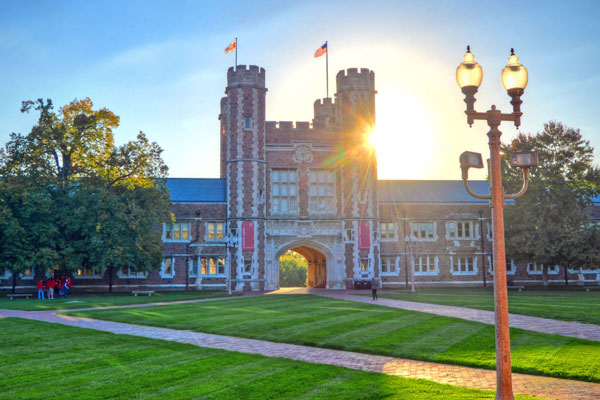
Engineering student, start-up founder and track star Deko Ricketts calls solar power “the engineer’s energy.” Here is Ricketts’ amazing journey to WashU, how he made the most of it and how he plans to address the global energy crisis after graduation.
Class Acts: The innovators and entrepreneurs
Meet a few more of the entrepreneurs and innovators who also happen to be graduating this spring. All of these students have launched businesses and developed innovative technologies that are improving human health, addressing global issues and helping investors achieve their goals.
Goldwater Scholars
Three juniors at Washington University in St. Louis have been awarded the Barry M. Goldwater Scholarship for the 2017-18 academic year. They are Emily Goering and Hannah Olsen, who are majoring in biochemistry, and Emma Streff, who is studying chemistry.
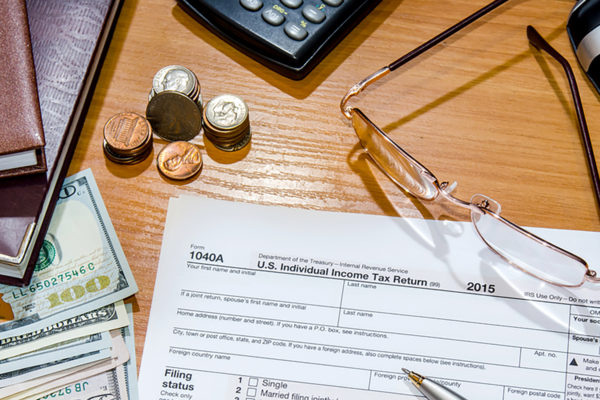
WashU Expert: Explaining the Trump tax proposal
President Trump has revealed his proposed tax plan, which involves, among other things, cutting the corporate tax rate and reducing tax brackets to three, down from seven. What do the proposed changes mean? Adam Rosenzweig, professor of law and tax law expert, explains.
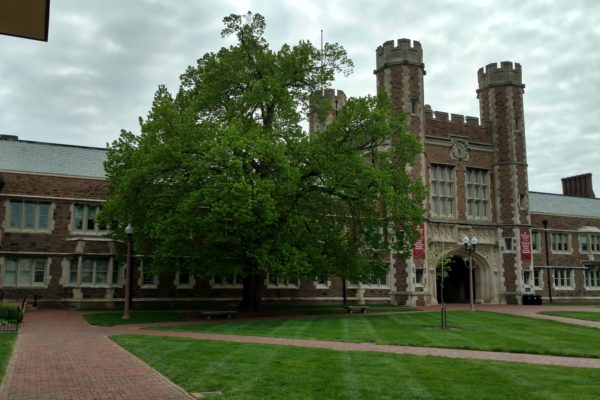
Honoring an American basswood on Arbor Day
Washington University in St. Louis is home to more than 4,000 trees. But this Arbor Day, Kent Theiling, grounds and landscape design manager, would like to recognize one special tree: the American basswood in Brookings Quadrangle. With a 48-inch trunk diameter, the tree is an estimated 104 years old, almost as old as Brookings Hall.
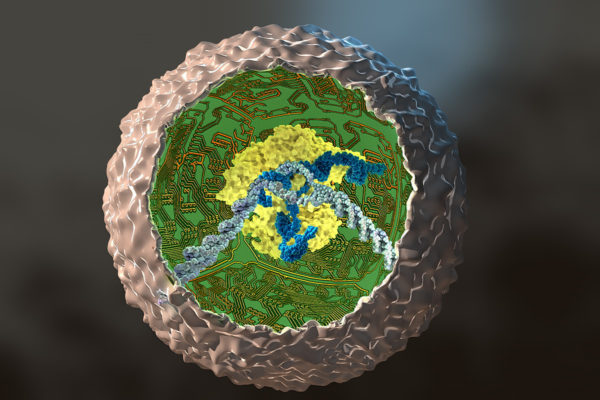
Stem cells edited to fight arthritis
Using new gene-editing technology, researchers at the School of Medicine have rewired mouse stem cells to fight inflammation caused by arthritis and other chronic conditions.
Six to receive honorary degrees at 156th Commencement
Washington University in St. Louis will award six honorary degrees during its 156th Commencement May 19. During the ceremony, which will begin at 8:30 a.m. in Brookings Quadrangle on the Danforth Campus, the university will bestow academic degrees on approximately 3,000 members of the Class of 2017.
Sadat, Van Essen to receive 2017 faculty achievement awards
Leila Sadat, an internationally renowned human rights expert, and David C. Van Essen, an authority on brain structure, function and development, will receive the university’s 2017 faculty achievement awards, Chancellor Mark S. Wrighton announced. Eric Leuthardt, MD, will be honored for innovation and entrepreneurship.
Energy and environment initiative turns 10, keeps growing
This Earth Day, leaders at Washington University in St. Louis announced a new name and an increased emphasis on the university’s united sustainability effort: the International Center for Energy, Environment and Sustainability, or InCEES.
WashU Expert: Trump’s Muslim ban based on animus
While courts around the United States have found President Trump’s travel ban on Muslim-majority nations unconstitutional, the courts may have overlooked an important point, says an expert on law and religion at Washington University in St. Louis.
View More Stories