Scientists uncover new details in how sense of smell develops
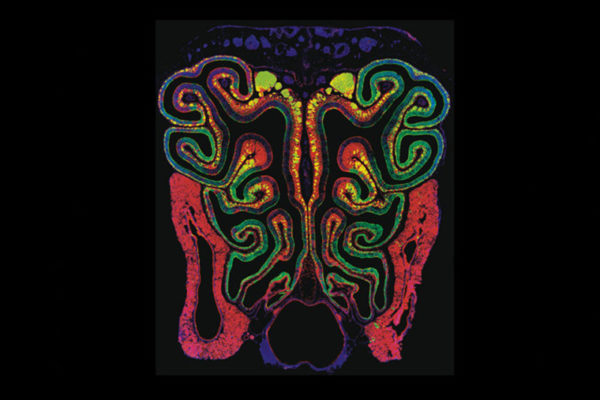
Researchers at the School of Medicine have uncovered new details in how a tissue called the olfactory epithelium develops in the nasal cavity. The findings could shed new light on why dogs have such a good sense of smell.
Brain tumors occur often in kids with common genetic syndrome
A new School of Medicine study shows that children born with neurofibromatosis (NF1), a common genetic syndrome, are much more likely to have brain tumors than previously thought.
Mallinckrodt boosts rare-disease research at Washington University
The School of Medicine has joined with Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals in a collaborative research partnership aimed at pursuing new therapies for patients with complex medical conditions, especially rare diseases that may have few or no treatment options. The global pharmaceutical company will fund up to $10 million over five years.
Can testosterone plus exercise improve healing after hip fracture?
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine are leading a national, multicenter study exploring whether testosterone plus exercise can restore physical abilities in elderly women who have broken a hip. The study is funded with a $15.6 million National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant.
Analysis of prostate tumors reveals clues to cancer’s aggressiveness
Researchers from the School of Medicine and other institutions have sequenced the whole genomes of more than 100 metastatic prostate tumors, revealing new information about what drives the aggressive forms of this cancer.
Lowering hospitals’ Medicare costs proves difficult
A payment system that provides financial incentives for hospitals that reduce health-care costs for Medicare patients did not lower costs as intended, according to a new study led by the School of Medicine.
Perfectionism in young children may indicate OCD risk
Studying young children, researchers at the School of Medicine found that kids who possess tendencies toward perfectionism and excessive self-control are twice as likely as other children to develop obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) by the time they reach their teens.
Decriminalizing pot doesn’t lead to increased use by young people
Researchers at the School of Medicine have found that in five states that decriminalized marijuana, there was no corresponding rise in the drug’s use among young people. In addition, marijuana-related arrests declined significantly.
New ALS therapy in clinical trials
New School of Medicine research indicates an investigational therapy for an inherited form of ALS extends survival and reverses signs of neuromuscular damage in mice and rats.
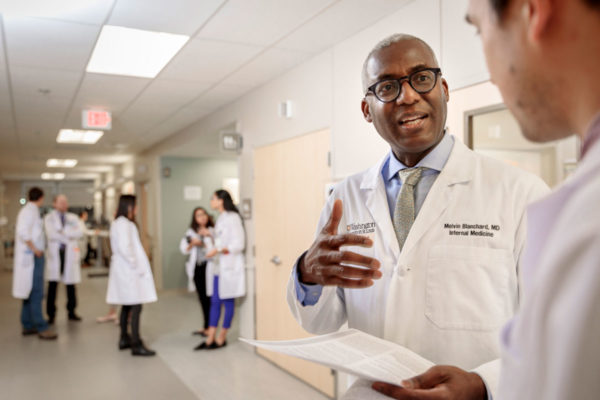
Report addresses national shortage of physician-scientist trainees
Projected demand for physician-scientists exceeds the expected supply, studies indicate. Melvin Blanchard, MD, director of the Division of Medical Education, led a multi-institution project to develop recommendations to improve U.S. training programs.
Older Stories