Gene variant linked to smoking longer, getting lung cancer sooner
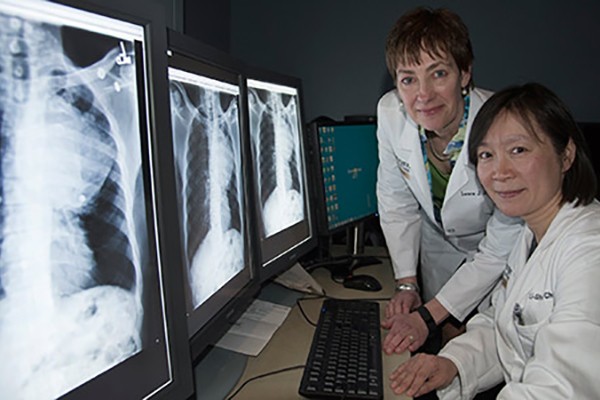
Smokers with a specific genetic variation are more likely to keep smoking longer than those who don’t have the gene variant. They’re also more likely to be diagnosed with lung cancer at a younger age, according to new research from Laura Jean Bierut, MD (left), and Li-Shiun Chen, MD, at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Study finds 1.2 percent of preschoolers on Medicaid use psychotropic drugs
A new study finds that that 1.2 percent of American preschool children on Medicaid are using psychotropic drugs, including antidepressants, mood stabilizers and medications for attention-deficit disorder. Using 2000-2003 Medicaid Analytic Extract data from 36 states, a group of researchers at the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis and at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis found preschoolers are receiving psychotropic medications despite limited evidence supporting safety or efficacy.
New Ebola study points to potential drug target
Opening the door for potential treatments for the deadly Ebola virus, scientists at Washington University and elsewhere have found that a way to kill the virus by interfering with its replication.
Report gives guidance to FDA on tobacco policy and public health
The Brown School’s Douglas A. Luke, PhD, professor and director of the Center for Public Health Systems Science at Washington University in St. Louis, was on an Institute of Medicine committee which recently released guidelines to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on using
agent-based models to improve the effect of tobacco control
policy on public health.
McCaskill holds roundtable discussion on aging at Washington University
As part of her series of Senior Listening Sessions across Missouri, Sen. Claire McCaskill held a roundtable discussion with experts on retirement security, elder justice and healthy aging March 31 at the Brown School’s Goldfarb Hall. Among the roundtable participants were seven from Washington University in St. Louis.
Study suggests ways to simplify health insurance enrollment
While the federal health-care law has reduced the number of uninsured people by about 10 million, challenges remain, including how to educate new enrollees about their coverage options. New research at Washington University shows that communicating information about the Affordable Care Act can be made simple.
Personalized melanoma vaccines marshal powerful immune response
Personalized melanoma vaccines can be used to marshal a powerful immune response against unique mutations in patients’ tumors, according to early data in a first-in-people clinical trial at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The research is a boost to cancer immunotherapy, a treatment strategy that unleashes the immune system to seek out and destroy cancer.
Exercise for older mouse mothers lowers risk of heart defects in babies
Older mice genetically prone to bear offspring with heart defects can reduce this risk to that of younger mouse mothers with the same genetic defect through exercise alone, according to new research at the School of Medicine. The study, led by Patrick Y. Jay, MD, PhD, also suggests that the increased risk of congenital heart defects is tied to the age of the mother and not the age of her eggs.
High-tech method allows rapid imaging of functions in living brain
Using a new high-speed, high-resolution imaging method, Lihong Wang, PhD, and his team at Washington University in St. Louis were able to see blood flow, blood oxygenation, oxygen metabolism and other functions inside a living mouse brain at faster rates than ever before.
Washington University develops genetic test for inherited kidney diseases
Many kidney disorders are difficult to diagnose. To address this problem, scientists and clinicians have developed a diagnostic test that identifies genetic changes linked to inherited kidney disorders. This testing is now available nationwide through Genomic Pathology Services (GPS) at the School of Medicine.
Older Stories