Testing begins for student-created app to aid Alzheimer’s diagnosis
With the aim of streamlining the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, a Washington University student-led team has designed an online app to help doctors more quickly evaluate patients. The app is being tested at the School of Medicine.
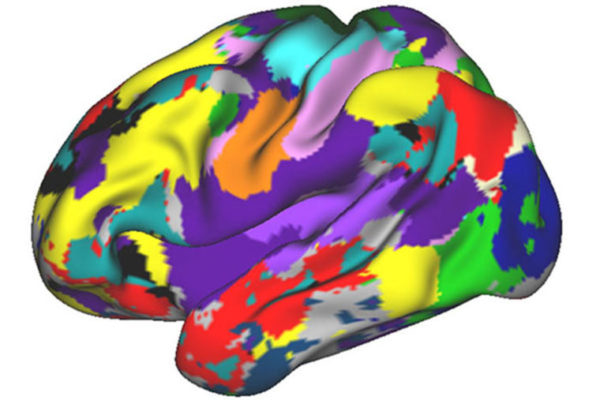
Scientists become subjects in brain-scanning project
A research group started in 2013 by two neuroscientists at the School of Medicine collected a massive amount of data on individual brains. The study’s subjects were the scientists themselves and eight others, all junior faculty or graduate students.
CRISPR sheds light on rare pediatric bone marrow failure syndrome
Using the gene editing technology CRISPR, scientists at the School of Medicine have shed light on a rare, sometimes fatal syndrome that causes children to gradually lose the ability to manufacture vital blood cells.
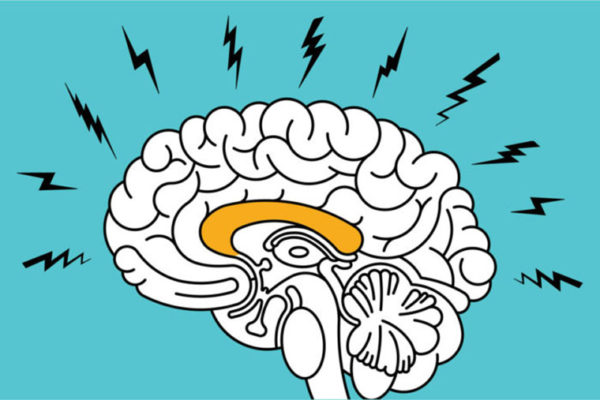
Anxious? Cellular roots of anxiety identified
New research from the School of Medicine sheds light on what might be happening in an anxious brain.
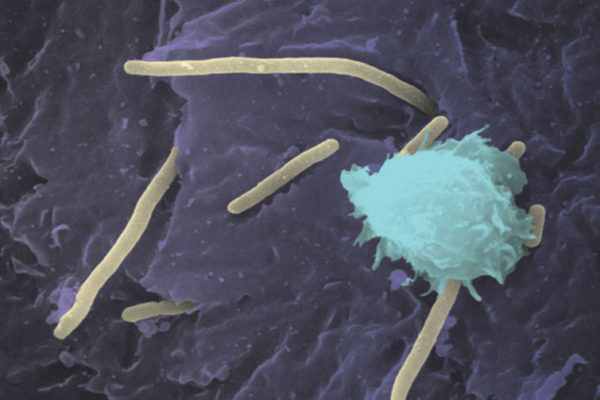
Aggressive UTI bacteria hijack copper, feed off it
Researchers at the School of Medicine have shown that E. coli bacteria — those at the root of hard-to-treat urinary tract infections (UTIs) — hijack trace amounts of copper in the body and use it as a nutrient to fuel growth. The finding may open the door to treating UTIs using drugs that work differently from traditional antibiotics.
A sodium surprise
Irregular heartbeat — or arrhythmia — can have sudden and often fatal consequences. A biomedical engineering team at Washington University in St. Louis examining molecular behavior in cardiac tissue recently made a surprising discovery that could someday impact treatment of the life-threatening condition.
Blood test IDs key Alzheimer’s marker
A study led by researchers at the School of Medicine suggests that measures of amyloid beta in the blood have the potential to help identify people with altered levels of amyloid in their brains or cerebrospinal fluid. The test could identify people who have started down the path toward Alzheimer’s years before symptoms occur.
Vaccines protect fetuses from Zika infection, mouse study shows
A new study in mice shows that females vaccinated before pregnancy and infected with Zika virus while pregnant bore young with no trace of the virus. The findings offer evidence that an effective vaccine administered prior to pregnancy can protect vulnerable fetuses.
Strategy to battle opioid epidemic encourages multilevel approach
Jose A. Moron-Concepcion, associate professor of anesthesiology the School of Medicine, studies the emotional component of pain and opioid receptors. He discusses some of the key points addressed in a new report on opioid abuse issued by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine.
In autism, genes drive early eye gaze abnormalities
New research has uncovered compelling evidence that genetics plays a major role in how children look at the world and whether they have a preference for gazing at people’s eyes and faces or at objects.The discovery by researchers at the School of Medicine and Emory University adds new detail to understanding the causes of autism spectrum disorder.
Older Stories