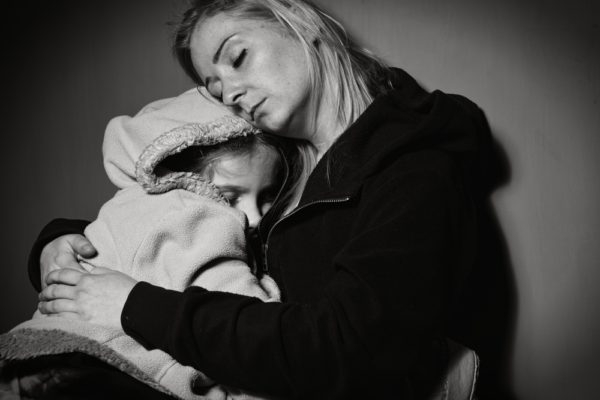
Act fast to pay attention
Want to improve your attention? Arts & Sciences brain sciences researcher Richard Abrams at Washington University in St. Louis finds that our attention may be guided by the most recent interactions with our environment.
Drugs that suppress immune system may protect against Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s disease is caused by the injury or death of brain cells known as dopaminergic neurons. A new School of Medicine study shows that people who take drugs that suppress the immune system are less likely to develop the disease, which is characterized by difficulty with movement.
Parenting, child care services have most potential to help low-income families
Child care, parenting and child health/health care are important factors in improving the lives of children in low-income families, according to a new study from the Brown School, which surveyed 211 helpline staff.
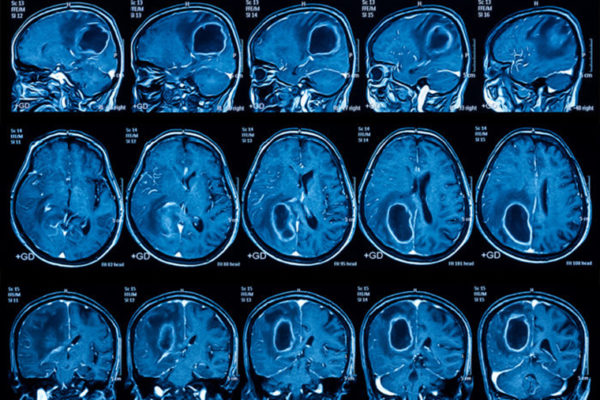
Brain cancer vaccine effective in some patients
Most people with the deadly brain cancer glioblastoma die less than 18 months after diagnosis. But a multicenter clinical trial of a personalized vaccine that targets the aggressive cancer has indicated improved survival rates for such patients. The study appears May 29 in the Journal of Translational Medicine.
Defects in tissue trigger disease-like transformation of cells
Homeowners know that one little termite can lead to big problems: while termites are efficient at gnawing away at wood, they can do even more damage if the wood is already broken or has another defect. Mechanical engineers at Washington University in St. Louis have found the same effect in some of the body’s tissue.
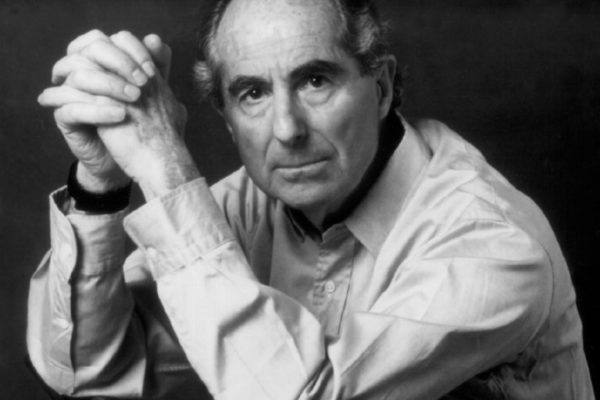
WashU Expert: Remembering Philip Roth
Philip Roth, who died May 22, was among the most influential American writers of the 20th and 21st centuries. He was also a playful yet unsparing and often provocative critic of American culture, said Matthew Shipe, lecturer in English in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis.
WashU Expert: Starbucks issue is bigger than PR
Starbucks’ leadership’s response to date demonstrates a broader consideration of the full range of management functions and stakeholders critical to the company’s success, according to Catherine Dunkin, lecturer in management at Olin Business School at Washington University in St. Louis.
Splitting the difference: One person, two minds
Arts & Science philosopher Lizzie Schechter uses elements of two philosophical traditions to propose a new way to think about split-brain subjects. Her new book “Self-Consciousness and ‘Split’ Brains: The Minds’ I,” will be published June 1.
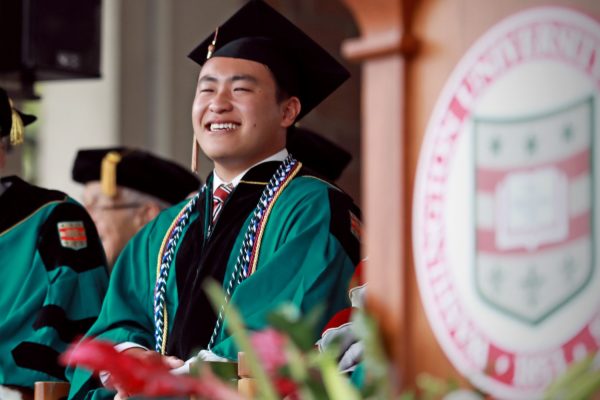
Senior class president William Feng’s message to the Class of 2018
Read the text of senior class president William Feng’s remarks to the Class of 2018. Feng received a bachelor’s degree from Olin Business School.
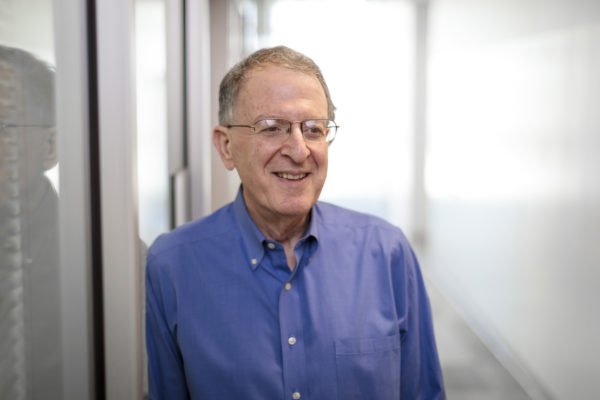
Gordon receives British Royal Society’s highest honor
The School of Medicine’s Jeffrey I. Gordon, MD, has received the 2018 Copley Medal from the Royal Society in Britain. He is being honored for his studies of human gut microbial communities, which have led to a fundamental shift in the way scientists understand the relationship between microbes, health and disease.
View More Stories