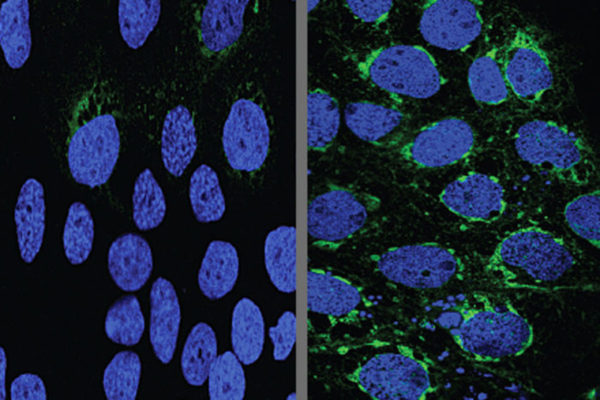
Type 1 diabetes risk linked to intestinal viruses
A new study led by the School of Medicine has found that viruses in the intestines may affect a person’s chance of developing Type 1 diabetes. Children who carried a specific virus belonging to the Circoviridae family were less likely to head down the path toward diabetes.
Malaria drug protects fetuses from Zika infection
Studying pregnant mice, researchers at the School of Medicine found that Zika virus manipulates the body’s normal barrier to infection. They also found that a malaria drug, hydroxychloroquine, interferes with this process, protecting the fetus from viral infection.
Popular heartburn drugs linked to higher death risk
Popular heartburn drugs called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have been linked to a variety of health problems, including serious kidney damage, bone fractures and dementia. Now, a new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis shows that longtime use of the drugs also is associated with an increased risk of death.
Siteman Cancer Center opens north St. Louis County location
Siteman Cancer Center will begin seeing patients July 1 at its newest satellite location, Christian Hospital in north St. Louis County. Siteman Cancer Center is based at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine, and the new location is Siteman’s fifth in the St. Louis area.
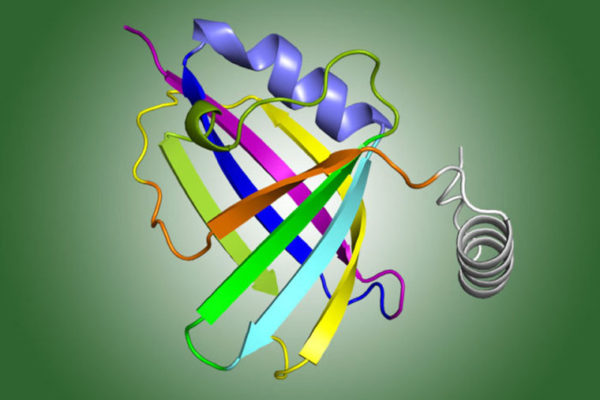
New clues found to common respiratory virus
Mapping the molecular structure of an RSV protein that interferes with the body’s ability to fight off the virus, researchers at the School of Medicine have found clues to how RSV causes disease. This could potentially lead to a vaccine or treatment.
Interrogating the archive
Artist Kari Varner examines the resiliency of nature, the specificity of place and the limits of our own perceptions.
Keep your distance
Why does biodiversity grade from exuberance at the equator through moderation at mid-latitudes toward monotony at higher ones? Data from an international network of long-term forest dynamics research sites is finally providing an answer.
Engineers examine chemo-mechanics of heart defect
Elastin and collagen serve as the body’s building blocks. Any genetic mutation short-circuiting their function can have a devastating, and often lethal, health impact. For the first time, new research led by engineers at Washington University in St. Louis takes a closer look at both genetic and mechanical attributes, to better understand a disorder that affects how elastin and collagen function.
Fat makes cells fat
Just as people endlessly calculate how to upsize or downsize, bacteria continually adjust their volume (their stuff) to fit inside their membrane (their space). But what limits their expansion? The answer will surprise you.
New parking system takes effect July 1
Washington University’s new parking and transportation management strategy is rolling out Saturday, July 1. Stay updated on the latest about permits, accessible parking, helping visitors navigate campus and more.
View More Stories