Preventing lead spread
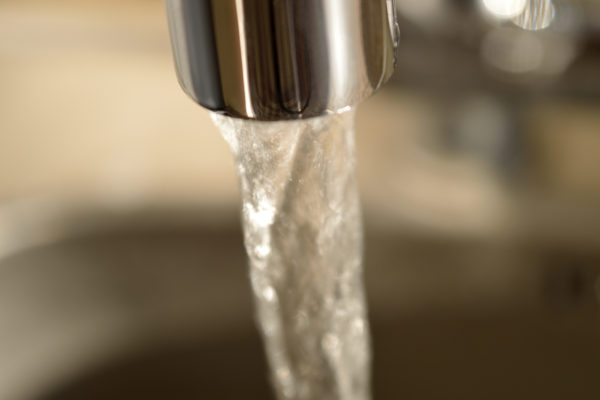
While lead pipes were banned decades ago, they still supply millions of American households with water each day. A team of engineers at Washington University in St. Louis has developed a new way to track where dangerous lead particles might be transported in the drinking-water supply during a common abatement procedure.
Nature: Silk Road evolved as ‘grass-routes’ movement
Nearly 5,000 years ago, the foundations for the vast east-west trade routes of the Great Silk Road were being carved by nomads moving herds to lush mountain pastures, suggests new Arts & Sciences research published in Nature.
Secrets of the shells
By growing phytoplankton called coccolithophores in the lab, scientists were able to understand the large biological overprint on the climate signal encoded by their remains, clearing the way for their use as climate proxies.
The father of the microbiome
Jeffrey I. Gordon, MD, is expanding our understanding of human health into nonhuman realms, studying the bacteria that take up residence in the gut and help define who we become. Indeed, this research suggests you are what you — and your microbes — eat.
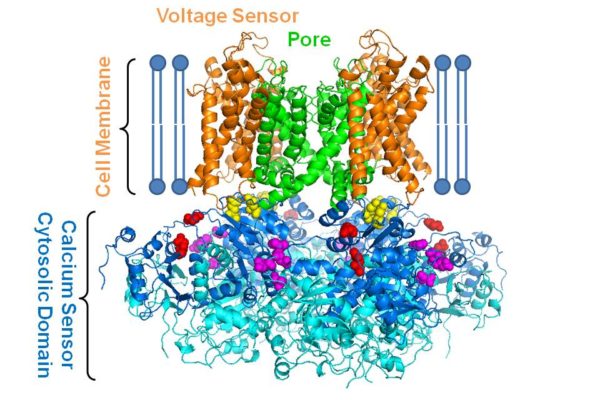
How molecular function affects high blood pressure, other diseases
By changing one small portion of a stimulus that influences part of one molecule’s function, engineers and researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have opened the door for more insight into how the molecule is associated with high blood pressure, autism and movement disorders.
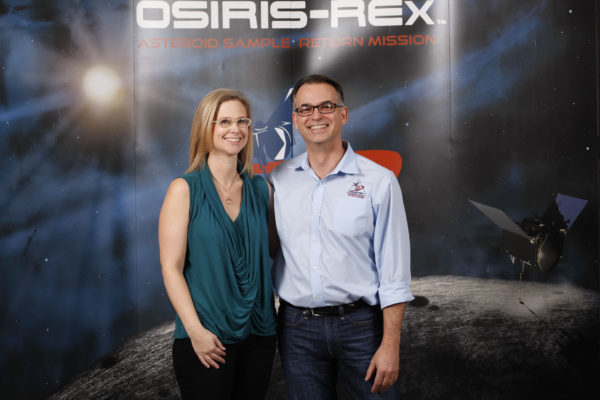
Exploring space, together
Dante Lauretta, PhD ’97, mission chief, and Kate Crombie, PhD ’97, project data archivist, are a husband-and-wife team working on NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission.
Three questions with Gautam Dantas on antibiotic resistance
A microbiology professor discusses antibiotic resistance and his lab’s efforts to help physicians fight antibiotic-resistant infections.
The power of tea
A team of engineers at Washington University in St. Louis and their German collaborators say a compound found in green tea could have lifesaving potential for patients with multiple myeloma and amyloidosis, who face often-fatal medical complications associated with bone-marrow disorders.
Phage: friend or foe?
As everyone has probably heard, antibiotics are less and less effective and there are fewer and fewer replacements for failing drugs in the pipeline. So what would happen if you got an infection that was resistant to all the known antibiotics? Would you die, or is there something else doctors could try as a last […]
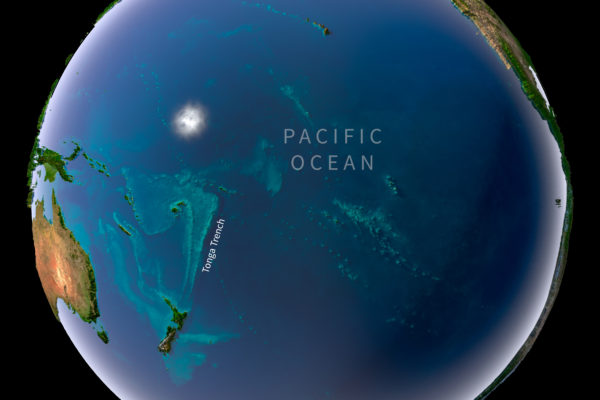
Water world
A team of seismologists analyzing the data from 671 earthquakes that occurred between 30 and 280 miles beneath the Earth’s surface in the Pacific Plate as it descended into the Tonga Trench were surprised to find a zone of intense earthquake activity in the downgoing slab. The pattern of the activity along the slab provided strong evidence that the earthquakes are sparked by the release of water at depth.
Older Stories