Engineers to study best way to maximize computer’s power
Benjamin Moseley, a computer scientist at Washington University in St. Louis, has received two multi-year grants from the National Science Foundation (NSF) totaling $900,000.
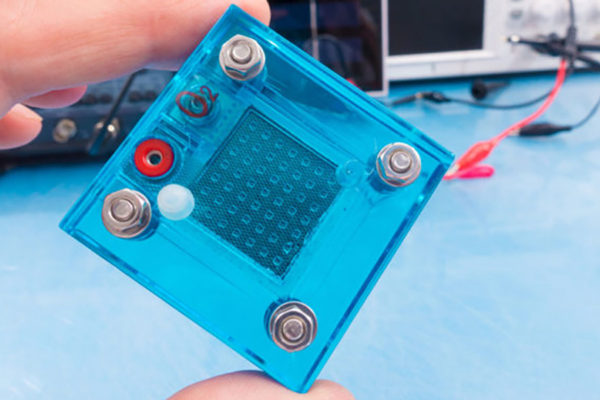
Creating longer-lasting fuel cells
Fuel cells could someday generate electricity for nearly any device that’s battery-powered, including automobiles, laptops and cellphones. An engineering team at Washington University in St. Louis has developed a new way to take a look inside these fuel cells, in an effort to extend their lifespans.
Which came first: big brains or demanding environments?
Researchers in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis are challenging the notion that environment drives the evolution of brain size. A new study was released Sept. 25 in the journal Nature Ecology and Evolution.
Metabolomics just got smaller
Scientists at Washington University estimate that the number of metabolites present in a data set could be 90 percent smaller than previously estimated.
Patti rolling on RIVER grant
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has awarded an eight-year, $5.85 million grant to Gary Patti, associate professor of chemistry in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, for research.
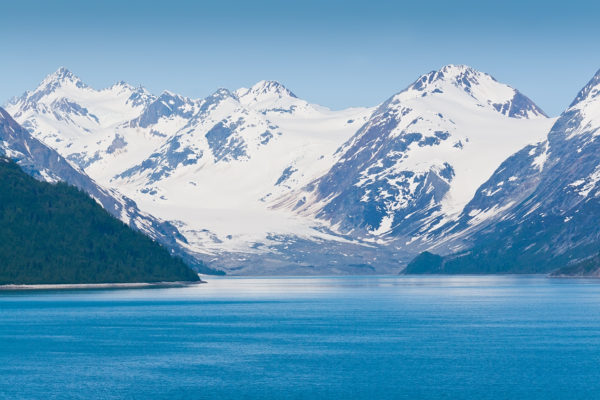
Wiens, Shore to study seismic activity on Alaskan coast
Douglas Wiens, the Robert S. Brookings Distinguished Professor in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, and Patrick Shore, staff scientist and lecturer in earth and planetary sciences in Arts & Sciences, will collaborate with eight other institutions on a $4.5 million National Science Foundation study of a volatile volcano and earthquake zone on the sea floor off the Alaskan Peninsula.
Pushing science and engineering to create new soft materials
A team of researchers from Washington University in St. Louis and Duke University has been award a prestigious National Science Foundation grant. The challenge: Push the boundaries of science to create new materials with a wide range of uses and applications.
Joining forces to advance the study of life on earth
Washington University is joining forces with the Missouri Botanical Garden and the Saint Louis Zoo to create the Living Earth Collaborative, a new academic center dedicated to advancing the study of biodiversity to help ensure the future of Earth’s species in their many forms.
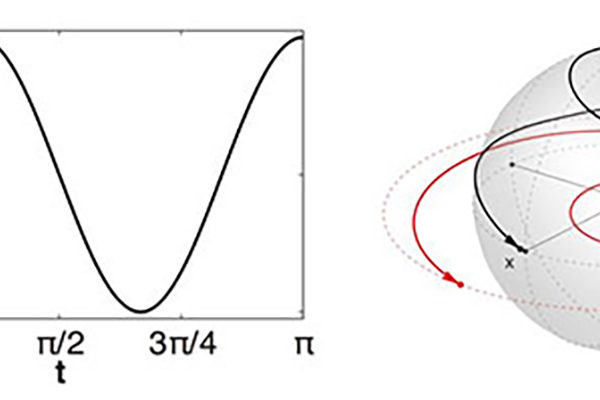
Decade of work pays off
For more than a decade, an engineer at Washington University in St. Louis has sought a better way for pulse design using the similarity between spins and springs by using numerical experiments.
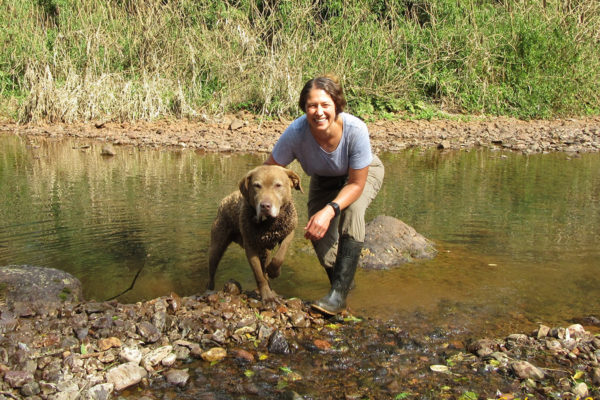
Research dog helps scientists save endangered carnivores
Scat-sniffing research dogs are helping scientists map out a plan to save reclusive jaguars, pumas, bush dogs and other endangered carnivores in the increasingly fragmented forests of northeastern Argentina, according to a new study from Washington University in St. Louis.
Older Stories