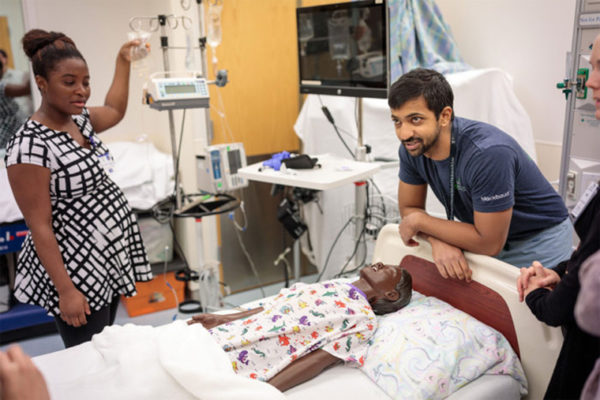
Course teaches medical trainees how to provide care in developing countries
A recent two-week crash course on global health helped prepare medical students, residents and fellows for clinical rotations and long-term careers in developing countries. Caring for such patients requires a different mindset for trainees accustomed to working in modern medical centers with updated technology and no shortage of supplies or medications.
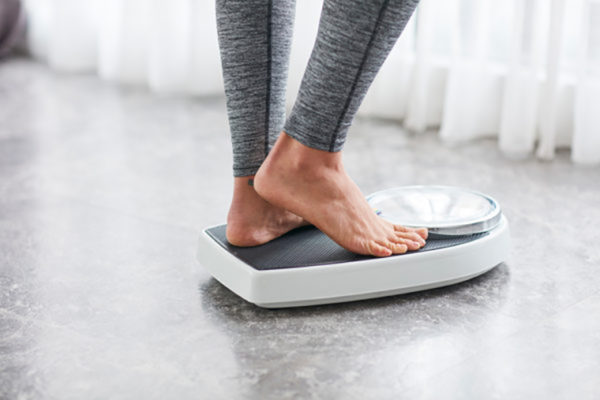
Obesity linked to increased risk of early-onset colorectal cancer
A new study led by the School of Medicine shows a link between weight gain and increased risk of young-onset colorectal cancer. Rates of colorectal cancer diagnosed in people under age 50 are going up and researchers are searching for possible reasons behind the increase.
In childbirth, when to begin pushing does not affect C-section rates
A multicenter study led by the School of Medicine and involving more than 2,400 first-time pregnant women, shows that the timing of pushing has no effect on whether women deliver vaginally or by C-section.
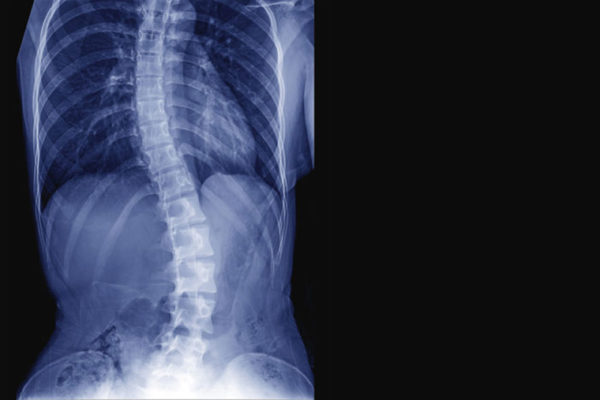
Scoliosis linked to essential mineral
An inability to properly use the essential mineral manganese could be to blame for some cases of severe scoliosis, according to a new study from the School of Medicine.
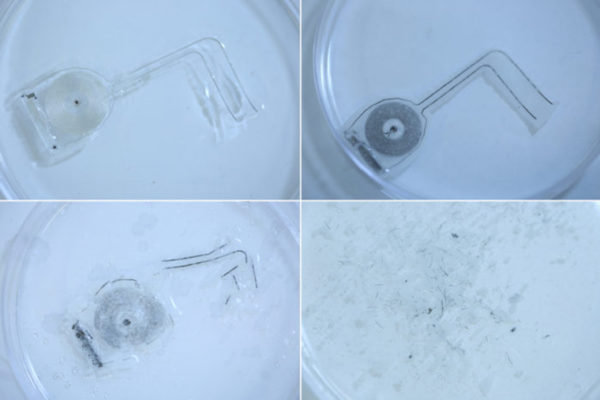
Implantable, biodegradable devices speed nerve regeneration in rats
Researchers at the School of Medicine and Northwestern have developed an implantable, bioabsorbable device that helps speed recovery of peripheral nerve damage in rats by stimulating injured nerves with electricity. The device degrades in a few weeks when exposed to saltwater, which mimics bodily fluid.
