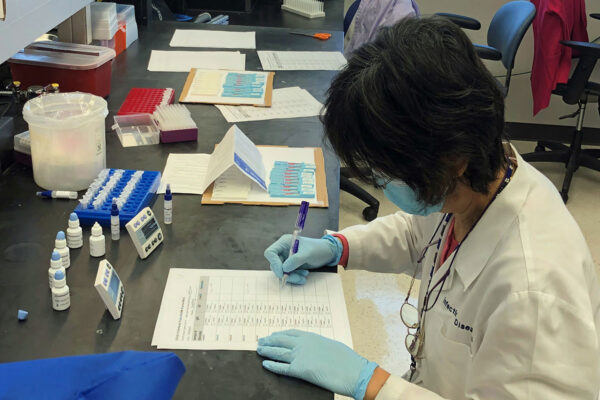
COVID-19 antibody tests evaluated as diagnostic test in low-resource settings
Faculty at the Washington University School of Medicine have joined an international effort led by the Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics and the World Health Organization (WHO) to evaluate COVID-19 antibody tests for use as diagnostics in places with limited resources.
Oral antibiotics work, shorten hospital stays for IV drug users with infections
A combination of IV and oral antibiotics can effectively treat invasive infections in people who inject illicit drugs, according to a study from Washington University School of Medicine. The findings mean that patients can leave the hospital and complete taking their prescribed antibiotics at home.
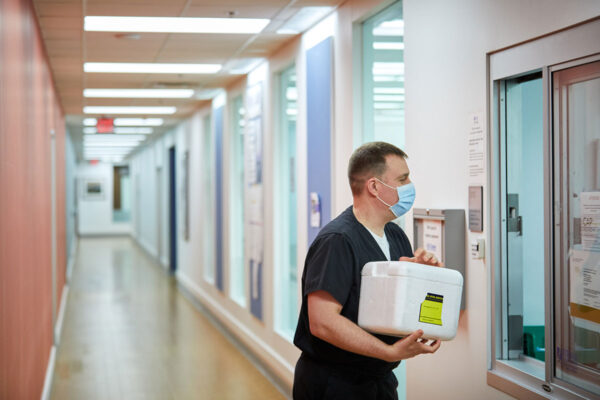
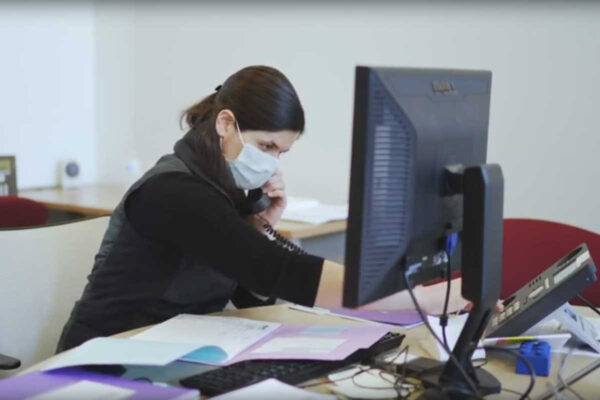
Patients with COVID-19 donate specimens to advance research efforts
School of Medicine physicians led efforts to create a repository for storing and managing specimens collected from patients with COVID-19. The samples are being distributed to investigators conducting COVID-19 research across the university.
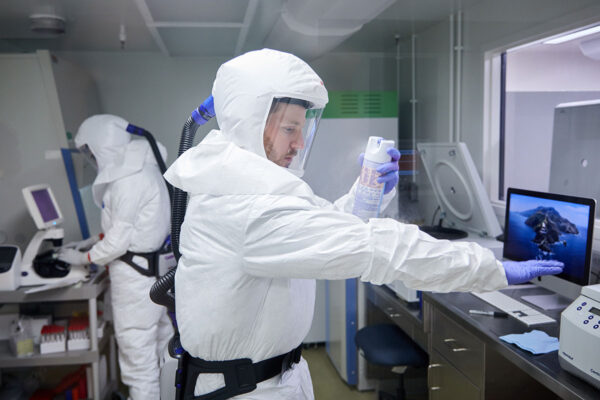
COVID-19 mouse model will speed search for drugs, vaccines
Scientists at the Washington University School of Medicine have developed a mouse model of COVID-19 that is expected to speed up the search for drugs and vaccines for the potentially deadly disease.
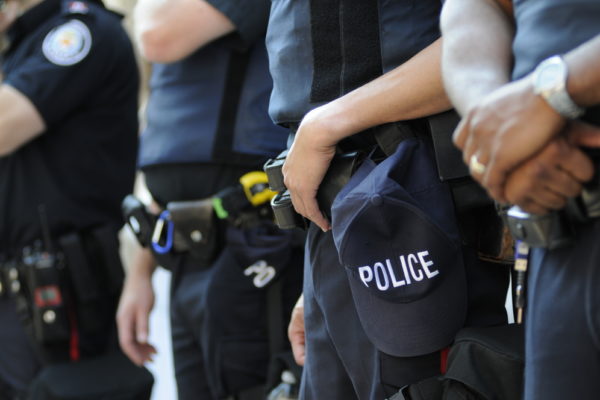
Explaining push to ‘defund police’
In the wake of national protests following the death of George Floyd, some activists are calling on cities to defund their police departments. But what does that mean exactly? Robert Motley, a PhD candidate in the Brown School and manager of the Race & Opportunity Lab at Washington University in St. Louis, explained it’s more of a reallocation of funds for public safety and health.
Medical students assist health departments in tracking COVID-19
More than 100 School of Medicine students have been volunteering to help local health departments perform case investigations and contact tracing, essential public health strategies to contain the spread of the novel coronavirus.
Antibiotic-destroying genes widespread in bacteria in soil and on people
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have found that genes that confer the power to destroy tetracyclines are widespread in bacteria that live in the soil and on people.
Ssewamala receives NIH grant to train HIV/AIDS Ugandan researchers
A $1.5 million grant to the Brown School will provide state-of-the-art training for 18 early-career researchers in Uganda to strengthen the capacity of research institutions in the country to address HIV/AIDS and its burden on child and adolescent mental health.
Lack of physical activity during COVID-19 may fuel childhood obesity
The childhood obesity rate in the United States may increase by 2.4% if school closures continue into December, finds a new study from the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis.
Experts urge caution in interpreting COVID-19 antibody tests
Blood tests for antibodies against the COVID-19 virus are becoming more available, but no test is perfectly reliable, so results must be carefully interpreted, Washington University School of Medicine experts say.
Older Stories