Gordon receives British Royal Society’s highest honor
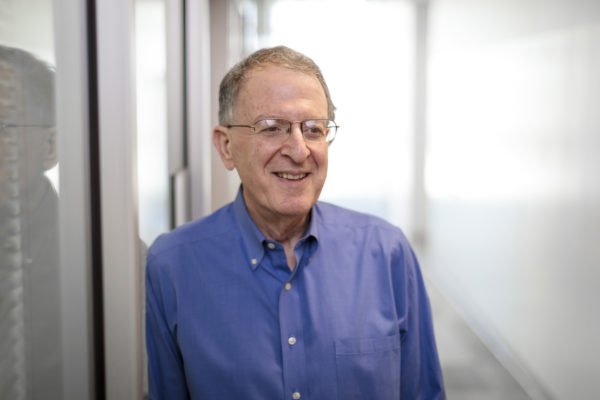
The School of Medicine’s Jeffrey I. Gordon, MD, has received the 2018 Copley Medal from the Royal Society in Britain. He is being honored for his studies of human gut microbial communities, which have led to a fundamental shift in the way scientists understand the relationship between microbes, health and disease.
New cohort of College Prep Scholars announced
Washington University in St. Louis has admitted 50 rising high school sophomores to its innovative College Prep Program, a multiyear initiative that prepares high-achieving students with limited financial resources for college. The students represent public, private and charter schools from across the region. They will live and study on campus for three summers, participating in science labs, preparing their college essays and studying with top university faculty.
Eczema drug effective against severe asthma
Two new studies of patients with difficult-to-control asthma show that the eczema drug dupilumab alleviates asthma symptoms and improves patients’ ability to breathe better than standard therapies. Researchers at the School of Medicine and colleagues elsewhere conducted the studies.
Clues found to early lung transplant failure
Researchers at the School of Medicine and colleagues at Northwestern University and elsewhere have uncovered new clues in early lung transplant failure.
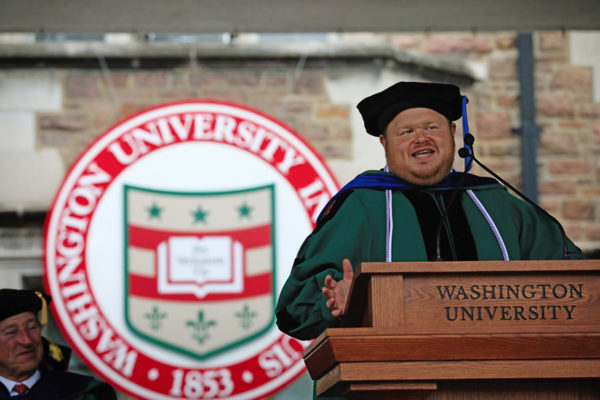
Graduate student speaker Donald Gerke’s address to the Class of 2018
Read the text of graduate student speaker Donald Gerke’s prepared remarks to the Class of 2018. Gerke received a doctorate from the Brown School.
Slaughter calls for an American renewal
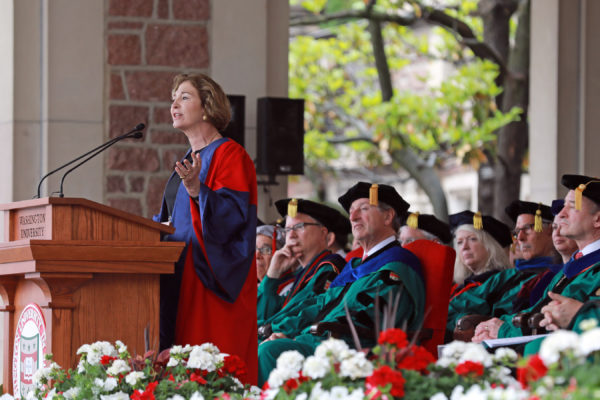
In a stirring speech to the Class of 2018, Anne-Marie Slaughter urged the graduates to be part of a great “American Renewal.”
Anne-Marie Slaughter’s 2018 Commencement address at Washington University in St. Louis
Anne-Marie Slaughter, a renowned foreign policy expert, scholar and former top State Department official, delivered the address at Washington University in St. Louis’ 157th Commencement ceremony. Read her remarks about American renewal delivered to the Class of 2018 on Friday, May 18, in Brookings Quadrangle on the Danforth Campus.
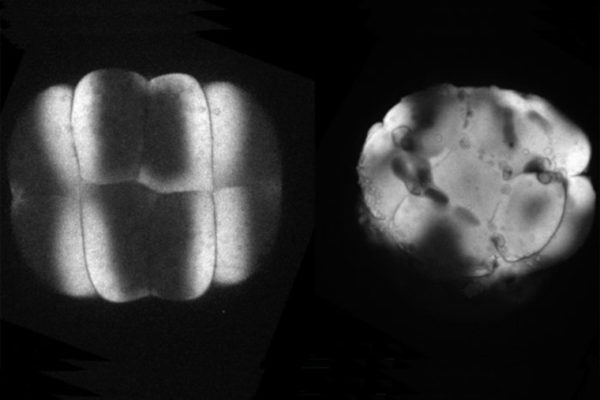
Revealing the mysteries of early development
Zebrafish embryos are transparent and develop outside the mother’s body, giving scientists a detailed view of early development. A research team led by Lila Solnica-Krezel, of the School of Medicine, is revealing new clues to how birth defects develop.
Commencement: time to celebrate the Class of 2018
As the more than 3,100 undergraduate, graduate and professional degree candidates at Washington University in St. Louis are ready to begin a new chapter in their lives, the university will recognize their achievements during its 157th Commencement this morning in Brookings Quadrangle.
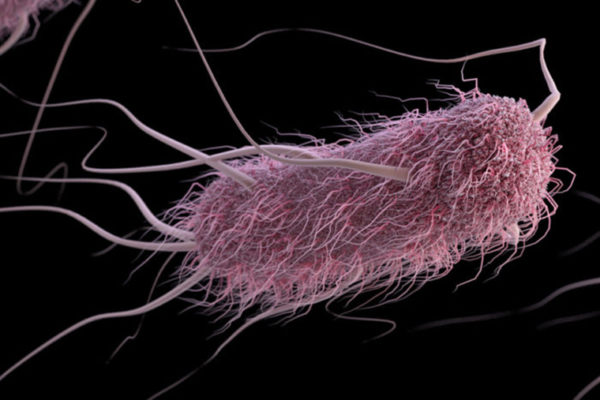
Blood type affects severity of diarrhea caused by E. coli
A new study from the School of Medicine shows that a kind of E. coli most associated with “travelers’ diarrhea” and children in underdeveloped areas of the world causes more severe disease in people with blood type A. The findings could lead to a vaccine that could potentially protect people with type A blood against the deadliest effects.
View More Stories