Washington People: Benjamin D. Humphreys
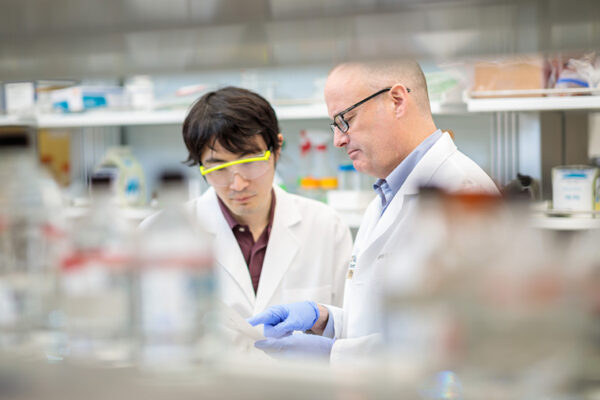
Nephrologist Benjamin Humphreys, MD, PhD, director of the Division of Nephrology at the School of Medicine, is a leading innovator in kidney research. Humphreys seeks to find better treatments to prevent kidney failure, a potentially fatal condition affecting 37 million Americans.
Flu antibody protects against numerous and wide-ranging strains
A human antibody that protects mice against a wide range of lethal flu viruses could be the key to a universal vaccine and better treatments for severe flu disease, according to a new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, and Scripps Research in La Jolla, Calif.
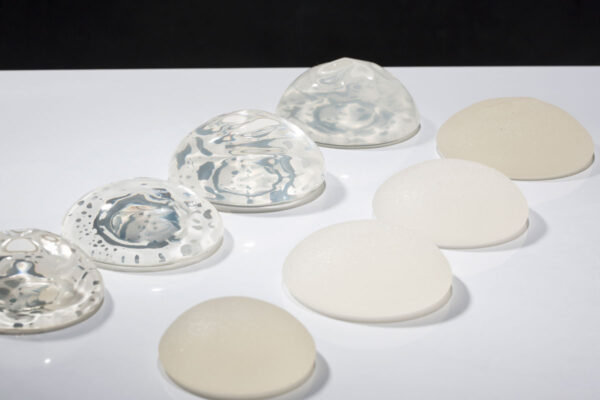
Surgeon weighs in on textured breast implants
Textured breast implants have been linked to a rare and sometimes fatal cancer. Terence M. Myckatyn, MD, who wrote about the issue in a commentary published Oct. 23 in JAMA Surgery, answers questions about the implants.
Drug reduces risk of pneumonia in newborn mice
Premature infants are at high risk of developing life-threatening lung infections, partly because their lungs are underdeveloped at birth. A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has found, in mice, that an inhaled drug promotes the development of lung immunity and reduces the risk of pneumonia.
Human gut microbes could make processed foods healthier
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis suggests the gut microbiome has an impact on how the body breaks down processed foods, such as cereals, pastas, chocolate and soda. The new knowledge could help in the development of healthier, more nutritious processed foods.
NIH funds centers to improve, diversify reference human genome
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) will provide $29.5 million to Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and collaborating institutions to improve the accuracy and diversity of the reference human genome sequence. The aim is to better reflect the spectrum of human diversity and make the reference genome a more useful research tool.
For hospitalized patients with fungal infections, specialists save lives
Fungal bloodstream infections are responsible for the deaths of more than 10,000 people every year. New research from the School of Medicine shows that the death rate can be reduced by 20% if infectious disease specialists oversee care of such patients.
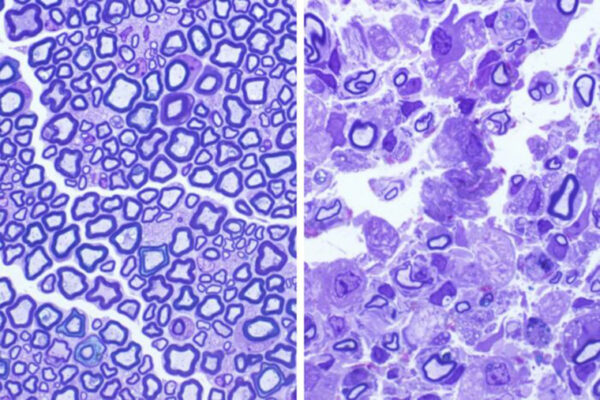
Cause of rare, fatal disorder in young children pinpointed
Scientists at the School of Medicine have pinpointed the precise cause of Krabbe disease, a neurodegenerative condition that usually causes death by age 3.
Radiation therapy effective against deadly heart rhythm
A single high dose of radiation aimed at the heart significantly reduces episodes of a potentially deadly rapid heart rhythm, according to results of a phase one/two study at the School of Medicine.
Brown School researchers begin low-income smoker study
Brown School researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have begun work on a five-year, $3.9 million study that tests an innovative approach to help low-income smokers quit: helping people establish rules banning smoking inside their homes.
Older Stories