Sculpted by starlight: A meteorite witness to the solar system’s birth
Researchers examine a 4.6 billion- year-old rock to better understand the solar system’s beginning, and a modern mystery.
Nowak, collaborators share new observations of famous black hole
Michael Nowak, research professor of physics in Arts & Sciences, is co-author of a study in The Astrophysical Journal Letters that shares unprecedented observations of the black hole in the galaxy M87.
How WashU scientists are helping NASA study the moon
An Arts & Sciences research team will help build a rover-mounted drill sensor to quantify the 3D distribution of water at the moon’s south pole. The team includes local St. Louis company Impossible Sensing.
Physicist Freese explores dark side of universe in McDonnell lecture
Katherine Freese, an influential scientist who is at the forefront of efforts to understand the universe as a whole, will present the McDonnell Distinguished Lecture. Her online lecture begins at 7 p.m. Thursday, March 25.
Amari receives Urey Award for career in cosmochemistry
Sachiko Amari, research professor of physics in Arts & Sciences, received the H. C. Urey Award from the European Association of Geochemistry for outstanding contributions advancing geochemistry.
Wang receives grant to study volatiles in early solar system
Kun Wang, assistant professor of earth and planetary sciences in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, received a $506,053 grant from the NASA Emerging Worlds program for his project, “Experimental Studies of Volatile Fractionation in the Early Solar System.”
NASA selects astrophysics mission to detect ultrahigh-energy neutrinos
Physicists in Arts & Sciences, including Brian Rauch, are part of a team funded by NASA to develop the concept for the most sensitive survey of cosmic ultra-high energy neutrinos ever conducted.
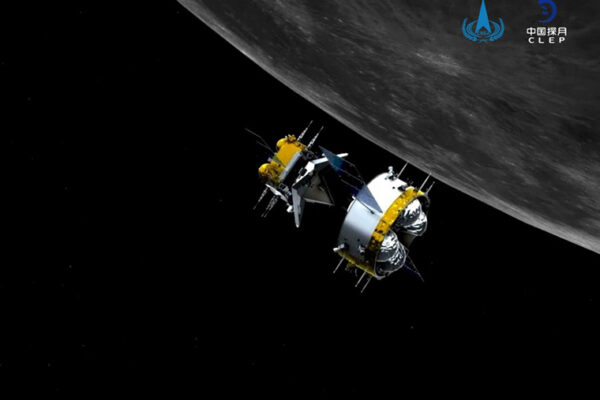
China probe returns with ‘treasure trove’ of moon rocks
The Chinese space agency announced Dec. 16 the return of a lunar probe bringing back the first fresh samples of rock and debris from the moon in more than 40 years. Bradley L. Jolliff, the Scott Rudolph Professor of Earth and Planetary Sciences in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, reflects on the scientific value of the samples.
McKinnon honored by American Geophysical Union
Bill McKinnon, professor of earth and planetary sciences in Arts & Sciences, is one of 62 geoscientists who have been elected to the American Geophysical Union’s 2020 class of fellows.
Powerful electrical events quickly alter surface chemistry on Mars and other planetary bodies
Dust-related electrochemistry can reshape Martian surface materials with physical and chemical changes observable after only hundreds of years. Similar electrical effects may be instrumental on Venus and Europa, according to new work from Alian Wang in Arts & Sciences.
Older Stories