Environmental injustice, population density and the spread of COVID-19 in minority communities
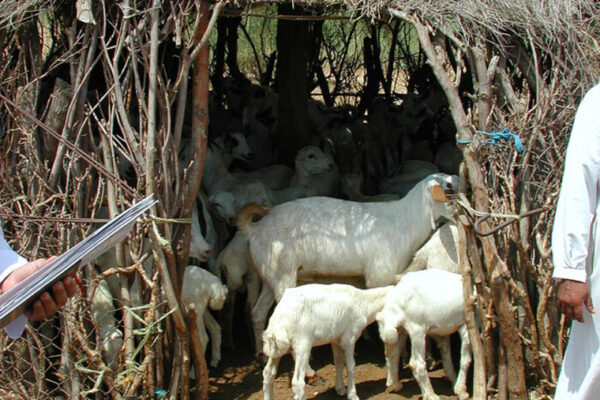
Research from the lab of Rajan Chakrabarty at the McKelvey School of Engineering connects environmental injustice to the spread of COVID-19 in communities with high minority populations.
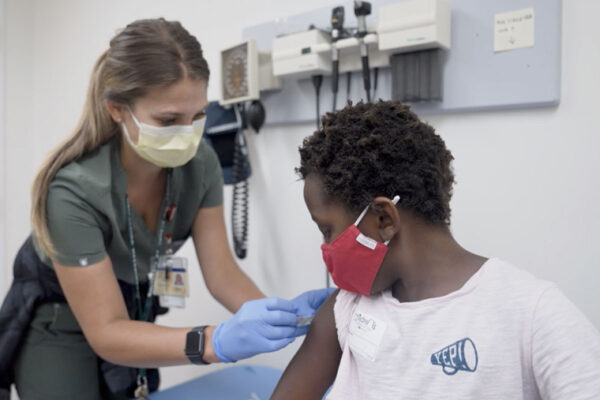
Pediatric COVID-19 vaccine trial underway
A pediatric COVID-19 vaccine clinical trial is underway in St. Louis. Led by Washington University School of Medicine, about 140 area children will receive the two-shot Moderna vaccine or a placebo at St. Louis Children’s Hospital as part of a clinical trial involving about 100 medical institutions in the U.S. and Canada.
Diabetes research center receives $4.3 million NIH grant
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), has awarded $4.3 million to renew the Washington University Center for Diabetes Translation Research.
Ssewamala receives $3.2M to address HIV stigma among Ugandan teens
Fred Ssewamala, the William E. Gordon Distinguished Professor at the Brown School, has received a grant to study the impact of a multilevel intervention to reduce HIV stigma and improve treatment outcomes among adolescents in Uganda.
Global Incubator Seed Grants awarded
A new round of recently awarded Global Incubator Seed Grants from the McDonnell International Scholars Academy will help kick-start more than a dozen high-impact, innovative projects taking place on five continents.
Deadly virus’s pathway to infect cells identified
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine and the University of Pittsburgh have discovered how Rift Valley fever virus enters cells, pointing the way to new therapies to treat the deadly disease.
COVID-19 long-haulers at risk of developing kidney damage, disease
A study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine and the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System shows that people who have had COVID-19, including those with mild cases, are at an increased risk of developing kidney damage as well as chronic and end-stage kidney diseases.
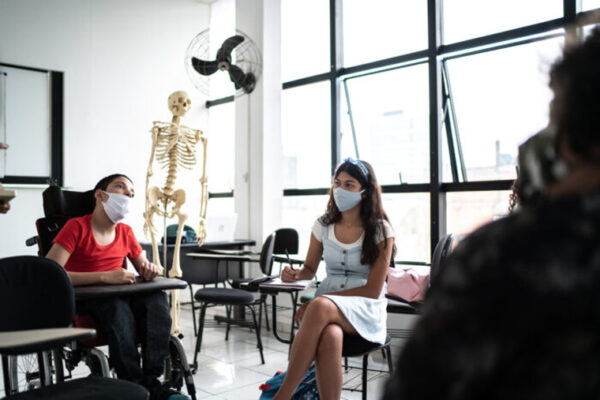
COVID-19 transmission at school rare for children with disabilities
A study led by Washington University School of Medicine, in collaboration with the Special School District of St. Louis County, found that rapid saliva test screenings contributed to exceedingly low transmission of the virus that causes COVID-19 among students, teachers and staff in those schools.
Early COVID-19 shutdowns helped St. Louis area avoid thousands of deaths
A new analysis from Washington University School of Medicine suggests that the St. Louis region avoided thousands of hospitalizations and deaths with early and coordinated public health measures as the COVID-19 pandemic was first taking hold.
Lifelines
A Doctor's Journey in the Fight for Public Health
In her latest book, Dr. Leana Wen talks about her battle on the frontline of public health. Previously the health commissioner for Baltimore and currently informing the public about the COVID-19 crisis as a CNN medical analyst, Wen knows what is costing Americans their lives and what can save them.
Older Stories