Lowering hospitals’ Medicare costs proves difficult
A payment system that provides financial incentives for hospitals that reduce health-care costs for Medicare patients did not lower costs as intended, according to a new study led by the School of Medicine.
Perfectionism in young children may indicate OCD risk
Studying young children, researchers at the School of Medicine found that kids who possess tendencies toward perfectionism and excessive self-control are twice as likely as other children to develop obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) by the time they reach their teens.
Decriminalizing pot doesn’t lead to increased use by young people
Researchers at the School of Medicine have found that in five states that decriminalized marijuana, there was no corresponding rise in the drug’s use among young people. In addition, marijuana-related arrests declined significantly.
New ALS therapy in clinical trials
New School of Medicine research indicates an investigational therapy for an inherited form of ALS extends survival and reverses signs of neuromuscular damage in mice and rats.
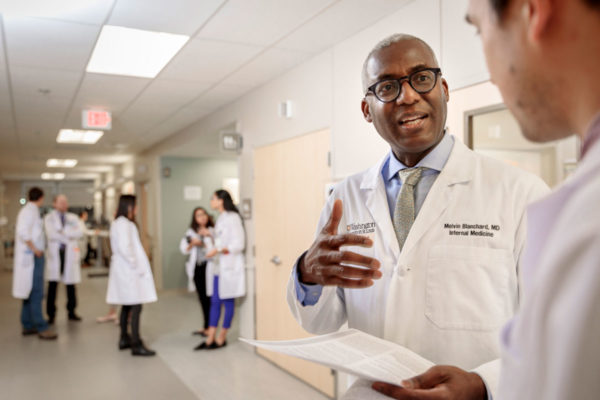
Report addresses national shortage of physician-scientist trainees
Projected demand for physician-scientists exceeds the expected supply, studies indicate. Melvin Blanchard, MD, director of the Division of Medical Education, led a multi-institution project to develop recommendations to improve U.S. training programs.
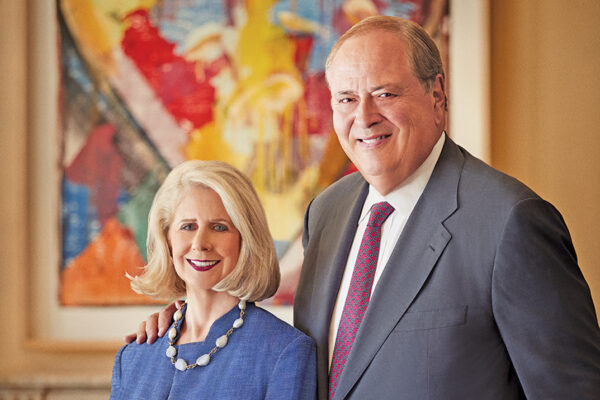
Alleviating human suffering
Longtime supporters of the medical school, Debra and George Couch are focused now on helping advance discoveries through precision medicine.
Non-opioid drug relieves pain in mice, targets immune cells
Researchers at the School of Medicine have found that inhibiting a receptor on immune cells called macrophages may help relieve pain in some patients, particularly those with chronic neuropathic pain, such as those with conditions like diabetic neuropathy.
Gene therapy method developed to target damaged kidney cells
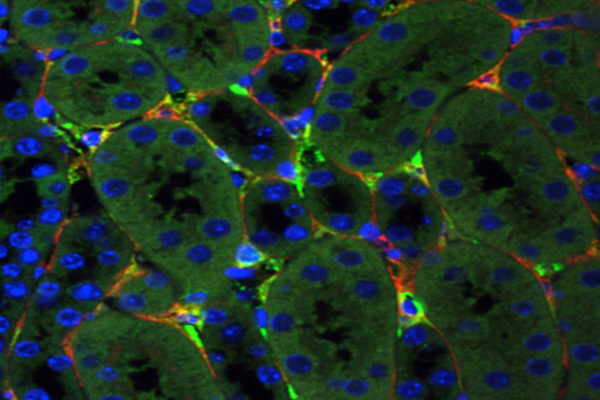
Research led by the School of Medicine has shown, in mice, that genetic material can be delivered to damaged cells in the kidneys, a key step toward developing gene therapy to treat chronic kidney disease.
Air pollution contributes significantly to diabetes globally
New research links outdoor air pollution — even at levels deemed safe — to an increased risk of diabetes globally, according to a study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the Veterans Affairs (VA) St. Louis Health Care System.
Chemotherapy-induced diarrhea traced to immune cells
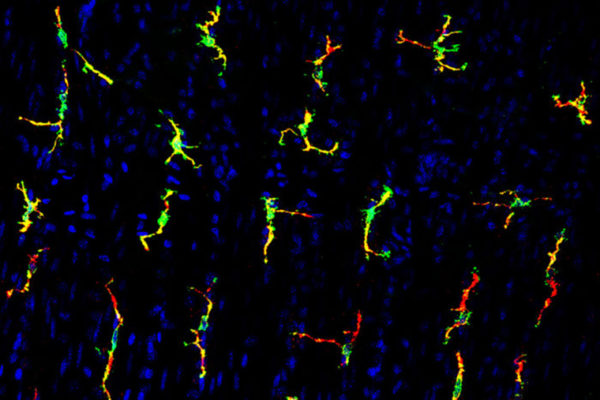
Washington University researchers have found that immune cells called macrophages can trigger smooth muscle contractions in the intestinal tract, independent of nerve cells. The research in mice holds potential for treating chemotherapy-induced diarrhea.
Older Stories