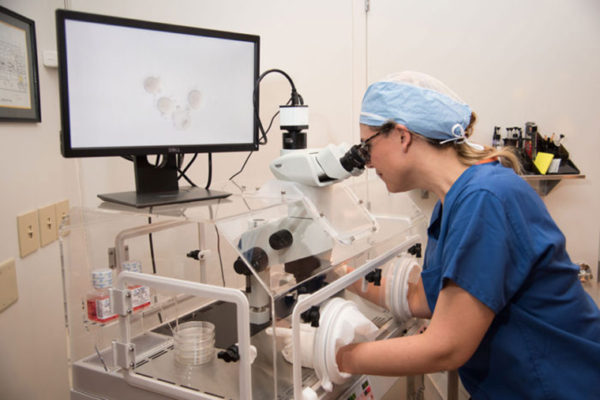
Detecting, diagnosing women’s cancers in new ways
The National Institutes of Health has awarded a Washington University in St. Louis faculty member in the School of Engineering & Applied Science a total of $1.3 million to study new imaging techniques designed to better fight breast and ovarian cancers.
Genetic errors associated with heart health may guide drug development
Natural genetic changes can put some people at high risk of certain conditions, such as breast cancer, Alzheimer’s disease or high blood pressure. But in rare cases, genetic errors also can have the opposite effect, protecting individuals with these helpful genetic mistakes from developing common diseases. A new study of such “beneficial” genetic mutations, led by the School of Medicine, may provide guidance on the design of new therapies intended to reduce the risk of heart attacks.
Insurance coverage for IVF increases chance of having baby
Women who pursue in vitro fertilization (IVF) to become pregnant are more likely to give birth if they have health insurance that covers the procedure, according to new research at the School of Medicine. The key reason is financial rather than medical: The high cost for one procedure prohibits many women from seeking a second if the first attempt fails.
Rogue breast tumor proteins point to potential drug therapies
Studying mice with breast tumors transplanted from patients, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and Baylor College of Medicine have analyzed the proteins present in these tumors. Some protein alterations can be used to identify drugs that may work against some cancers.
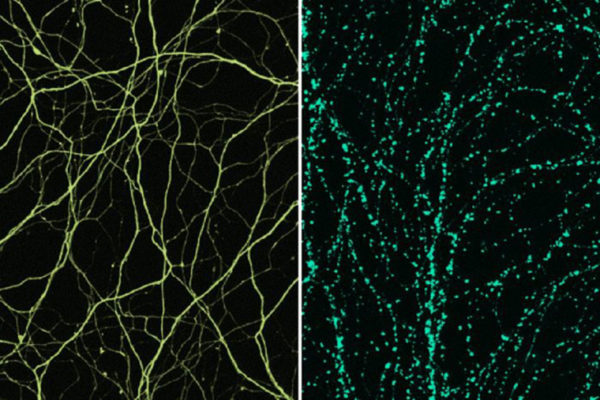
Scientists get closer look at living nerve synapses
The brain hosts an extraordinarily complex network of interconnected nerve cells that are constantly exchanging electrical and chemical signals at speeds difficult to comprehend. Now, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report they have been able to achieve — with a custom-built microscope — the closest view yet of living nerve synapses.
Surprising culprit in nerve cell damage identified
Scientists at the School of Medicine have implicated a specific molecule in the self-destruction of axons, the wiring of the nervous system. Understanding just how that damage occurs may help researchers find a way to halt it.
Spinal cord stimulation relieves back pain without opioids
Doctors who treat back pain are exploring new approaches that help some patients avoid opioid drugs. One option available at the Washington University Pain Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital involves stimulating the spinal cord with very short pulses of electricity.
A probiotic stress fix
An engineer at Washington University in St. Louis is working to create a probiotic that would help protect the host from the negative health effects of adrenaline surges. The new probiotic could easily be mixed into yogurt or taken in pill form.
WashU Experts: Science cuts would cause ‘chilling effect’
Proposed federal budget cuts to two major programs could translate into fewer treatments, fewer cures, fewer drug findings, fewer researchers and fewer breakthroughs in areas where the United States is a world leader, say science and health experts at Washington University in St. Louis.
$7 million aimed at illuminating the genetics of Alzheimer’s disease
Two new studies led by the School of Medicine aim to clarify the genetic underpinnings of Alzheimer’s disease. Funded by grants totaling $7 million from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), researchers seek to find ways to predict who will develop the disease as well as new targets for therapies.
Older Stories