Scanning for clues to our ancient past
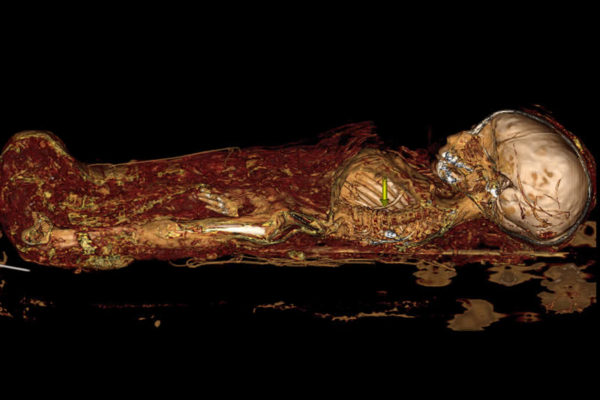
The mummified remains of a 7-month-old baby boy and pieces of skull from two teenage Triceratops underwent computed tomography (CT) scans Sept. 16 at the School of Medicine, in hopes researchers could learn more about the ancient past.
Newly ID’d role of major Alzheimer’s gene suggests possible therapeutic target
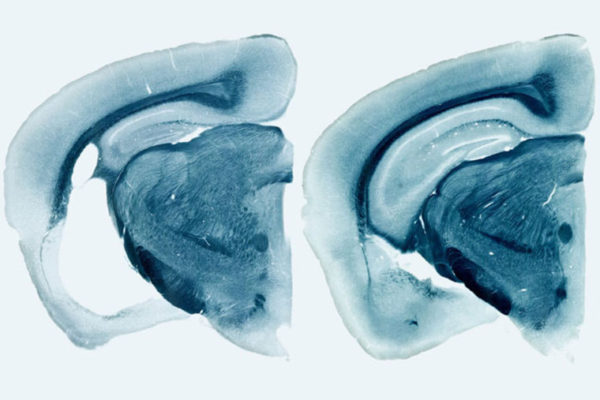
A study led by researchers at the School of Medicine shows that the presence of ApoE4 exacerbates the brain damage caused by toxic tangles of a different Alzheimer’s-associated protein: tau. In the absence of ApoE, tau tangles did very little harm to brain cells.
Scientists find way to convert bad body fat into good fat
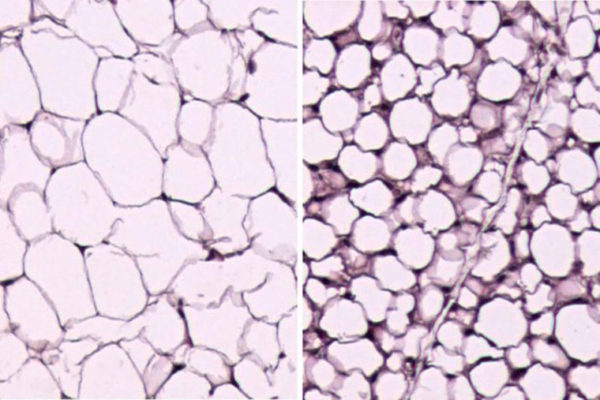
Research at the School of Medicine has identified a way to convert bad, white fat into good, brown fat, at least in mice. The findings raise the prospect of developing more effective treatments, in people, for obesity and diabetes related to weight gain.
Pet, pest allergens linked to reduced asthma risk
An ongoing study at the School of Medicine is aimed at understanding what factors may increase or decrease the risk of developing asthma in childhood.
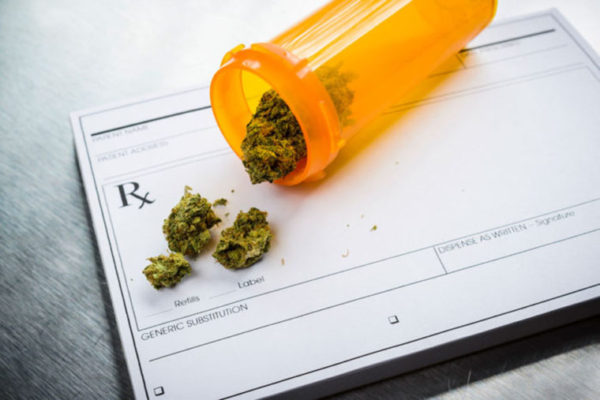
Medical students not trained to prescribe medical marijuana
Although medical marijuana is now legal in more than half of the states in the country, researchers at the School of Medicine have found that medical marijuana is rarely addressed in medical education.
Medical history can point to earlier Parkinson’s disease diagnosis
Researchers at the School of Medicine have analyzed Medicare claims data of more than 200,000 people to develop an algorithm to predict whether a patient one day will be diagnosed with Parkinson’s.
Does improving cardiovascular health reduce risk of dementia?
Researchers at the School of Medicine are recruiting volunteers for a national study that is exploring whether strategies to improve cardiovascular health also reduce the risk of dementia in those at risk for Alzheimer’s disease.
Does health insurance status affect childhood cancer survival?
Privately insured children and those with Medicaid at the time of a cancer diagnosis experience largely similar survival trends, with slight evidence for an increased risk of cancer death in children who were uninsured at diagnosis, finds a new study from the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis.
Potential new therapy relieves chronic itch
Research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has identified immune signaling molecules that are essential for activating neurons in the skin to cause chronic itching.
Human skin cells transformed directly into motor neurons
Scientists at the School of Medicine have converted skin cells from healthy adults directly into motor neurons without going through a stem cell state.
Older Stories