Vitamin D relieves joint, muscle pain for breast cancer patients
High-dose vitamin D relieves joint and muscle pain for many breast cancer patients taking estrogen-lowering drugs, according to a new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Scientists receive $13.7 million to develop new multiple myeloma treatments
Researchers at the School of Medicine have been awarded $13.7 million from the National Cancer Institute (NCI) to create new therapies for multiple myeloma, a cancer of the immune system. Led by Samuel Achilefu, PhD, (pictured) and Gregory Lanza, MD, PhD, at the newly created Center for Multiple Myeloma Nanotherapy, scientists will work to develop nanomaterials and drugs to treat the disease.
Unanue receives Sanofi-Institut Pasteur Award
Emil R. Unanue, MD, an internationally renowned immunologist at the School of Medicine, has received a Sanofi-Institut Pasteur Award for his invaluable contributions to the field of immunology. The annual awards honor scientists who have made outstanding contributions to biomedical research in fields that profoundly affect global health.
Xbox gaming technology may improve X-ray precision
With the aim of producing high-quality X-rays with minimal radiation exposure, researchers at the School of Medicine have developed a new approach to imaging patients. Using proprietary software developed for the Microsoft Kinect system, the team has adapted hands-free technology used for the popular Xbox system to aid radiographers when taking X-rays.
New center emphasizes student teamwork
To further the goal of improving patient safety and quality in health care, three institutions — the Goldfarb School of Nursing at Barnes-Jewish College, St. Louis College of Pharmacy and Washington University School of Medicine — have created the Center for Interprofessional Education (CIPE) at Washington University Medical Center.
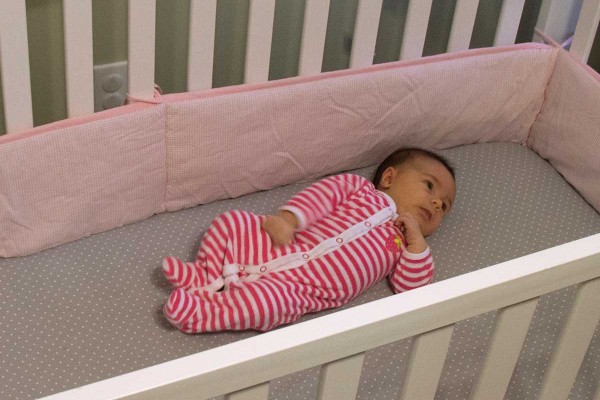
Study shows increase in infant deaths attributed to crib bumpers
A new study shows that the number of infant deaths and injuries attributed to crib bumpers has spiked significantly in recent years, prompting the researchers to call for a nationwide ban on the bedding accessory. The findings indicate that in the majority of incidents studied, crib bumpers were the sole cause of harm, rebutting beliefs that other items also in the cribs caused the deaths and injuries.
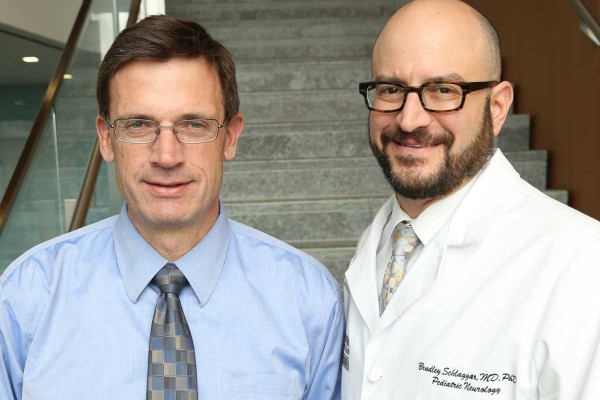
$6.5 million to fund research, treatment of developmental disabilities
Researchers at the School of Medicine have received a five-year, $6.5 million grant to study the physiological underpinnings of developmental disabilities in children and to use the findings to search for novel ways to improve such children’s lives. The grant renews funding for the university’s Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities Research Center (IDDRC), which is directed by John N. Constantino, MD (left) and Bradley L. Schlaggar, MD, PhD.
Personalized drug screening on horizon for multiple myeloma patients
A personalized method for testing the effectiveness of drugs that treat multiple myeloma may predict quickly and more accurately the best treatments for individual patients with the bone marrow cancer. The process, developed by scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, also may aid patients with leukemia or lymphoma.
Clinical trial in trauma patients to evaluate drug that stops excessive bleeding
In trauma patients experiencing severe bleeding, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis will evaluate a drug already approved to minimize blood loss in people suffering from hemophilia — a genetic clotting disorder — or heavy menstrual periods.
For kids prone to wheezing with respiratory infections, early antibiotics help
In children whose colds tend to progress and lead to severe wheezing and difficulty breathing — such that they are given oral corticosteroids as rescue therapy — researchers have shown that giving a common antibiotic at the first sign of symptoms can reduce the risk of the episode developing into a severe lower respiratory tract illness.
Older Stories