WashU Expert: Trump’s new NAFTA won’t lower domestic drug prices
President Donald Trump has touted his new United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement as a way to boost the American economy. It may not, however, have any impact on one of his other campaign promises: reducing prescription costs for U.S. consumers, says a drug pricing expert at Washington University in St. Louis.
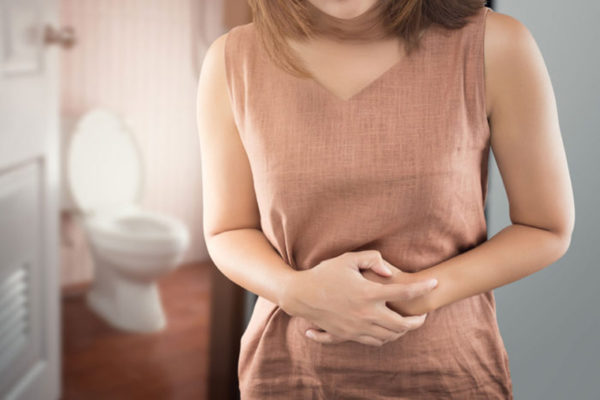
Viruses in blood lead to digestive problems
A new study in mice from the School of Medicine shows that viruses that target the nervous system can kill neurons in the gut that coordinate the process of moving waste along. Such viruses may be involved in causing people’s digestive woes.
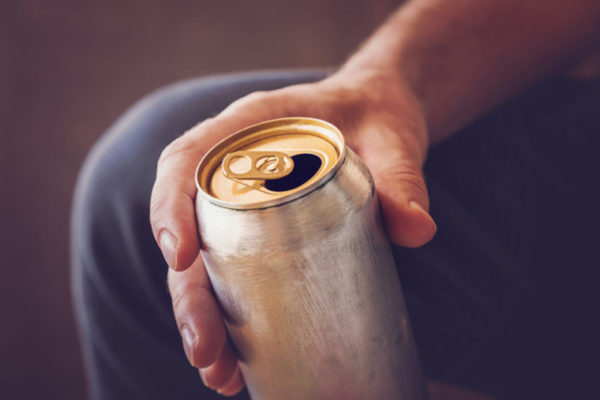
Even light drinking increases risk of death
Analyzing data from more than 400,000 people, researchers at the School of Medicine have found that consuming one to two drinks four or more times per week — an amount deemed healthy by current guidelines — increases the risk of premature death by 20 percent.
Fighting the vaccine wars on the side of science
Michael Kinch’s new book, “Between Hope and Fear: A History of Vaccines and Human Immunity,” tells the story of the people behind vaccines and how the human body fights infection.
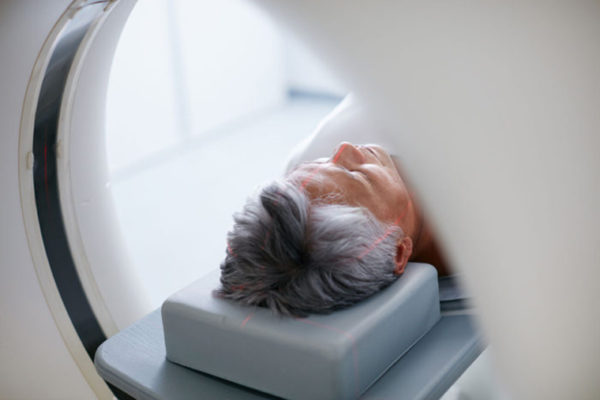
Overlooked signal in MRI scans reflects amount, kind of brain cells
An MRI scan often generates an ocean of data, most of which is never used. When overlooked data is analyzed using a new technique developed at the School of Medicine, they surprisingly reveal how many and which brain cells are present – and show where cells have been lost through injury or disease. The findings could lead to new treatments for a variety of brain diseases.
Older Stories