Vaccine targets identified for deadly form of malaria
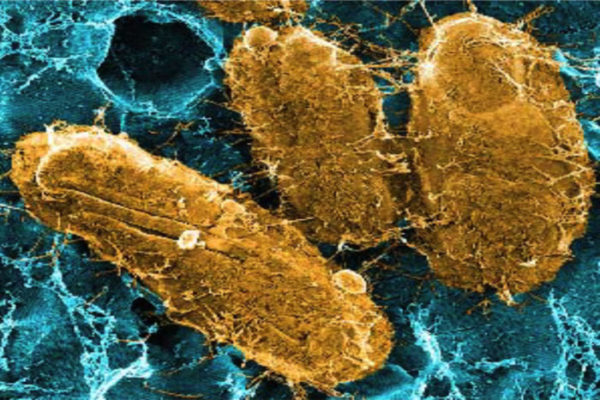
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a potential vaccine target against Plasmodium vivax, a parasite that causes malaria in millions of people worldwide every year.
Culprit identified as a major cause of vision loss
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a pathway involved in harming rods and cones in the retina and have found a way to halt that damage.
Nanoparticle injections may be future of osteoarthritis treatment
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have shown in mice that they can inject nanoparticles into an injured joint suffering from osteoarthritis and suppress inflammation immediately following an injury, reducing the destruction of cartilage.
$10 million gift creates Bursky Center for Human Immunology and Immunotherapy
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has received a $10 million gift to support research that harnesses the immune system to fight cancer, infectious diseases, and disorders caused by autoimmunity and immune deficiencies. The gift from Andrew M. and Jane M. Bursky will advance cutting-edge work at the newly named Andrew M. and Jane M. Bursky Center for Human Immunology and Immunotherapy Programs.
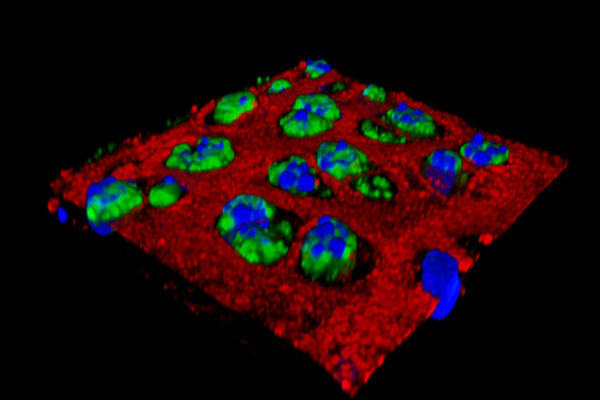
Researchers identify protein critical in causing chronic UTIs
Researchers have identified a potential way to prevent chronic urinary tract infections (UTIs). Their research points to a key protein that bacteria use to latch onto the bladder and cause UTIs, according to scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Vaccinating mice against the protein reduces the ability of bacteria to cause severe disease.
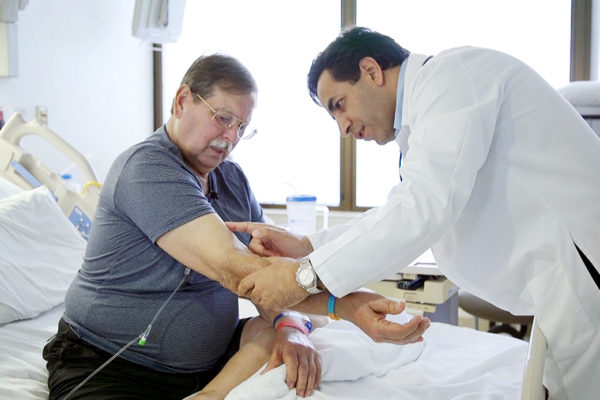
New immunotherapy for leukemia shows promise in small clinical trial
A team at the School of Medicine is evaluating a new immunotherapy against acute myeloid leukemia. The treatment harnesses the immune system’s “natural killer” cells, putting them through a training period in the lab to help them attack leukemia cells in the blood.
New explanation offered for symptoms of fragile X syndrome
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found another possible explanation for some of the symptoms of fragile X syndrome. The study, published Sept. 20 in Cell Reports, provides a new way of looking at the underlying causes of the syndrome and suggests new targets for treatment.
The shape-shifting protein behind Alzheimer’s disease
New research from Washington University in St. Louis shows that the protein behind Alzheimer’s disease shape-shifts, changing its internal structure in order to infiltrate brain cells and become toxic.
Ebola focus of $13 million grant
A $13 million grant to study how the Ebola virus replicates has been awarded to a team led by Gaya Amarasinghe, associate professor of pathology and immunology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Med school study examines firearms in the home
A survey of parents in Missouri and Illinois reveals that about half of the children in the families queried spent time in homes that have firearms. However, few reported talking about gun safety with their children’s pediatricians.
Older Stories