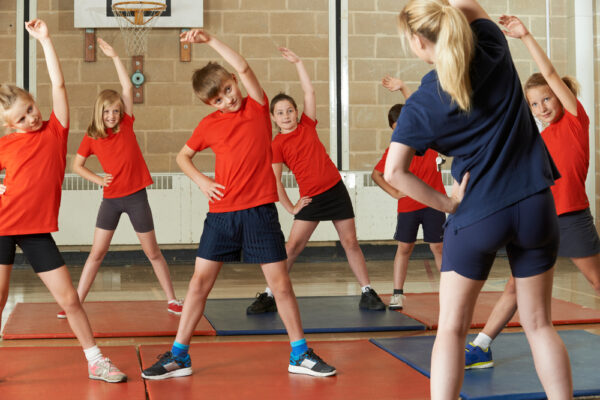
Lack of physical activity during COVID-19 may fuel childhood obesity
The childhood obesity rate in the United States may increase by 2.4% if school closures continue into December, finds a new study from the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis.
Experts urge caution in interpreting COVID-19 antibody tests
Blood tests for antibodies against the COVID-19 virus are becoming more available, but no test is perfectly reliable, so results must be carefully interpreted, Washington University School of Medicine experts say.
COVID-19 study looks at genetics of healthy people who develop severe illness
Washington University School of Medicine is one of more than 30 genome sequencing hubs worldwide participating in a study to sequence the DNA of young, healthy adults and children who develop severe COVID-19 despite having no underlying medical problems.
Brown School researchers awarded $3.2 million grant to study child growth, development in Haiti
Trish Kohl and Lora Iannotti, associate professors at Washington University’s Brown School, have received a five-year $3.2 million grant from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health to study stunted growth and development in children in Haiti.
Students, faculty providing coronavirus-related outreach to Latino population
Spanish-speaking students and faculty at the School of Medicine have collaborated with community leaders to create and disseminate information in Spanish about the novel coronavirus for the St. Louis region’s Latino population.
COVID-19 in-home monitoring program launched
An in-home monitoring program for COVID-19 patients who are not sick enough to be hospitalized has been launched by the School of Medicine and BJC HealthCare. By keeping close watch over COVID patients, doctors hope to identify signs of deterioration early so that they can intervene and, ideally, keep more people out of the hospital.
On the front lines in fight against COVID-19
In the COVID-19 wards of Barnes-Jewish Hospital, where Washington University physicians are fighting an exhausting battle against a new, baffling and sometimes lethal disease with the help of the hospital’s nurses, other medical professionals and support staff.
Research in most university labs moved from bench to internet
COVID-19 has touched seemingly every aspect of life, and that includes laboratory work on the Medical and Danforth campuses. Most labs have responded by taking steps to temporarily shut down bench work and take that work online, while others have shifted their focus to the coronavirus.
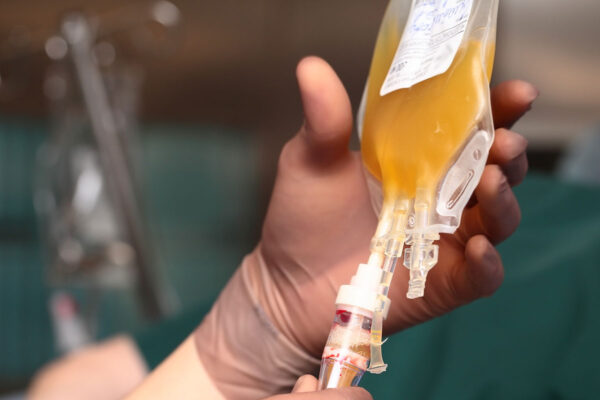
COVID-19 survivors needed to donate blood plasma
COVID-19 survivors are needed to donate blood plasma. Infectious diseases physicians at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed an expanded access program to give blood plasma from COVID-19 survivors to critically ill patients.
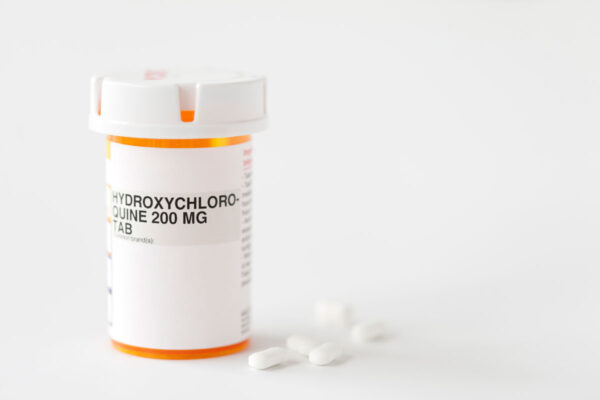
Clinical trial launches to evaluate antimalarial drugs for COVID-19 treatment
Washington University School of Medicine is launching a clinical trial for patients hospitalized with COVID-19 at Barnes-Jewish Hospital. The study will investigate whether two different antimalarial drugs, including hydroxychloroquine, alone or in combination with a common antibiotic is effective in treating COVID-19 patients.
Older Stories