Foodborne fungus impairs intestinal wound healing in Crohn’s disease
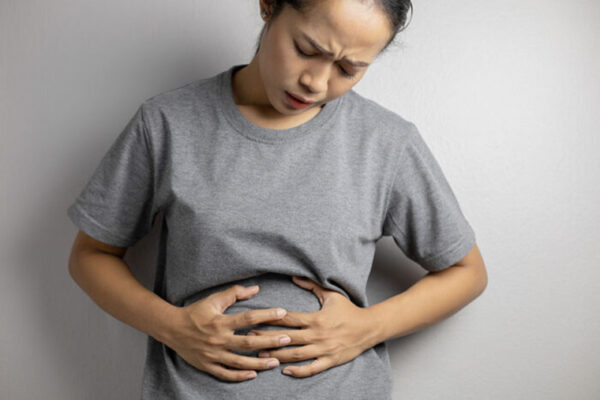
A foodborne fungus that is harmless to most people exacerbates gastrointestinal symptoms in people with Crohn’s disease by preventing intestinal ulcers from healing, according to a new study from the School of Medicine and the Cleveland Clinic.
‘What we’re made of’
One year since COVID-19 upended our lives, we thank the WashU community and look ahead to better days.
One pandemic year later, what’s next?
As we mark the one-year anniversary today of the World Health Organization first declaring a global COVID-19 pandemic, Washington University in St. Louis experts, including from its School of Medicine, look both back and ahead.
Promising role for whole genome sequencing in guiding blood cancer treatment
A new study from the School of Medicine shows that whole genome sequencing is at least as accurate — and often better than — conventional genetic tests that help determine the treatment for a patient’s blood cancer.
Washington University launches strategic planning process
With an aim to be bold, transformative and collaborative, Washington University has officially begun its strategic planning process to develop a roadmap that will guide the university’s future over the next decade.
How to cope with pandemic anniversary emotions
Rebecca Lester, professor of sociocultural anthropology at Washington University in St. Louis, offers advice for coping with the emotions brought on by COVID-19 anniversaries and moving forward.
Comparing pandemic spending patterns in U.S. and Israel
The pandemic is exacerbating preexisting social and economic inequalities in the U.S. and abroad, finds a new study from the Social Policy Institute at Washington University in St. Louis.
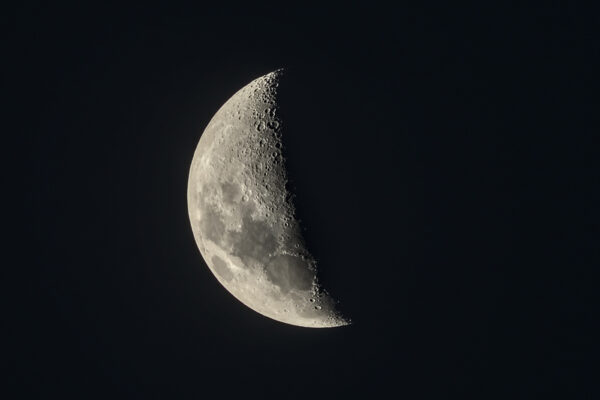
How WashU scientists are helping NASA study the moon
An Arts & Sciences research team will help build a rover-mounted drill sensor to quantify the 3D distribution of water at the moon’s south pole. The team includes local St. Louis company Impossible Sensing.
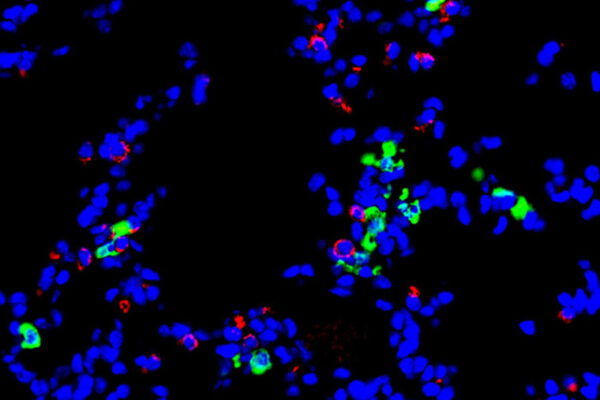
Immune cell implicated in development of lung disease following viral infection
Scientists at the School of Medicine have implicated a type of immune cell in the development of chronic lung disease that sometimes is triggered following a respiratory viral infection. The study was published in The Journal of Immunology.
‘You’re Paid What You’re Worth’
With his new book, “You’re Paid What You’re Worth,” Jake Rosenfeld, associate professor of sociology, challenges the idea that we’re paid according to objective criteria, while placing power and social conflict at the heart of economic analysis.
View More Stories