CRISPR enhances gene therapy to fight inherited diseases
School of Medicine scientists have combined the gene-editing tool CRISPR with a deactivated virus to deliver a healthy gene to a precise location in the bodies of living mice. And more importantly, the researchers demonstrated that the inserted gene remained properly activated in mice for at least six months.
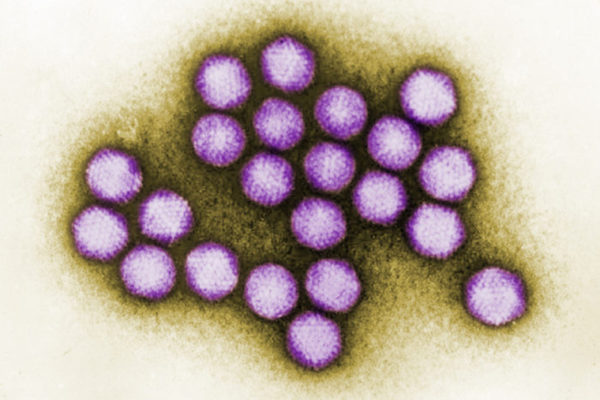
Antibiotic use increases risk of severe viral disease in mice
Doctors recommend against taking antibiotics for viral infections because they don’t kill viruses — and they promote antibiotic resistance. A new study from the School of Medicine suggests another reason to avoid the pills: Taking antibiotics increases susceptibility to subsequent viral infection, at least in mice.
Drug compound shows promise against rheumatoid arthritis
Scientists have designed a new drug compound that dials down inflammation, suggesting possible future uses against autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. The new inhibitor is more selective than other compounds, according to new School of Medicine research.
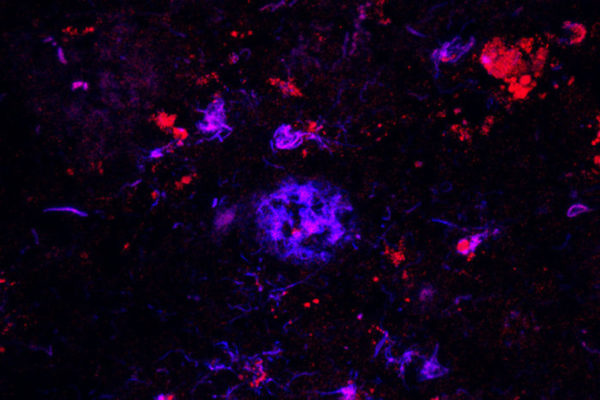
Antibody removes Alzheimer’s plaques, in mice
Sticky amyloid plaques play a role in Alzheimer’s disease. School of Medicine researchers have shown that an antibody targeting a minor part of the plaques – a protein known as APOE – can sweep away the damaging plaques, opening potential treatment options.
Diabetes intervention works best at home
A public health research team at the Brown School has taken one of the most effective diabetes intervention programs and made it more accessible by partnering with an existing home-visit organization dedicated to working with mothers of preschool-aged children.
Building a healthy workspace
A team of Washington University in St. Louis researchers designed a study — and made a toolkit available to the public — to measure the effects that a deliberately designed environment can have on physical activity, the environment and collaboration.
Link between two key Alzheimer’s proteins explained
Researchers at the School of Medicine are getting a clearer picture of the connection between tau and amyloid beta, the two proteins at the heart of Alzheimer’s disease. Their insights may lead to new treatments.
Infectious diseases docs may be lifesaving for patients with antibiotic-resistant infections
For patients with difficult-to-treat, drug-resistant infections, seeing an infectious diseases specialist can be a lifesaver. Such patients experienced significantly lower mortality rates when treated by physicians specializing in infectious diseases, according to a School of Medicine study.
Higher doses of radiation don’t improve survival in prostate cancer
A new study shows that higher doses of radiation do not improve survival for many patients with prostate cancer, compared with the standard radiation treatment. The analysis, which included 104 radiation therapy oncology groups across North America, was led by researchers at the School of Medicine.
Proposed Medicaid work requirements would affect fewer in Missouri
Proposed rules surrounding Medicaid recipients would affect a far smaller proportion of Missouri’s population than other states with similar legislation, according to research from the Center for Health Economics and Policy at Washington University in St. Louis.
Older Stories