New tech can get oxygen, fuel from Mars’ salty water
A new electrolysis system that makes use of briny water could provide astronauts on Mars with life-supporting oxygen and fuel for the ride home, according to engineers at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, who developed the system.
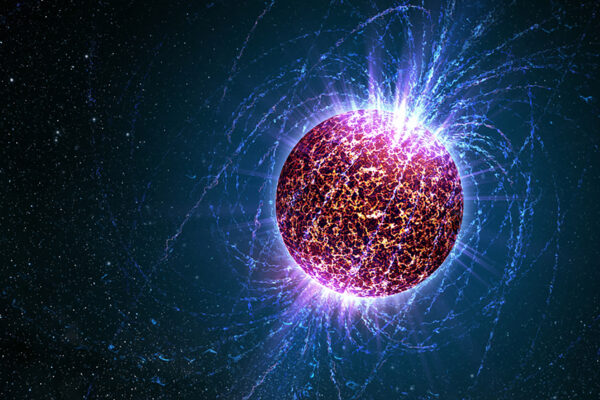
Looking skin deep at the growth of neutron stars
Researchers from physics and chemistry in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis leveraged data from nuclear scattering experiments to make stringent constraints on how neutrons and protons arrange themselves in the nucleus. Their predictions are tightly connected to how large neutron stars grow and what elements are likely synthesized in neutron star mergers.
Meteorite study suggests Earth may have always been wet
A new study finds that Earth’s water may have come from materials that were present in the inner solar system at the time the planet formed — instead of that water being delivered by far-reaching comets or asteroids. The research co-authored by physicist Lionel Vacher in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis is published Aug. 28 in Science.
The Sirens of Mars
Searching for life on another world
Empathetic and evocative, The Sirens of Mars offers an unlikely natural history of a place where no human has ever set foot, while providing a vivid portrait of our quest to defy our isolation in the cosmos.
Electrically charged dust storms drive Martian chlorine cycle
New research from Washington University in St. Louis planetary scientists shows that Martian dust storms, like the one that eventually shut down the Opportunity rover, drive the cycle of chlorine from surface to atmosphere and may shed light on the potential for finding life on Mars.
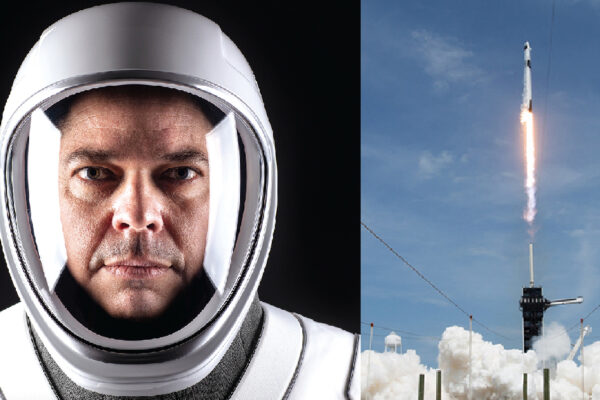
Soaring into history
On May 30, 2020, WashU alumnus Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley became the first astronauts in NASA’s history to launch from a commercially built and operated spacecraft, the SpaceX Crew Dragon. For the Demo-2 mission, the two are testing the spacecraft’s transportation system for future missions.
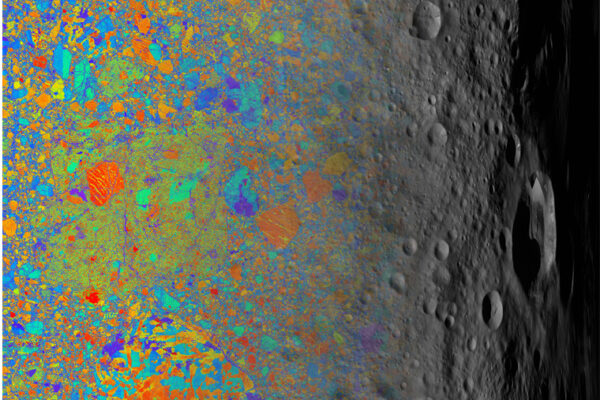
Ancient micrometeoroids carried specks of stardust, water to asteroid 4 Vesta
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis are the first to study presolar materials that landed on a planet-like body. Their findings may help solve the mystery: where did all the water on Earth come from?
Fail Better with Andrew Bass
Develop an open-source nuclear detection system. That was the charge from the U.S. Department of Defense to members of its new internship program, the X-Force Fellowship. Washington University in St. Louis sophomore Andrew Bass had been selected to serve in the pilot cohort and arrived at Cape Canaveral in Florida convinced he would fail.
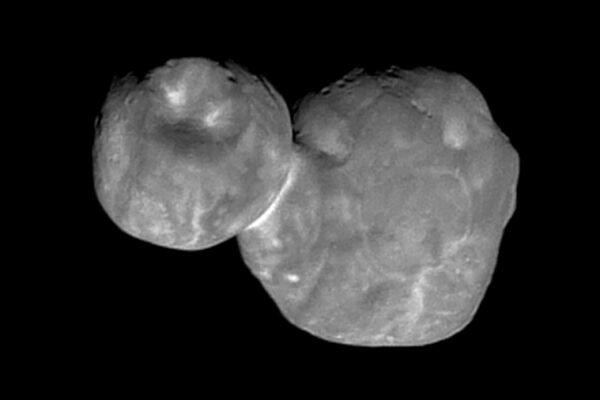
Arrokoth close-up reveals how planetary building blocks were constructed
William B. McKinnon, professor of earth and planetary sciences in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, led one of three new studies that together provide a far more complete picture of the composition and origin of Arrokoth. The new research published in Science points to the resolution of a longstanding scientific controversy about how such primitive planetary building blocks called planetesimals were formed.
What a meteorite is teaching us about space history
Presolar grains — tiny bits of solid interstellar material formed before the sun was born — are sometimes found in primitive meteorites. But a noble gas analysis from physicists in Arts & Sciences reveals evidence of presolar grains in part of a meteorite where they are not expected to be found.
Older Stories