Flavor of the moment
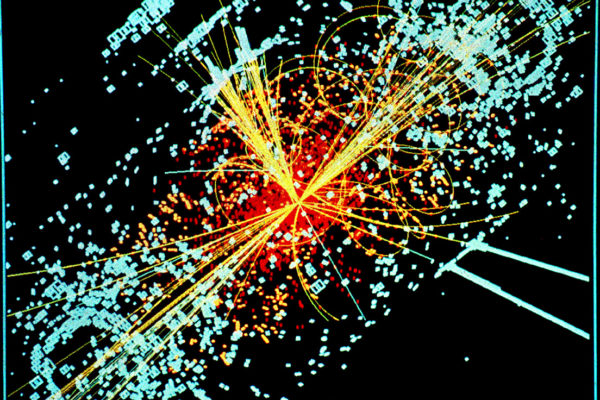
In a new paper in the journal Physical Review Letters, Bhupal Dev, assistant professor of Physics in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, describes how future accelerators could crash together charged particles in a new way to shed light on their behavior.
Fortune — and nature — favors the bold
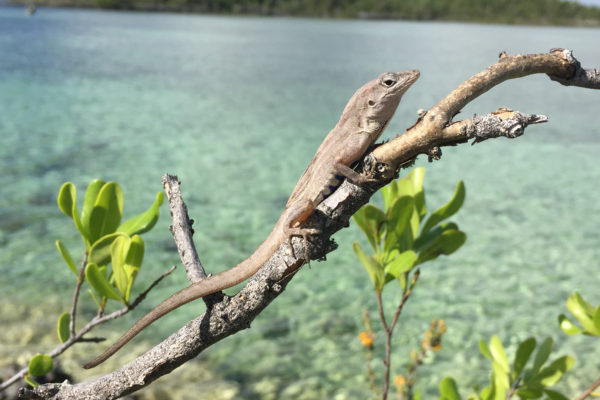
Natural selection acts on behavioral traits, says evolutionary biologist Jonathan Losos, who helped lead a replicated field experiment with anole lizards on eight small islands in the Caribbean, as reported in the June 1 issue of Science
Act fast to pay attention
Want to improve your attention? Arts & Sciences brain sciences researcher Richard Abrams at Washington University in St. Louis finds that our attention may be guided by the most recent interactions with our environment.
Self-Consciousness and ‘Split’ Brains
The Mind's I
Elizabeth Schechter argues that there are in fact two minds: subjects of experience and intentional agents inside each split-brain human being: right and left. On the other hand, each split-brain subject is nonetheless one of us. The key to reconciling these two claims is to understand the ways in which each of us is transformed […]
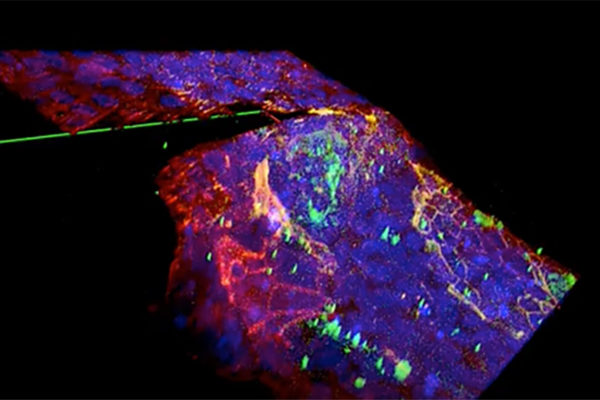
Defects in tissue trigger disease-like transformation of cells
Homeowners know that one little termite can lead to big problems: while termites are efficient at gnawing away at wood, they can do even more damage if the wood is already broken or has another defect. Mechanical engineers at Washington University in St. Louis have found the same effect in some of the body’s tissue.
Splitting the difference: One person, two minds
Arts & Science philosopher Lizzie Schechter uses elements of two philosophical traditions to propose a new way to think about split-brain subjects. Her new book “Self-Consciousness and ‘Split’ Brains: The Minds’ I,” will be published June 1.
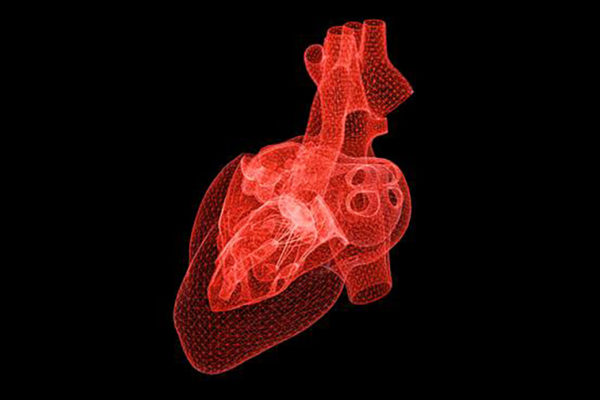
An ‘unprecedented look’ into the protein behind hypertension, epilepsy and other conditions
The seemingly unrelated conditions of hypertension, epilepsy and overactive bladder may be linked by electrical activity in a protein long studied by a biomedical engineer at Washington University in St. Louis. After new technology recently revealed the structure of the protein, his lab will collaborate with two others to take an unprecedented look into its molecular mechanisms, potentially leading to the development of new drugs for these and other conditions.
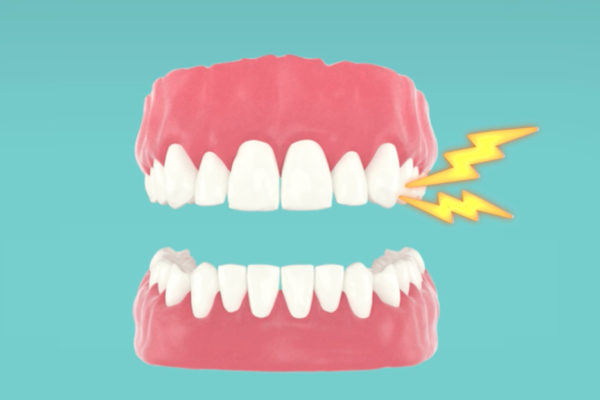
Using tooth sensors to detect disease
An interdisciplinary team of researchers from the School of Medicine and the School of Engineering & Applied Science is redefining the notion of a wisdom tooth. The team is developing technology that could someday be used to detect early signs of certain diseases in high-risk patients.
Bugged out by climate change
Warmer summer and fall seasons and fewer winter freeze-thaw events have led to changes in the relative numbers of different types of bugs in the Arctic, says Amanda Koltz, a postdoctoral fellow in Arts & Sciences. The study relies on the longest-standing, most comprehensive data set on arctic arthropods in the world today: a catalogue of almost 600,000 flies, wasps, spiders and other creepy-crawlies collected at the Zackenberg field station on the northeast coast of Greenland from 1996-2014.
Faculty, students participate in climate summit April 22-24
Washington University faculty and students will moderate panels at the Saint Louis Climate Summit, hosted by Saint Louis University. Students, faculty and staff can attend an evening with Bill Nye of “Science Guy” fame and environmentalist Carl Pope on April 23 for free by showing their IDs at the ticket booth.
Older Stories