What’s so hard about counting craters?
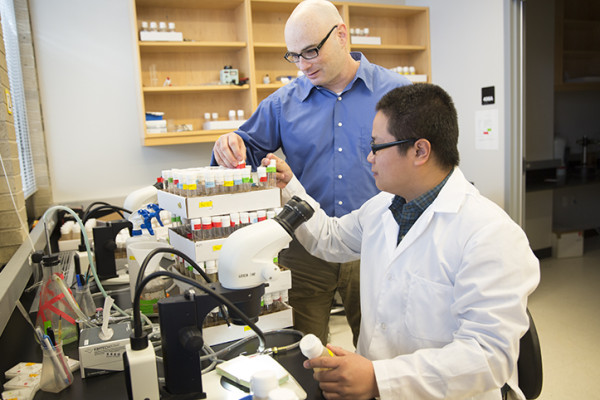
The journal Icarus published a study this month that compared lunar crater counts by eight professionals with crowdsourced counts by volunteers. The professional crater counts varied by as much as a factor of two. Two of the professionals, both planetary scientists at Washington University in St. Louis, explain why they weren’t surprised.
Washington University to re-establish sociology department
Washington University in St. Louis is re-establishing its sociology department after a nearly 25-year hiatus, Barbara A. Schaal, PhD, dean of the Faculty of Arts & Sciences, has announced.
Scientists find a molecular clue to the complex mystery of auxin signaling in plants
Plants fine-tune the response of their cells to the potent plant hormone auxin by means of large families of proteins that either step on the gas or put on the brake in auxin’s presence. Scientists at Washington University have learned that one of these proteins, a transcription factor, has an interaction region that, like a button magnet, has a positive and negative face. Because of this domain, the protein can bind two other proteins or even chains of proteins arranged back-to-front.
From high school dropout to landing Curiosity on Mars: Adam Steltzner on how ‘Curiosity Changed My Life’
Nothing in Adam Steltzner’s younger years pointed to his becoming NASA’s chief engineer for the highly delicate landing of the Curiosity rover on Mars. He flunked high school geometry and dropped out to join a rock band. On March 26, Steltzner will tell how “Curiosity Changed My Life” for the Assembly Series. His presentation, which will begin at 6 p.m. in Graham Chapel, is free and open to the public.
A novel mechanism for fast regulation of gene expression
Yehuda Ben-Shahar and his team at Washington University in St. Louis have discovered that some mRNAs have a side job unrelated to making the protein they encode. They act as regulatory molecules as well, preventing other genes from making protein by marking their mRNA molecules for destruction.
Meditation on the brain
For decades, neuroscientist Richard Davidson, PhD, has been conducting research on the positive impact of contemplative practices such as meditation on the brain. The work may have important ramifications for treating mental disorders. Davidson was on campus this month to deliver the Witherspoon Memorial Lecture on Religion and Science for the Assembly Series and a talk for the Department of Psychology.
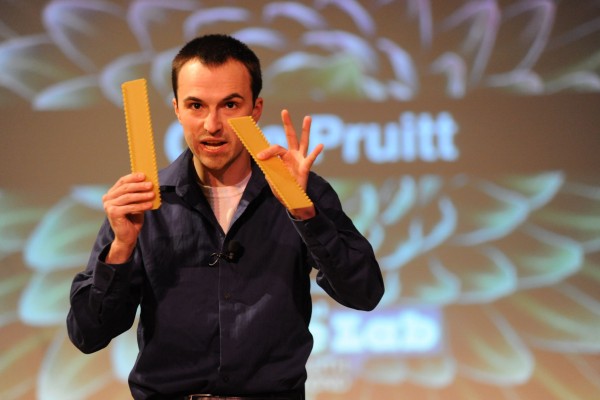
Stand-up science
The St. Louis FameLab, a science communication competition sponsored by National Geographic and NASA, recently gave young scientists a chance to present their science to nonscientists in three minutes. Efforts such as this are becoming increasingly common as scientists try to reconnect with the public. Some universities now require three-minute video presentations for every thesis or dissertation — or even for every published journal article.
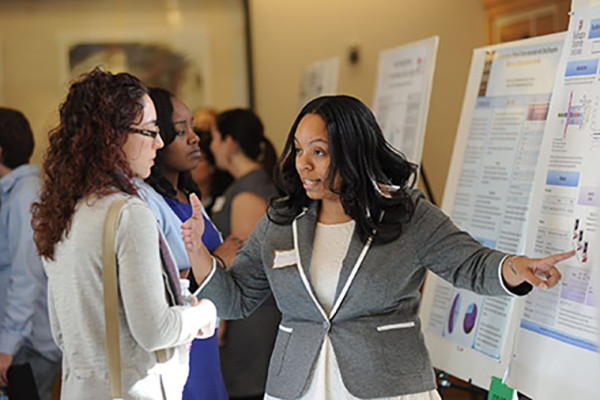
Grad, professional students present research while honing communication skills during annual event
Graduate and professional students presented their research during the 19th Annual Graduate Student Research Symposium, held Feb. 22 in Whitaker Hall. Suthatip Jullamon, a law student, explains her research comparing class-action law in Thailand with the U.S.
Research aims to improve repair of rotator cuff injuries
With a five-year, $3.1 million grant from the National Institutes of Health, Washington University orthopedic researchers and engineers are working to enhance rotator cuff repair surgery.
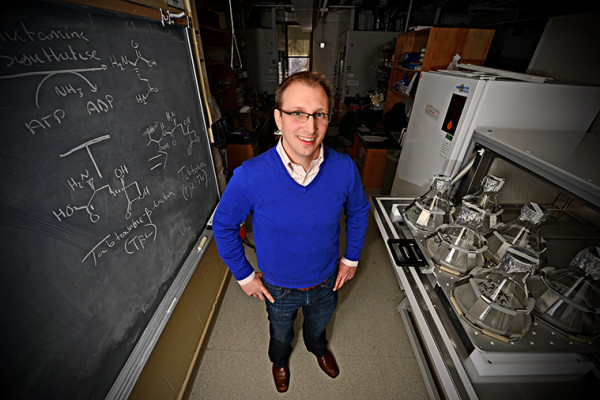
New drugs for bad bugs
Washington University in St Louis chemist Timothy Wencewicz says we’ll stay ahead of antibiotic resistance only if we find drugs with new scaffolds, or core chemical structures. One promising candidate, an antibiotic made by a bacterium than infects plants, caught his attention because it contains an “enchanted ring,” the beta-lactam ring that is found in penicillin. In this drug candidate, however, it acts against a different target than the penicillins.
Older Stories