NSF funds research on nitrogen fixation
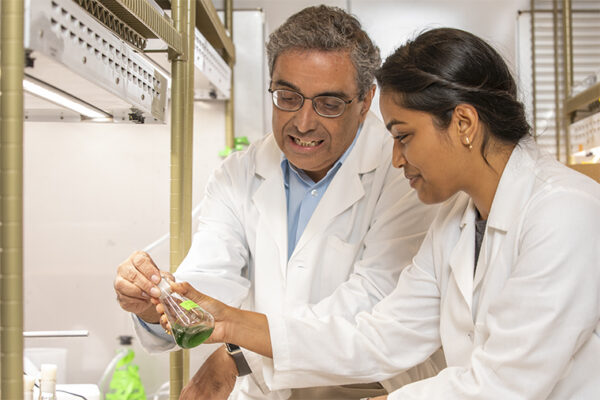
Himadri B. Pakrasi, professor of biology in Arts & Sciences and director of InCEES, was recently awarded a $1.2-million grant for a collaborative study of cyanobacteria with the ultimate purpose of producing nitrogen-fixing crop plants.
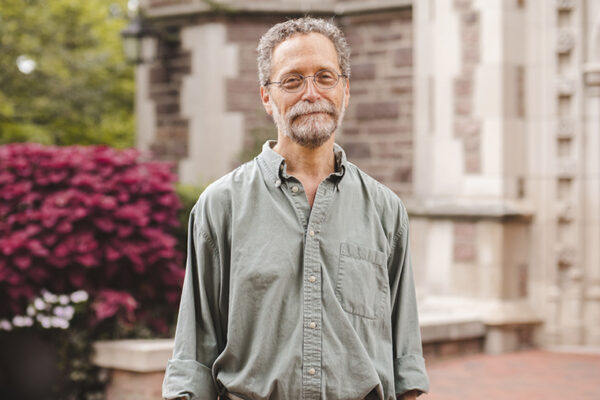
Washington People: Stan Braude
Stan Braude, professor of practice in biology, is a talented teacher who instills in his students the skills they need to prepare for life outside of Washington University. Take it from his students, though — because if you ask him, he will give all the credit to Joe (his St. Bernard).
Understanding criticality and the brain’s neural networks
New research from Washington University in St. Louis confirms that the brain tunes itself to a point where it is as excitable as it can be without tipping into disorder, similar to a phase transition. The new research from Keith Hengen, assistant professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, is published Oct. 7 in the journal Neuron.
Brave new world
Faced with extreme weather events and unprecedented environmental change, animals and plants are scrambling to catch up — with mixed results. A new model developed by Carlos Botero, assistant professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, helps to predict the types of changes that could drive a given species to extinction.
Hiding in plain sight
Early rice growers unwittingly gave barnyard grass a big hand, helping to give root to a rice imitator that is now considered one of the world’s worst agricultural weeds. The new research from biologist Kenneth Olsen in Arts & Sciences was published this week in Nature Ecology & Evolution.
Big brains or big guts: Choose one
A global study comparing 2,062 birds finds that, in highly variable environments, birds tend to have either larger or smaller brains relative to their body size. New research from Carlos Botero, assistant professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, finds birds with smaller brains tend to use ecological strategies that are not available to big-brained counterparts.
Mosquitoes push northern limits with time-capsule eggs to survive winters
New Arts & Sciences research from Washington University in St. Louis shows that invasive mosquitoes at the northern limit of their current range are surviving conditions that are colder than those in their native territory. This new evidence of rapid local adaptation could have implications for efforts to control the spread of this invasive species.
Caught on camera
Researchers from the Tyson Research Center at Washington University in St. Louis and St. Louis College of Pharmacy have set up 34 motion-activated cameras to capture images of wildlife in area parks and green spaces. Students and volunteers help identify the species in an effort promote local biodiversity and improve the coexistence of humans and wildlife.
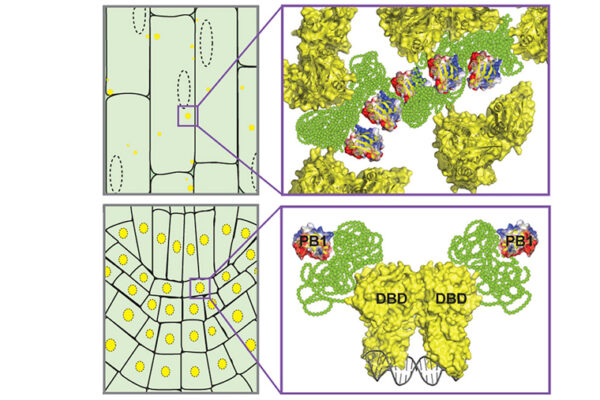
Sticky proteins help plants know when — and where — to grow
When it comes to plant growth and development, one hormone is responsible for it all: auxin. New Washington University in St. Louis research has uncovered a mechanism by which it can affect a plant in a myriad of ways.
WashU Expert: Proposed changes will stamp out ‘countless species’
The Trump Administration’s proposed overhaul of the landmark Endangered Species Act will “hasten the extinction of countless species,” says Jonathan Losos, director of the Living Earth Collaborative at Washington University in St. Louis and an international biodiversity expert.
Older Stories