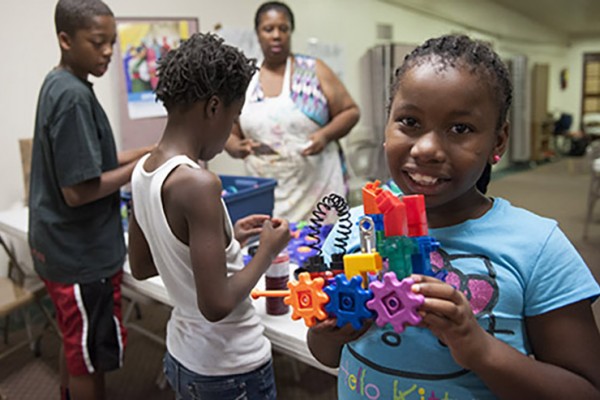Apte receives young investigator award
Rajendra S. Apte, MD, PhD, the Paul A. Cibis Distinguished Professor of Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences, is the first recipient of the Presidents’ Young Investigator Award from the American Society of Retina Specialists.
Applications sought for K12 career development program
Applications for the K12 Clinical Hematology Research Career Development Program scholars are being accepted through Oct. 20.
Monthly transfusions reduce strokes in children with sickle cell anemia
A new multi-institutional study that originated at the School of Medicine showed that giving monthly blood transfusions to young sickle cell anemia patients who already had experienced silent strokes reduced by 58 percent their risk of another stroke, silent or otherwise.
Proteins critical to wound healing identified
Mice missing two important proteins of the vascular system develop normally and appear healthy in adulthood, as long as they are not injured in some way. If they are, their wounds don’t heal properly, a new study shows. The research has possible implications for treating diseases involving abnormal blood vessel growth, including in the skin and eye.
#feeling sick: Can Twitter help better identify foodborne illness cases?
An estimated 55 million to 105 million people in the United States suffer from foodborne illnesses each year, resulting in costs of $2-$4 billion annually. What if Twitter could be used to track those cases and more quickly identify the source of the problem? A new analysis by a researcher at Washington University in St. Louis Brown School shows that new technology might better allow health departments to engage with the public to improve foodborne illness surveillance.
Medical center summer concert to be held Aug. 23
Musically talented members of the Washington University Medical Center community will be featured in a summer concert at 4 p.m. Saturday, Aug. 23, in the lobby of the Center for Advanced Medicine.
Building on success
The inaugural Health and Engineeering Careers Summer Camp took place in late July at West Side Missionary Baptist Church in St. Louis. Numerous Washington University in St. Louis groups co-sponsored the event, which aimed to encourage underrepresented children to focus on science and math subjects. Here, 10-year-old Deja Stallworth proudly shows off the robot she made.
Raichle among Kavli honorees at White House
Marcus E. Raichle, MD, was among a group of 2014 Kavli Prize winners honored with a White House reception in late July. Raichle, the Alan A. and Edith L. Wolff Distinguished Professor, was one of three scientists awarded the Kavli Prize in Neuroscience on May 29.
Study reveals how Ebola blocks immune system
The Ebola virus, in the midst of its biggest outbreak on record, is a master at evading the body’s immune system. But researchers at the School of Medicine and elsewhere have learned one way the virus dodges the body’s antiviral defenses, providing important insight that could lead to new therapies.
Potential drug therapy for kidney stones identified in mouse study
New research in mice suggests that a class of drugs approved to treat leukemia and epilepsy also may be effective against kidney stones. Pictured is the surface of a kidney stone with calcium oxalate crystals.
Older Stories