Surgery for early prostate cancer may not save lives
Part of a major 20-year study, new research provides further evidence that surgery is unnecessary for early-stage prostate cancer, although some men whose disease is further along may benefit.
Sleep, Alzheimer’s link explained
Research from Washington University School of Medicine, Radboud University Medical Centre in the Netherlands, and Stanford University shows that disrupting just one night of sleep in healthy, middle-aged adults causes an increase in a brain protein associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Type 1 diabetes risk linked to intestinal viruses
A new study led by the School of Medicine has found that viruses in the intestines may affect a person’s chance of developing Type 1 diabetes. Children who carried a specific virus belonging to the Circoviridae family were less likely to head down the path toward diabetes.
Malaria drug protects fetuses from Zika infection
Studying pregnant mice, researchers at the School of Medicine found that Zika virus manipulates the body’s normal barrier to infection. They also found that a malaria drug, hydroxychloroquine, interferes with this process, protecting the fetus from viral infection.
Popular heartburn drugs linked to higher death risk
Popular heartburn drugs called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have been linked to a variety of health problems, including serious kidney damage, bone fractures and dementia. Now, a new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis shows that longtime use of the drugs also is associated with an increased risk of death.
Siteman Cancer Center opens north St. Louis County location
Siteman Cancer Center will begin seeing patients July 1 at its newest satellite location, Christian Hospital in north St. Louis County. Siteman Cancer Center is based at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine, and the new location is Siteman’s fifth in the St. Louis area.
New clues found to common respiratory virus
Mapping the molecular structure of an RSV protein that interferes with the body’s ability to fight off the virus, researchers at the School of Medicine have found clues to how RSV causes disease. This could potentially lead to a vaccine or treatment.
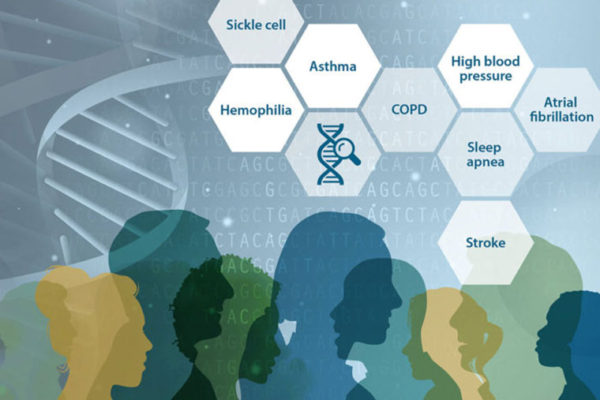
$10 million DNA sequencing effort aims to shed light on lung diseases
Washington University’s McDonnell Genome Institute has received $10 million from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) to sequence the DNA of people from diverse ethnic backgrounds, in an effort to identify the genetic roots of COPD and other lung disorders.
UTI treatment reduces E. coli, may offer alternative to antibiotics
A new study from the School of Medicine has found that a molecular decoy can target and reduce UTI-causing bacteria in the gut. With a smaller pool of disease-causing bacteria, the researchers say the risk of having a UTI goes down.
Makeup of vaginal microbiome linked to preterm birth
In a study of predominantly African-American women — who have a much higher rate of delivering babies early compared with other racial groups — researchers at the School of Medicine showed that a decrease in the diversity of vaginal microbes of pregnant women between the first and second trimesters is associated with preterm birth.
Older Stories